Abstract
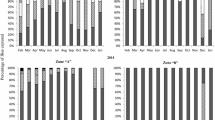
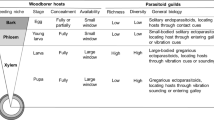
Populations of hymenopteran parasitoids associated with larval stages of the invasive emerald ash borer (EAB) Agrilus planipennis Fairmaire (Coleoptera: Buprestidae) were surveyed in 2009 and 2010 in the recently invaded areas in north central United States (Michigan), where two introduced EAB larval parasitoids, Tetrastichus planipennisi Yang and Spathius agrili Yang were released for classical biological control. Results from two years of field surveys showed that several hymenopteran parasitoids have become associated with EAB in Michigan. Among these parasitoids, the gregarious species T. planipennisi was the most abundant, accounting for 93% of all parasitoid individuals collected in 2009 (immediately after field release) and 58% in 2010 (a year later after field releases). Low levels (1–5%) of parasitism of EAB larvae by T. planipennisi were consistently detected at survey sites in both years. Separately, the abundance of the native parasitoid, Atanycolus spp., increased sharply, resulting in an average parasitism rate of EAB larvae from <0.5% in 2009 to 19% in 2010. Other parasitoids such as Phasgonophora sulcata Westwood, Spathius spp., Balcha indica Mani & Kaul, Eupelmus sp., and Eurytomus sp. were much less abundant than T. planipennisi and Atanycolus spp., and each caused <1% parasitism. Besides hymenopteran parasitoids, woodpeckers consumed 32–42% of the immature EAB stages present at our study sites, while undetermined biotic factors (such as microbial disease and host tree resistance) caused 10–22% mortality of observed EAB larvae. Relevance of these findings to the potential for biological control of EAB in the invaded areas of North America is discussed.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barter GW (1957) Studies of the bronze birch borer, Agrilus anxius Gory, in New Brunswick. Can Entomol 89:12–36
Bauer LS, Liu H-P, Haack RA, Miller DL, Patrice TR (2004) Natural enemies of emerald ash borer in southeastern Michigan. In: Mastro V, Reardon R (Compilers) Proceedings of the emerald ash borer research and technology meeting, Port Huron, MI. USDA FS FTET-2004-02, pp 33–34
Bauer LS, Liu H-P, Haack RA, Gao R, Zhao T, Miller DL, Petrice TR (2005) Emerald ash borer natural enemy surveys in Michigan and China. In: Mastro V, Reardon R (Compilers) Proceedings of emerald ash borer research and technology development meeting, Romulus, MI. USDA FS FHTET-2004-15, pp 71–72
Bauer LS, Liu H-P, Miller DL, Gould JR (2008) Developing a classical biological control program for Agrilus planipennis (Coleoptera: Buprestidae), an invasive ash pest in North America. Newsl Mich Entomol Soc 47:1–5
Bauer LS, Gould JR, Duan JJ (2010) Can biological control of emerald ash borer save our ash? Mich Entomol Soc Newsl 55:26–27
Bogran CE, Heinz HM, Ciomperlik MA (2002) Interspecific competition among insect parasitoids: field experiments with whiteflies as hosts in cotton. Ecology 83:653–668
Bray M, Bauer MD, Poland TM, Haack RA, Cognato AI, Smith JJ (2011) Genetic analysis of emerald ash borer (Agrilus planipennis Fairmaire) populations in Asia and North America. Biol Invasions. doi:10.1007/s10530-011-9970-5
Canadian Food Inspection Agency (2011) Emerald Ash Borer—Agrilus planipennis, published online at http://www.inspection.gc.ca/english/plaveg/pestrava/agrpla/agrplae.shtml
Cappaert DL, McCullough DG (2009) Occurrence and seasonal abundance of Atanycolus cappaerti (Hymenoptera: Buprestidae), a native parasitoid of emerald ash borer, Agrilus planipennis (Coleoptera: Buprestidae). Great Lakes Entomol 42:16–29
