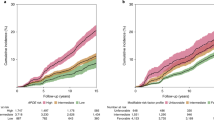
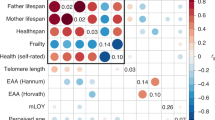
Abstract
The apolipoprotein E (apoE) is a classic example of a gene exhibiting pleiotropism. We examine potential pleiotropic associations of the apoE2 allele in three biodemographic cohorts of long-living individuals, offspring, and spouses from the Long Life Family Study, and intermediate mechanisms, which can link this allele with age-related phenotypes. We focused on age-related macular degeneration, bronchitis, asthma, pneumonia, stroke, creatinine, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, diseases of heart (HD), cancer, and survival. Our analysis detected favorable associations of the ε2 allele with lower LDL-C levels, lower risks of HD, and better survival. The ε2 allele was associated with LDL-C in each gender and biodemographic cohort, including long-living individuals, offspring, and spouses, resulting in highly significant association in the entire sample (β = −7.1, p = 6.6 × 10−44). This allele was significantly associated with HD in long-living individuals and offspring (relative risk [RR] = 0.60, p = 3.1 × 10−6) but this association was not mediated by LDL-C. The protective effect on survival was specific for long-living women but it was not explained by LDL-C and HD in the adjusted model (RR = 0.70, p = 2.1 × 10−2). These results show that ε2 allele may favorably influence LDL-C, HD, and survival through three mechanisms. Two of them (HD- and survival-related) are pronounced in the long-living parents and their offspring; the survival-related mechanism is also sensitive to gender. The LDL-C-related mechanism appears to be independent of these factors. Insights into mechanisms linking ε2 allele with age-related phenotypes given biodemographic structure of the population studied may benefit translation of genetic discoveries to health care and personalized medicine.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anand R, Prakash SS, Veeramanikandan R et al (2014) Association between apolipoprotein E genotype and cancer susceptibility: a meta-analysis. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 140:1075–1085
Araki S, Koya D, Makiishi T et al (2003) APOE polymorphism and the progression of diabetic nephropathy in Japanese subjects with type 2 diabetes: results of a prospective observational follow-up study. Diabetes Care 26:2416–2420
Burt TD, Agan BK, Marconi VC et al (2008) Apolipoprotein (apo) E4 enhances HIV-1 cell entry in vitro, and the APOE epsilon4/epsilon4 genotype accelerates HIV disease progression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105:8718–8723
Christensen K, Johnson TE, Vaupel JW (2006) The quest for genetic determinants of human longevity: challenges and insights. Nat Rev Genet 7:436–448
Corder EH, Saunders AM, Strittmatter WJ et al (1993) Gene dose of apolipoprotein E type 4 allele and the risk of Alzheimer’s disease in late onset families. Science 261:921–923
Corder EH, Saunders AM, Risch NJ et al (1994) Protective effect of apolipoprotein-E type-2 allele for late-onset Alzheimer-disease. Nat Genet 7:180–184
Corella D, Ordovas JM (2014) Aging and cardiovascular diseases: the role of gene-diet interactions. Ageing Res Rev 18:53–73
Coresh J, Selvin E, Stevens LA et al (2007) Prevalence of chronic kidney disease in the United States. JAMA 298:2038–2047
de Bont N, Netea MG, Demacker PN et al (1999) Apolipoprotein E knock-out mice are highly susceptible to endotoxemia and Klebsiella pneumoniae infection. J Lipid Res 40:680–685
De Feo E, Simone B, Persiani R et al (2012) A case-control study on the effect of Apolipoprotein E genotypes on gastric cancer risk and progression. BMC Cancer 12:494
de Jong PT (2006) Age-related macular degeneration. N Engl J Med 355:1474–1485
Eichner JE, Dunn ST, Perveen G et al (2002) Apolipoprotein E polymorphism and cardiovascular disease: a HuGE review. Am J Epidemiol 155:487–495
Eto M, Horita K, Morikawa A et al (1995) Increased frequency of apolipoprotein epsilon 2 allele in non-insulin dependent diabetic (NIDDM) patients with nephropathy. Clin Genet 48:288–292
Franco OH, Karnik K, Osborne G et al (2009) Changing course in ageing research: the healthy ageing phenotype. Maturitas 63:13–19
Govindaraju D, Atzmon G, Barzilai N (2015) Genetics, lifestyle and longevity: lessons from centenarians. Appl Transl Genomics 4:23–32
Hauser PS, Narayanaswami V, Ryan RO (2011) Apolipoprotein E: from lipid transport to neurobiology. Prog Lipid Res 50:62–74
Hunsicker LG, Adler S, Caggiula A et al (1997) Predictors of the progression of renal disease in the Modification of Diet in Renal Disease Study. Kidney Int 51:1908–1919
Katan MB (1986) Apolipoprotein E isoforms, serum cholesterol, and cancer. Lancet 1:507–508
Khan TA, Shah T, Prieto D et al (2013) Apolipoprotein E genotype, cardiovascular biomarkers and risk of stroke: systematic review and meta-analysis of 14,015 stroke cases and pooled analysis of primary biomarker data from up to 60,883 individuals. Int J Epidemiol 42:475–492
Kimura H, Suzuki Y, Gejyo F et al (1998) Apolipoprotein E4 reduces risk of diabetic nephropathy in patients with NIDDM. Am J Kidney Dis 31:666–673
Klaver CC, Kliffen M, van Duijn CM et al (1998) Genetic association of apolipoprotein E with age-related macular degeneration. Am J Hum Genet 63:200–206
Kulminski AM (2013) Unraveling genetic origin of aging-related traits: evolving concepts. Rejuvenation Res 16:304–312
