Abstract
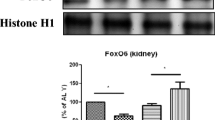
Insulin-induced PI3K/Akt activation is known to inhibit a family of Forkhead transcription factors (FOXO), which can lead to increased oxidative stress in several model organisms. One of major transcription factors activated by oxidative stress and responsible for the production of many proinflammatory cytokines is NF-κB. In the present study, We were carried out to determine the relationship between FOXO1 and NF-κB activation using HEK293T cells and aged kidney isolated from ad libitum fed (AL) and 40% calorie restriction (CR) rats. Results showed that phosphorylation of FOXO1 and NF-κB activation were significantly increased in old rats. Moreover, FOXO1 phosphorylation and NF-κB activation were shown to be significantly lower in the CR rats compared with 24–month-old AL rats. To further explore the molecular link between FOXO and NF-κB, we performed transfection experiments with FOXO-mutant plasmid in cultured HEK293T cells. Treatment of the cell with insulin led to NF-κB activation through the phosphorylation of FOXO via the PI3K/Akt pathway. These results indicate that insulin promoted NF-κB activation through phosphorylation of FOXO1 by upregulating PI3K/Akt signaling. We conclude that the phosphorylation of FOXO1 regulates NF-κB nuclear translocation by activating PI3K/Akt during aging, which was suppressed by the hypoinsulinemic action of CR.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Accili D, Arden KC (2004) FoxOs at the crossroads of cellular metabolism, differentiation, and transformation. Cell 117:421–426
Azevedo-Martins AK, Lortz S, Lenzen S, Curi R, Eizirik DL, Tiedqe M (2003) Improvement of the mitochondrial antioxidant defense status prevents cytokine-induced nuclear factor-κB activation in insulin-producing cells. Diabetes 52:93–101
Baldwin AS (1996) The NF-κB and IκB proteins: new discoveries and insights. Annu Rev Immunol 14:649–681
Birkenkamp KU, Coffer PJ (2003) Regulation of cell survival and proliferation by the FOXO (forkhead box, class O) subfamily of forkhead transcription factors. Biochem Soc Trans 31:292–297
Bluher M, Kahn BB, Kahn CR (2003) Extended longevity in mice lacking the insulin receptor in adipose tissue. Science 299:572–574
Brunet A, Bonni A, Zigmond MJ, Lin MZ, Juo P, Hu LS, Anderson MJ, Arden KC, Blenis J, Greenberg ME (1999) Akt promotes cell survival by phosphorylating and inhibiting a Forkhead transcription factor. Cell 96:857–868
Burgering BM, Medema RH (2003) Decisions on life and death: FOXO Forkhead transcription factors are in command when PKB/Akt is off duty. J Leukoc Biol 73:689–701
Coschigano KT, Holland AN, Riders ME, List EO, Flyvbjerg A, Kopchick JJ (2003) Deletion, but not antagonism, of the mouse growth hormone receptor results in severely decreased body weights, insulin, and insulin-like growth factor 1 levels and increased life span. Endocrinology 144:3799–3810
Craft S (2005) Insulin resistance syndrome and Alzheimer’s disease: age- and obesity-related effects on memory, amyloid, and inflammation. Neurobiol Aging 26:65–69
Dandona P, Aljada A, Mohanty P (2002) The anti-inflammatory and potential anti-atherogenic effect of insulin: a new paradigm. Diabetologia 45:924–930
Durham SK, Suwanichkul A, Scheimann AO, Yee D, Jackson JG, Barr FG, Powell DR (1999) FKHR binds the insulin response element in the insulin-like growth factor binding protein-1 promoter. Endocrinology 140:3140–3146
Erol A (2007) Insulin resistance is an evolutionarily conserved physiological mechanism at the cellular level for protection against increased oxidative stress. BioEssays 29:811–818
Fabrizio P, Pozza F, Pletcher SD, Gendron CM, Longo VD (2001) Regulation of longevity and stress resistance by Sch9 in yeast. Science 292:288–290
Habib AC, Creminon Y, Frobert J, Grassi P, Pradelles P, Maclouf J (1993) Demonstration of an inducible cyclooxygenase in human entothelial cells using antibodies raised against the carboxyl-terminal region of the cyclooxygenase-2. J Biol Chem 268:23448–23454
Honda Y, Honda S (1999) The daf-2 gene network for longevity regulates oxidative stress resistance and Mn-superoxide dismutase gene expression in Caenorhabditis elegans. FASEB J 13:1385–1393
