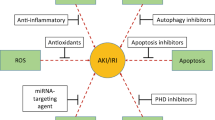
The phenomenon of ischemic preconditioning was discovered in 1986 in experiments with the heart, and then it was observed in almost all organs, the kidneys included. This phenomenon is underlain by conditioning of the tissues with short ischemia/reperfusion cycles intended for subsequent exposure to pathological ischemia. Despite the kidneys are not viewed as so vital organs as the brain or the heart, the acute ischemic injury to kidneys is a widespread pathology responsible for the yearly death of almost 2 million patients, while the number of patients with chronic kidney disease is estimated as hundreds of millions or nearly 10% adult population the world over. Currently, it is believed that adaptation of the kidneys to ischemia by preconditioning is the most effective way to prevent the development of acute kidney injury, so deep insight into its molecular mechanisms will be a launch pad for creating the nephroprotective therapy by elevating renal tolerance to oxygen deficiency. This review focuses on the key signaling pathways of kidney ischemic preconditioning, the potential pharmacological mimetics of its key elements, and the limitations of this therapeutic avenue associated with age-related decline of ischemic tolerance of the kidneys.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ermolenko VM, Nikolaev AYu. Acute Renal Failure. Moscow, 2010. Russian.
Meerson FZ. Adaptation, Stress, and Prophylaxis. Moscow, 1981. Russian.
Abete P, Cacciatore F, Testa G, Della-Morte D, Galizia G, de Santis D, Calabrese C, Cioppa A, Ferrara N, Rengo F. Ischemic preconditioning in the aging heart: from bench to bedside. Ageing Res. Rev. 2010;9(2):153-162. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arr.2009.07.001
Andrianova NV, Jankauskas SS, Zorova LD, Pevzner IB, Popkov VA, Silachev DN, Plotnikov EY, Zorov DB. Mechanisms of age-dependent loss of dietary restriction protective effects in acute kidney injury. Cells. 2018;7(10):178. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/cells7100178
Andrianova NV, Zorova LD, Pevzner IB, Popkov VA, Chernikov VP, Silachev DN, Plotnikov EY, Zorov DB. Resemblance and differences in dietary restriction nephroprotective mechanisms in young and old rats. Aging (Albany NY). 2020;12(18):18 693-18 715. doi: 10.18632/aging.103960
Bagnasco S, Good D, Balaban R, Burg M. Lactate production in isolated segments of the rat nephron. Am. J. Physiol. 1985; 248(4, Pt 2):F522-F526. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1985. 248.4.F522
Chatauret N, Badet L, Barrou B, Hauet T. Ischemia-reperfusion: From cell biology to acute kidney injury. Prog. Urol. 2014; 24(Suppl. 1):S4-S12. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/S1166-7087(14)70057-0
Della-Morte D, Cacciatore F, Salsano E, Pirozzi G, Del Genio MT, D’Antonio I, Gargiulo G, Palmirotta R, Guadagni F, Rundek T, Abete P. Age-related reduction of cerebral ischemic preconditioning: myth or reality? Clin. Interv. Aging. 2013;8:1055-1061. doi: https://doi.org/10.2147/CIA.S47462
Diwan V, Kant R, Jaggi AS, Singh N, Singh D. Signal mechanism activated by erythropoietin preconditioning and remote renal preconditioning-induced cardioprotection. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2008;315(1-2):195-201. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-008-9808-3
Haase VH. Hypoxia-inducible factors in the kidney. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2006;291(2):F271-F281. doi: https://doi.org/10.1152/ajprenal.00071.2006
Hausenloy DJ, Yellon DM. New directions for protecting the heart against ischaemia-reperfusion injury: targeting the Reperfusion Injury Salvage Kinase (RISK)-pathway. Cardiovasc. Res. 2004;61(3):448-460. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cardiores.2003.09.024
Honda N, Hishida A. Pathophysiology of experimental nonoliguric acute renal failure. Kidney Int. 1993;43(3):513-521. doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/ki.1993.78
Jankauskas SS, Pevzner IB, Andrianova NV, Zorova LD, Popkov VA, Silachev DN, Kolosova NG, Plotnikov EY, Zorov DB. The age-associated loss of ischemic preconditioning in the kidney is accompanied by mitochondrial dysfunction, increased protein acetylation and decreased autophagy. Sci. Rep. 2017;7:44430. doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/srep44430
Jankauskas SS, Silachev DN, Andrianova NV, Pevzner IB, Zorova LD, Popkov VA, Plotnikov EY, Zorov DB. Aged kidney: can we protect it? Autophagy, mitochondria and mechanisms of ischemic preconditioning. Cell Cycle. 2018;17(11):1291-1309. doi: https://doi.org/10.1080/15384101.2018.1482149
Joo JD, Kim M, D’Agati VD, Lee HT. Ischemic preconditioning provides both acute and delayed protection against renal ischemia and reperfusion injury in mice. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2006;17(11):3115-3123. doi: https://doi.org/10.1681/ASN.2006050424
Juhaszova M, Zorov DB, Yaniv Y, Nuss HB, Wang S, Sollott SJ. Role of glycogen synthase kinase-3beta in cardioprotection. Circ. Res. 2009;104(11):1240-1252. doi: https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.109.197996.