Kulminski AM, Ukraintseva SV, Arbeev KG et al (2008) Health-protective and adverse effects of the apolipoprotein E epsilon2 allele in older men. J Am Geriatr Soc 56:478–483
Kulminski AM, Culminskaya I, Arbeev KG et al (2013) The role of lipid-related genes, aging-related processes, and environment in healthspan. Aging Cell 12:237–246
Kulminski AM, Arbeev KG, Culminskaya I et al (2014) Age, gender, and cancer but not neurodegenerative and cardiovascular diseases strongly modulate systemic effect of the apolipoprotein e4 allele on lifespan. PLoS Genet 10:e1004141
Liberopoulos E, Siamopoulos K, Elisaf M (2004) Apolipoprotein E and renal disease. Am J Kidney Dis 43:223–233
Liu H, Shui IM, Platz EA et al (2015) No association of ApoE genotype with risk of prostate cancer: a nested case-control study. Cancer Epidemiol Biomark Prev 24:1632–1634
Mahley RW, Rall SC Jr (2000) Apolipoprotein E: far more than a lipid transport protein. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet 1:507–537
Mahley RW, Weisgraber KH, Huang Y (2009) Apolipoprotein E: structure determines function, from atherosclerosis to Alzheimer’s disease to AIDS. J Lipid Res 50(Suppl):S183–188
Martin GM, Bergman A, Barzilai N (2007) Genetic determinants of human health span and life span: progress and new opportunities. PLoS Genet 3:e125
Matteini AM, Fallin MD, Kammerer CM et al (2010) Heritability estimates of endophenotypes of long and health life: the Long Life Family Study. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 65:1375–1379
Nesse RM, Ganten D, Gregory TR et al (2012) Evolutionary molecular medicine. J Mol Med (Berl) 90:509–522
Oda H, Yorioka N, Ueda C et al (1999) Apolipoprotein E polymorphism and renal disease. Kidney Int Suppl 71:S25–27
Oeppen J, Vaupel JW (2002) Demography. Broken limits to life expectancy. Science 296:1029–1031
Olshansky SJ, Perry D, Miller RA et al (2007) Pursuing the longevity dividend: scientific goals for an aging world. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1114:11–13
Pedersen CB, Gotzsche H, Moller JO et al (2006) The Danish civil registration system. A cohort of eight million persons. Dan Med Bull 53:441–449
Poulain M, Herm A, Pes G (2013) The Blue Zones: areas of exceptional longevity around the world. Vienna Yearb Popul Res 1:87–108
Prentice R, Breslow N (1978) Retrospective studies and failure time models. Biometrika 65:153–158
Rajpathak SN, Liu Y, Ben-David O et al (2011) Lifestyle factors of people with exceptional longevity. J Am Geriatr Soc 59:1509–1512
Roselaar SE, Daugherty A (1998) Apolipoprotein E-deficient mice have impaired innate immune responses to Listeria monocytogenes in vivo. J Lipid Res 39:1740–1743
Schultz DW, Klein ML, Humpert A et al (2003) Lack of an association of apolipoprotein E gene polymorphisms with familial age-related macular degeneration. Arch Ophthalmol 121:679–683
Schupf N, Barral S, Perls T et al (2013) Apolipoprotein E and familial longevity. Neurobiol Aging 34:1287–1291
Sebastiani P, Hadley EC, Province M et al (2009) A family longevity selection score: ranking sibships by their longevity, size, and availability for study. Am J Epidemiol 170:1555–1562
Seshasai RK, Katz R, de Boer IH et al (2012) Apolipoprotein E and kidney function in older adults. Clin Nephrol 78:174–180
Sierra F, Hadley E, Suzman R et al (2008) Prospects for Life Span Extension. Annu Rev Med 60:457–469
Song Y, Stampfer MJ, Liu S (2004) Meta-analysis: apolipoprotein E genotypes and risk for coronary heart disease. Ann Intern Med 141:137–147
Suri S, Heise V, Trachtenberg AJ et al (2013) The forgotten APOE allele: a review of the evidence and suggested mechanisms for the protective effect of APOE varepsilon2. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 37:2878–2886
Thakkinstian A, Bowe S, McEvoy M et al (2006) Association between apolipoprotein E polymorphisms and age-related macular degeneration: a HuGE review and meta-analysis. Am J Epidemiol 164:813–822
Vaupel JW (2010) Biodemography of human ageing. Nature 464:536–542
Vijg J, Suh Y (2005) Genetics of longevity and aging. Annu Rev Med 56:193–212
Watson MA, Gay L, Stebbings WS et al (2003) Apolipoprotein E gene polymorphism and colorectal cancer: gender-specific modulation of risk and prognosis. Clin Sci (Lond) 104:537–545
Wilson PW, Schaefer EJ, Larson MG et al (1996) Apolipoprotein E alleles and risk of coronary disease. A meta-analysis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 16:1250–1255
Yao X, Dai C, Fredriksson K et al (2012) Human apolipoprotein E genotypes differentially modify house dust mite-induced airway disease in mice. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 302:L206–215
Yashin AI, Arbeev KG, Kulminski A et al (2010) “Predicting” parental longevity from offspring endophenotypes: data from the Long Life Family Study (LLFS). Mech Ageing Dev 131:215–222
Acknowledgments
The Long Life Family Study is funded by U01AG023749, U01AG023744 and U01AG023712 from the National Institute on Aging. This work was supported by the National Institute on Aging (Grant Numbers U01 AG023712, P01 AG043352, R01 AG047310).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
No conflict of interests exist.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kulminski, A.M., Raghavachari, N., Arbeev, K.G. et al. Protective role of the apolipoprotein E2 allele in age-related disease traits and survival: evidence from the Long Life Family Study. Biogerontology 17, 893–905 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10522-016-9659-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10522-016-9659-3