Huang C, Li J, Ding M, Leonard SS, Wang L, Castranova V, Vallyathan V, Shi X (2001) UV induces phosphorylation of protein kinase B (Akt) at Ser 473 and Thr 308 in mouse epidermal CI 41 cells through hydrogen peroxide. J Biol Chem 276:40234–40240
Iwasaki K, Gleiser CA, Masoro EJ, McMahan CA, Seo EJ, Yu BP (1988) The influence of dietary protein source on longevity and age-related disease processes of Fischer rats. J Gerontol 43:5–12
Kerr LD (1995) Electrophoretic mobility shift assay. Method Enzymol 254:619–632
Kim D, Kim S, Koh H, Yoon SO, Chung AS, Cho KS, Chung J (2001) Akt/PKB promotes cancer cell invasion via increased motility and metalloproteinase production. FASEB J 15:1953–1962
Kim HJ, Kim KW, Yu BP, Chung HY (2000) The effect of age on cyclooxygenases-2 gene expression: NF-κB activation and IκBα degradation. Free Radic Bio Med 28:683–692
Kim HJ, Jung KJ, Yu BP, Cho CG, Chung HY (2002) Influence of aging and calorie restriction on MAPKs activity in rat kidney. Exp Gerontol 37:1041–1053
Kops GJ, Dansn TB, Polderman PE, Saarloos I, Wirtz KW, Coffer PJ, Huang TT, Bos JL, Medema RH, Burgering BM (2002) Forkhead transcription factor FOXO3a protects quiescent cells from oxidative stress. Nature 419:316–321
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685
Lawlor MA, Alessi DR (2001) PKB/Akt: a key mediator of cell proliferation, survival and insulin responses? J Cell Sci 114:2903–2910
Lin K, Dorman JB, Rodan A, Kenyon C (1997) daf-16: an HNF-3/forkhead family member that can function to double the life-span of Caenorhabditis elegans. Science 278:1319–1322
Lin L, Hron JD, Peng SL (2004) Regulation of NF-κB, Th activation, and autoinflammation by the forkhead transcription factor Foxo3a. Immunity 21:203–213
Matsumoto M, Han S, Kitamura T, Accili D (2006) Dual role of transcription factor FOXO1 in controlling hepatic insulin sensitivity and lipid metabolism. J Clin Invest 116:2464–2472
Mounier C, Dumas V, Posner BI (2006) Regulation of hpatic insulin-like growth factor binding protein-1 gene expression by Insulin: central role for mammalian target of rapamycin independent of forkhead box O proteins. Endocrinology 147:2383–2391
Ozes ON, Mayo LD, Gustin JA, Pfeffer SR, Pfeffer LM, Donner DB (1999) NF-kappaB activation by tumour necrosis factor requires the Akt serine–threonine kinase. Nature 401:82–85
Pahl HL (1999) Activators and target genes of Rel/NF-κB transcription factors. Oncogene 18:6853–6866
Sizemore N, Leung S, Stark GR (1999) Activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase in response to interleukin-1 leads to phosphorylation and activation of the NF-kappaB p65/RelA subunit. Mol Cell Biol 19:4798–4805
Tang ED, Nunez G, Barr FG, Guan KL (1999) Negative regulation of the forkhead transcription factor FKHR by Akt. J Biol Chem 274:16741–16746
Tatar M, Kopelman A, Epstein D, Tu MP, Yin CM, Garofalo RS (2001) A mutant Drosophila insulin receptor homolog that extends lifespan and impairs neuroendocrine function. Science 292:107–110
Tomita M, Shimokawa I, Higami Y, Yanagihara-Outa K, Kawahara T, Tanaka K, Ikeda T, Shindo H (2001) Modulation by dietary restriction in gene expression related to insulin-like growth factor-1 in rat muscle. Aging (Milano) 13:273–281
Van der Heide LP, Hoekman MFM, Smidt MP (2004) The ins and outs of FoxO shuttling: mechanisms of FoxO translocation and transcriptional regulation. Biochem J 380:297–309
Yu BP (2005) Calorie restriction as a potent anti-aging intervention: suppression of oxidative stress. In: Rattan SIS (ed) Aging intervention and therapies, World Sci Pub, pp 193–217
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by KOSEF and MOST through National Nuclear Technology Program (2006–04978 and 2007–00376). We are thankful to the “Aging Tissue Bank” (R21–2000–000–00021–0) granted by Korea Science and Engineering Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, D.H., Kim, J.Y., Yu, B.P. et al. The activation of NF-κB through Akt-induced FOXO1 phosphorylation during aging and its modulation by calorie restriction. Biogerontology 9, 33–47 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10522-007-9114-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10522-007-9114-6