Kapitsinou PP, Haase VH. Molecular mechanisms of ischemic preconditioning in the kidney. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2015;309(10):F821-F834. doi: https://doi.org/10.1152/ajprenal.00224.2015
Kim DH, Kim JY, Yu BP, Chung HY. The activation of NFkappaB through Akt-induced FOXO1 phosphorylation during aging and its modulation by calorie restriction. Biogerontology. 2008;9(1):33-47. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10522-007-9114-6
Kim J, Jang HS, Park KM. Reactive oxygen species generated by renal ischemia and reperfusion trigger protection against subsequent renal ischemia and reperfusion injury in mice. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2010;298(1):F158-F166. doi: https://doi.org/10.1152/ajprenal.00474.2009
Laplante M, Sabatini DM. mTOR signaling at a glance. J. Cell Sci. 2009;122(Pt 20):3589-3594. doi: https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.051011
Lee HT, Emala CW. Protective effects of renal ischemic preconditioning and adenosine pretreatment: role of A(1) and A(3) receptors. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2000;278(3):F380-F387. doi: https://doi.org/10.1152/ajprenal.2000.278.3.F380
Menting TP, Wever KE, Ozdemir-van Brunschot DM, Van der Vliet DJ, Rovers MM, Warle MC. Ischaemic preconditioning for the reduction of renal ischaemia reperfusion injury. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2017;3(3):CD010777. doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD010777.pub2
Murry CE, Jennings RB, Reimer KA. Preconditioning with ischemia: a delay of lethal cell injury in ischemic myocardium. Circulation. 1986;74(5):1124-1136. doi: https://doi.org/10.1161/01.cir.74.5.1124
Ortiz A, Justo P, Sanz A, Lorz C, Egido J. Targeting apoptosis in acute tubular injury. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2003;66(8):1589-1594. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/s0006-2952(03)00515-x
Park KM, Chen A, Bonventre JV. Prevention of kidney ischemia/reperfusion-induced functional injury and JNK, p38, and MAPK kinase activation by remote ischemic pretreatment. J. Biol. Chem. 2001;276(15):11870-11876. doi: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M007518200
Plotnikov EY, Kazachenko AV, Vyssokikh MY, Vasileva AK, Tcvirkun DV, Isaev NK, Kirpatovsky VI, Zorov DB. The role of mitochondria in oxidative and nitrosative stress during ischemia/reperfusion in the rat kidney. Kidney Int. 2007; 72(12):1493-1502. doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ki.5002568
Sharples EJ, Patel N, Brown P, Stewart K, Mota-Philipe H, Sheaff M, Kieswich J, Allen D, Harwood S, Raftery M, Thiemermann C, Yaqoob MM. Erythropoietin protects the kidney against the injury and dysfunction caused by ischemiareperfusion. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2004;15(8):2115-2124. doi: https://doi.org/10.1097/01.ASN.0000135059.67385.5D
Silachev DN, Isaev NK, Pevzner IB, Zorova LD, Stelmashook EV, Novikova SV, Plotnikov EY, Skulachev VP, Zorov DB. The mitochondria-targeted antioxidants and remote kidney preconditioning ameliorate brain damage through kidney- to-brain cross-talk. PLoS One. 2012;7(12):e51553. doi: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0051553
Wever KE, Menting TP, Rovers M, van der Vliet JA, Rongen GA, Masereeuw R, Ritskes-Hoitinga M, Hooijmans CR, Warlé M. Ischemic preconditioning in the animal kidney, a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One. 2012;7(2):e32296. doi: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0032296
Wu HH, Hsiao TY, Chien CT, Lai MK. Ischemic conditioning by short periods of reperfusion attenuates renal ischemia/reperfusion induced apoptosis and autophagy in the rat. J. Biomed. Sci. 2009;16(1):19. doi: https://doi.org/10.1186/1423-0127-16-19
Zager RA, Burkhart KM, Gmur DJ. Postischemic proximal tubular resistance to oxidant stress and Ca2+ ionophore-induced attack. Implications for reperfusion injury. Lab. Invest. 1995;72(5):592-600.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Byulleten’ Eksperimental’noi Biologii i Meditsiny, Vol. 171, No. 5, pp. 532-537, May, 2021
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Plotnikov, E.Y. Ischemic Preconditioning of the Kidney. Bull Exp Biol Med 171, 567–571 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-021-05270-9
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-021-05270-9