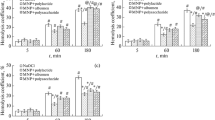
We compared dose-dependent influence of magnetic nanoparticles (MNP) coated with different shells on ROS generation during incubation with whole human blood. ROS generation was evaluated using luminol dependent chemiluminescence. MNP with polylactide shell in concentrations of 0.2-2.0 mg/ml had no effect on spontaneous chemiluminescence, while MNP with polysaccharide shell induced a dose dependent enhanced spontaneous chemiluminescence that increased during incubation (1-3 h). MNP with albumin shell in concentrations of 0.2 mg/ml gradually enhanced spontaneous chemiluminescence during incubation, but increasing the concentration neutralized this effect.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gareev KG, Pugach VS, Evreinova NV, Naumisheva EB, Panov MF, Korolev DV. Development of magnetic nanoparticles’ surface modification methods with saccharide protective shell. Biosfera. 2017;(3):76-81. Russian.
Toropova YG, Pechnikova NA, Zelinskaya IA, Korolev DV, Gareev KG, Markitantova AS, Bogushevskaya VD, Povolotskaya AV, Manshina AA. Hemocompatibility of magnetic magnethite nanoparticles and magnetite-silica composites in vitro. Byull. Sib. Med. 2018;17(3):157-167. doi: https://doi.org/10.20538/1682-0363-2018-3-157-167. Russian.
Faraji M, Yamini Y, Rezaee M. Magnetic nanoparticles: synthesis, stabilization, functionalization, characterization, and applications. J. Iran. Chem. Soc. 2010;7(1). doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03245856
Feng Q, Liu Y, Huang J, Chen K, Huang J, Xiao K. Uptake, distribution, clearance, and toxicity of iron oxide nanoparticles with different sizes and coatings. Sci. Rep. 2018;8(1):2082. doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-19628-z
Gaharwar US, Meena R, Rajamani P. Iron oxide nanoparticles induced cytotoxicity, oxidative stress and DNA damage in lymphocytes. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2017;37(10):1232-1244. doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/jat.3485
Karade VC, Parit SB, Dawkar VV, Devan RS, Choudhary RJ, Kedge VV, Pawar NV, Kim JH, Chougale AD. A green approach for the synthesis of α-Fe2O3 nanoparticles from Gardenia resinifera plant and it’s In vitro hyperthermia application. Heliyon. 2019;5(7):e02044. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e02044
Khanna P, Ong C, Bay BH, Baeg GH. Nanotoxicity: an interplay of oxidative stress, inflammation and cell death. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2015;5(3):1163-1180. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/nano5031163
Kharitonskii PV, Gareev KG, Ionin SA, Bogachev YV, Klimenkov BD, Kononova IE, Moshnikov VA, Ryzhov VA. Microstructure and magnetic state of Fe3O4-SiO2 colloidal particles. J. Magn. 2015;20(3):221-228. doi: https://doi.org/10.4283/JMAG.2015.20.3.221
Liao F, Chen L, Liu Y, Zhao D, Peng W, Wang W, Feng S. The size-dependent genotoxic potentials of titanium dioxide nanoparticles to endothelial cells. Environ. Toxicol. 2019;34(11):1199-1207. doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/tox.22821
Nune SK, Gunda P, Thallapally PK, Lin YY, Forrest ML, Berkland CJ. Nanoparticles for biomedical imaging. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2009;6(11):1175-1194. doi: https://doi.org/10.1517/17425240903229031
Price PM, Mahmoud WE, Al-Ghamdi AA, Bronstein LM. Magnetic drug delivery: where the field is going. Front. Chem. 2018;6:619. doi: https://doi.org/10.3389/fchem.2018.00619
Reddy UA, Prabhakar PV, Mahboob M. Biomarkers of oxidative stress for in vivo assessment of toxicological effects of iron oxide nanoparticles. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2017;24(6):1172-1180. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sjbs.2015.09.029
Toropova YG, Golovkin AS, Malashicheva AB, Korolev DV, Gorshkov AN, Gareev KG, Afonin MV, Galagudza MM. In vitro toxicity of FemOn, FemOn-SiO2 composite, and SiO2-FemOn core-shell magnetic nanoparticles. Int. J. Nanomedicine. 2017;12:593-603. doi: https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S122580
Verma J, Lal S, Van Noorden CJ. Nanoparticles for hyperthermic therapy: synthesis strategies and applications in glioblastoma. Int. J. Nanomedicine. 2014;9:2863-2877. doi: https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S57501
Zorin VN, Gareev KG, Naumisheva EB, Postnov VN, Evreinova NV, Korolev DV. Magnetic nanoparticles for medical application with a coating deposited with various methods. J. Physics: Conference Ser. 2018;1124. doi: https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1124/3/031009
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Byulleten’ Eksperimental’noi Biologii i Meditsiny, Vol. 17, No. 1, pp. 95-99, January, 2021
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Toropova, Y.G., Motorina, D.S., Zelinskaya, I.А. et al. Generation of Reactive Oxygen Species by Human Whole Blood Cells Exposed to Iron Oxide Magnetic Nanoparticles Coated with Different Shells. Bull Exp Biol Med 171, 77–80 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-021-05176-6
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-021-05176-6