Cappaert D, McCullough DG, Poland TM, Siegert NW (2005) Emerald ash borer in North America: a research and regulatory challenge. Am Entomol 51:152–165
Castrillo LA, Griggs MH, Vandenberg JD (2008) Quantitative detection of Beauveria bassiana GHA (Ascomycota:Hypocreales), a potential microbial control agent of the emerald ash borer, by use of real-time PCR. Biol Control 45:163–169
Duan JJ, Fuester RW, Wildonger J, Taylor PH, Barth S, Spichiger SE (2009) Parasitoids attacking the emerald ash borer (Coleoptera: Buprestidae) in western Pennsylvania. Florida Entomol 92:588–592
Duan JJ, Ulyshen MD, Bauer LS, Gould J, van Driesche R (2010) Measuring the impact of biotic factors on populations of immature emerald ash borer (Coleoptera: Buprestidae). Environ Entomol 39:1513–1522
Duan JJ, Yurchenko G, Gould J, Wang X-Y, Yang Z-Q, Bauer LS, Abell KJ, van Driesche R (2011) The impact of biotic factors on populations of the emerald ash borer: a comparison between its native northeast Asian and newly invaded north American ranges. Emerald ash borer biological control. In: McManus K, Gottschalk K (eds) Proceedings, 22nd U.S. Department of Agriculture Interagency Research Forum on Invasive Species, 2011 January, Annapolis, MD, USDA Forest Service, Gen. Tech. Rep. NRSP–xx, Newton Square, PA (in press)
Elkinton JS, Buonaccorsi JP, Bellows TS, van Driesche RG (1992) Marginal attack rate, k-values and density dependence in the analysis of contemporaneous mortality factors. Res Pop Ecol 34:29–44
Emerald Ash Borer Information (2011) Emerald ash borer information, published online at http://www.emeraldashborer.info/homeownerinfo.cfm
Gould JR, Ayer T, Fraser I (2011) Effects of rearing conditions on reproduction of Spathius agrili (Hymenoptera: Braconidae), a parasitoid of the emerald ash borer (Coleoptera: Buprestidae). J Econ Entomol 104:379–387
Haack RA, Eendek JE, Liu HP, Marchant KR, Petrice TR, Poland RM, Ye H (2002) The emerald ash borer: a new exotic pest in North America. Newsl Mich Entomol Soc 47:1–5
Hackett-Jones E, Cobbold C, White A (2009) Coexistence of multiple parasitoids on a single host due to differences in parasitoid phenology. Theor Ecol 2:19–31
Hawkins BA (1994) Pattern and process in host-parasitoid interactions. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Kilham L (1965) Differences in feeding behavior of male and female hairy woodpeckers. Wilson Bull 77:134–145
Kula RR, Knight KS, Rebbeck J, Cappaert DL, Bauer LS, Gandhi KJK (2010) Leluthia astigma (Ashmead) (Hymenoptera: Braconidae: Doryctinae) as a parasitoid of Agrilus planipennis Fairmaire (Coleoptera: Buprestidae: Agrilinae), with an assessment of host associations for Nearctic species of Leluthia Cameron. Proc Entomol Soc Wash 112:246–257
Lindell CA, McCullough DG, Cappaert D, Apostolou NM, Roth MB (2008) Factors influencing woodpecker predation on emerald ash borer. Am Mid Nat 159:434–444
Liu H, Bauer LS (2006) Susceptibility of Agrilus planipennis (Coleoptera: Buprestidae) to Beauveria bassiana and Metarhizium anisopliae. J Econ Entomol 99:1096–1103
Liu H-P, Bauer LS, Gao R-T, Zhao T-H, Petrice RT, Haack RA (2003) Exploratory survey for the emerald ash borer, Agrilus planipennis (Coleoptera: Buprestidae), and its natural enemies in China. Great Lakes Entomol 36:191–204
Liu H-P, Bauer LS, Miller DL, Zhao T-H, Gao RT, Song L, Luan Q, Jin R, Gao C (2007) Seasonal abundance of Agrilus planipennis (Coleoptera: Buprestidae) and its natural enemies Oobius agrili (Hymenoptera: Encyrtidae) and Tetrastichus planipennisi (Hymenoptera: Eulophidae) in China. Biol Control 42:61–71
