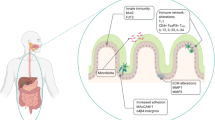
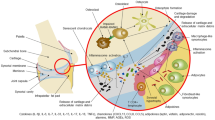
Rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps is characterized by chronic inflammation and hyperplasia of the nasal mucosa. The key mechanism for polyp formation is the expression of molecules that regulate proliferation and inflammation. We studied immunolocalization of bone morphogenetic protein-2 (BMP-2) and IL-1β in the nasal mucosa in patients aged 35-70 years (n=70, mean age 57.4±1.52 years). The typology of polyps was determined depending on the distribution of inflammatory cells, subepithelial edema, the presence of fibrosis and cysts. The immunolocalization of BMP-2 and IL-1β had the same pattern in edematous, fibrous, and eosinophilic (allergic) polyps. Goblet and connective tissue cells, microvessels and terminal sections of the glands were positively stained. BMP-2+ and IL-1β+ cells predominated in polyps of the eosinophilic type. BMP-2/IL-1β can be considered as a specific marker of inflammatory remodeling of the nasal mucosa in refractory rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pawankar R, Nonaka M. Inflammatory mechanisms and remodeling in chronic rhinosinusitis and nasal polyps. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2007;7(3):202-208. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11882-007-0073-4
Ordovas-Montanes J, Dwyer DF, Nyquist SK, Buchheit KM, Vukovic M, Deb C, Wadsworth MH 2nd, Hughes TK, Kazer SW, Yoshimoto E, Cahill KN, Bhattacharyya N, Katz HR, Berger B, Laidlaw TM, Boyce JA, Barrett NA, Shalek AK. Allergic inflammatory memory in human respiratory epithelial progenitor cells. Nature. 2018;560:649-654. doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-018-0449-8
Cho SW, Kim DY. Lessons from localized chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps. Allergy Asthma Immunol. Res. 2021;13(6):827-829. doi: https://doi.org/10.4168/aair.2021.13.6.827
Tian P, Sun Y, Li Y, Liu X, Wan L, Li J, Ma Y, Xu A, Fu Y, Zou H. A global analysis of tandem 3’UTRs in eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps. PLoS One. 2012;7(11):e48997. doi: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0048997
Kim JY, Lim S, Lim HS, Kim YS, Eun KM, Khalmuratova R, Seo Y, Kim JK, Kim YS, Kim MK, Jin S, Han SC, Pyo S, Hong SN, Park JW, Shin HW, Kim DW. Bone morphogenetic protein-2 as a novel biomarker for refractory chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2021;148(2):461-472.e13. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2021.02.027
Kuzubova NA, Titova ON. T2-associated diseases: focus on the comorbid patient. Med. Sovet. 2020;(17):57-64. Russian. doi: https://doi.org/10.21518/2079-701X-2020-17-57-64
Wang RN, Green J, Wang Z, Deng Y, Qiao M, Peabody M, Zhang Q, Ye J, Yan Z, Denduluri S, Idowu O, Li M, Shen C, Hu A, Haydon RC, Kang R, Mok J, Lee MJ, Luu HL, Shi LL. Bone Morphogenetic Protein (BMP) signaling in development and human diseases. Genes Dis. 2014;1(1):87-105. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gendis.2014.07.005
Khalmuratova R, Lee M, Park JW, Shin HW. Evaluation of neo-osteogenesis in eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis using a nasal polyp murine model. Allergy Asthma Immunol. Res. 2020;12(2):306-321. doi: https://doi.org/10.4168/aair.2020.12.2.306
Kostiv RE, Matveeva NY, Kalinichenko SG. Localization of VEGF, TGF-β1, BMP-2, and apoptosis factors in hypertrophic nonunion of human tubular bones. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2022;173(1):160-168. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-022-05513-3
Mishina Y. Function of bone morphogenetic protein signaling during mouse development. Front. Biosci. 2003;8:d855-d869. doi: https://doi.org/10.2741/1097
Miyazono K, Kamiya Y, Morikawa M. Bone morphogenetic protein receptors and signal transduction. J. Biochem. 2010;147(1):35-51. doi: https://doi.org/10.1093/jb/mvp148
Yan C, Grimm WA, Garner WL, Qin L, Travis T, Tan N, Han YP. Epithelial to mesenchymal transition in human skin wound healing is induced by Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha through Bone morphogenic Protein-2. Am. J. Pathol. 2010;176(5):2247-2258. doi: https://doi.org/10.2353/ajpath.2010.090048
Rosendahl A, Pardali E, Speletas M, Ten Dijke P, Heldin CH, Sideras P. Activation of bone morphogenetic protein/Smad signaling in bronchial epithelial cells during airway inflammation. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2002;27(2):160-169. doi: https://doi.org/10.1165/ajrcmb.27.2.4779
Kalinichenko SG, Matveeva NY, Kostiv RY, Edranov SS. The effect of calcium phosphate biodegradable coatings of titanium implants on cell differentiation and apoptosis in rat bone tissue after experimental fracture. Biomed. Mater. Eng. 2021;32(1):53-62. doi: https://doi.org/10.3233/BME-201119
Matveeva NYu, Pavlush DG, Kalinichenko SG. Expression of pro- and anti-apoptotic molecules in the mucous membrane of the nasal cavity with polypous rhinosinusitis. Vestn. Otolorin. 2020;85(3):43-47. Russian. doi: https://doi.org/10.17116/otorino20208503143
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Byulleten’ Eksperimental’noi Biologii i Meditsiny, Vol. 174, No. 10, pp. 462-467, October, 2022
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Matveeva, N.Y., Pavlush, D.G. & Kalinichenko, S.G. BMP-2 and IL-1β as Markers of Nasal Mucosa Inflammation in Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps. Bull Exp Biol Med 174, 455–459 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-023-05728-y
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-023-05728-y