Lyons B (2008) Emerald ash borer: it’s here to stay, let’s learn how to manage it. Forest Health and Biodiversity Newsletter 12(1):1–5
McCullough DG, Siegert NW (2007) Estimating potential emerald ash borer (Coleoptera: Buprestidae) populations using ash inventory data. J Econ Entomol 100:1577–1586
Memmott J, Godfray HCJ, Gauld ID (1994) The structure of a tropical host parasitoid community. J Anim Ecol 63:521–540
Parry D (1995) Larval and pupal parasitism of forest tent caterpillar, Malacosoma disstria Hübner (Lepidoptera: Lasiocampidae), in Alberta Canada. Can Entomol 127:877–893
Rebek EJ, Herms DA, Smitley DR (2008) Interspecific variation in resistance to emerald ash borer (Coleoptera: Buprestidae) among North American and Asian ash (Fraxinus spp.). Environ Entomol 37:242–246
Reitz RR (1996) Interspecific competition between two parasitoids of Helicoverpa zea: Eucelatoria bryani and E. rubentis. Entomol Exp Appl 79:227–234
SAS Institute Inc (2008) JMP® 8 introductory guide. SAS Institute Inc, Gary, NC
Siegert NW, McCullough DG, Tluczek AR (2007) Two years under the bark: towards understanding multiple-year development of emerald ash borer larvae. In: Mastro V, Lance D, Reardon R, Parra G (Compilers) proceedings of the emerald ash borer and asian longhorned beetle research and technology development meeting, Cincinnati, Ohio, 29 October–2 November 2006. FHTET-2007-04, USDA Forest Service Forest Health Technology Enterprise Team, Morgantown, W. VA, pp 34–36
Ulyshen MD, Duan JJ, Bauer LS, Ivich F (2010) Suitability and accessibility of immature Agrilus planipennis (Coleoptera: Buprestidae) stages to Tetrastichus planipennisi (Hymenoptera: Eulophidae). J Econ Entomol 103:1080–1085
USDA APHIS (2007) The proposed release of three parasitoids for the biological control of the emerald ash borer (Agrilus planipennis) in the continental United States: environmental assessment. Federal Register 72:28947–28948, Docket No. APHIS-2007-006
Yang Z-Q, Strazanac JS, Marsh PM, van Achterberg C, Choi W-Y (2005) First recorded parasitoid from China of Agrilus planipennis: A new species of Spathius (Hymenoptera: Braconidae: Doryctinae). Ann Entomol Soc Am 98:636–642
Yang Z-Q, Srazanac JS, Yao Y-X, Wang X-Y (2006) A new species of emerald ash borer parasitoid from China belonging to the genus Tetrastichus Haliday (Hymenoptera: Eulophidae). Proc Entomol Soc Wash 108:550–558
Zhang Y-Z, Huang D-W, Zhao T-H, Liu H-P, Bauer LS (2005) Two new species of egg parasitoids (Hymenoptera: Encyrtidae) of wood-boring beetle pests from China. Phytoparasitica 53:253–260
Acknowledgments
We thank student employees Anthony Paul Capizzo, Tim Watt and Jane Slater, and Deborah L. Miller of the USDA Forest Service, Northern Research Station, East Lansing, Michigan, USA for assistance in the laboratory and field. We are also grateful to Craig Oppel, Roger Fuester, and Doug Luster (USDA Agricultural Research Service, Beneficial Insects Introduction Research Units) for helpful comments to the earlier version of the manuscript. The project is supported in part by USDA Forest Service, State and Private Forestry.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Handling Editor: Mark Hoddle
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Duan, J.J., Bauer, L.S., Abell, K.J. et al. Population responses of hymenopteran parasitoids to the emerald ash borer (Coleoptera: Buprestidae) in recently invaded areas in north central United States. BioControl 57, 199–209 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10526-011-9408-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10526-011-9408-0