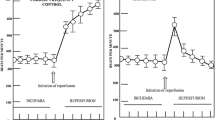
Gaseous transmitters were assayed in rat blood during catecholamine-induced damage to the heart. Hypercatecholaminemia was modeled by single subcutaneous injection of 0.1% epinephrine hydrochloride in a dose of 2 mg/kg. The blood concentrations of NO, H2S, and CO were measured. The catecholamine-induced damage to the myocardium resulted in phasic changes in the blood levels of gaseous transmitters: CO concentration increased in 1 h, H2S increased in 24 h, and NO concentration increased in 72 h after injection.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kursov SV, Beletskiy OV, Lyzogub KI, Lyzogub MV. Blood carboxyhemoglobin monitoring for evaluation of severity of traumatic shock and reperfusion injuries (analytical review with results of our own observations). Medistina Neotlozhnykh Sostoyanii. 2017;(1):32-38. Russian.
Makarenko EV, Pimanov SI, Chupakhina OP, Shilenok AV, Kut’ko SE, Pilant DA. Stress-induced (takotsubo) cardiomyopathy. Vestn. Vitebsk. Gos. Med. Univer. 2012;11(1):157-165. Russian.
Khidirova LD, Mayanskaya NN. Inflammatory reactions in experimental myocardial damage. Rats. Farmakoter. Kardiol. 2012;8(5):717-720. Russian.
Beutler E, West C. Simplified determination of carboxyhemoglobin. Clin. Chem. 1984;30(6):871-874.
Guo SB, Duan ZJ, Wang QM, Zhou Q, Li Q, Sun XY. Endogenous carbon monoxide downregulates hepatic cystathionine-γ-lyase in rats with liver cirrhosis. Exp. Ther. Med. 2015;10(6):2039-2046.
King AL, Polhemus DJ, Bhushan S, Otsuka H, Kondo K, Nicholson CK, Bradley JM, Islam KN, Calvert JW, Tao YX, Dugas TR, Kelley EE, Elrod JW, Huang PL, Wang R, Lefer DJ. Hydrogen sulfide cytoprotective signaling is endothelial nitric oxide synthase-nitric oxide dependent. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 2014;111(8):3182-3187.
Kobayashi A, Mizukami H, Sakamoto N, Yamaki T, Kunii H, Nakazato K, Takeishi Y. Endogenous carbon monoxide concentration in blood elevates in acute coronary syndrome of nonsmoker population. Fukushima J. Med. Sci. 2015;61(1):72-78.
Miranda KM, Espey MG, Wink DA. A rapid, simple spectrophotometric method for simultaneous detection of nitrate and nitrite. Nitric Oxide. 2001;5(1):62-71.
Oh GS, Pae HO, Lee BS, Kim BN, Kim JM, Kim HR, Jeon SB, Jeon WK, Chae HJ, Chung HT. Hydrogen sulfide inhibits nitric oxide production and nuclear factor-kappaB via heme oxygenase-1 expression in RAW264.7 macrophages stimulated with lipopolysaccharide. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2006;41(1):106-119.
Qu K, Chen CP, Halliwell B, Moore PK, Wong PT. Hydrogen sulfide is a mediator of cerebral ischemic damage. Stroke. 2006;37(3):889-893.
Rose P, Moore PK, Zhu YZ. H2S biosynthesis and catabolism: new insights from molecular studies. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2017;74(8):1391-1412.
Stein AB, Bolli R, Dawn B, Sanganalmath SK, Zhu Y, Wang OL, Guo Y, Motterlini R, Xuan YT. Carbon monoxide induces a late preconditioning-mimetic cardioprotective and antiapoptotic milieu in the myocardium. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2012;52(1):228-236.
Wang J, Lu S, Moënne-Loccoz P, Ortiz de Montellano PR. Interaction of nitric oxide with human heme oxygenase-1. J. Biol. Chem. 2003;278(4):2341-2347.
Wang R. Shared signaling pathways among gasotransmitters. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 2012;109(23):8801-8802.
Whiteman M, Li L, Kostetski I, Chu SH, Siau JL, Bhatia M, Moore PK. Evidence for the formation of a novel nitrosothiol from the gaseous mediators nitric oxide and hydrogen sulphide. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006;343(1):303-310.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Byulleten’ Eksperimental’noi Biologii i Meditsiny, Vol. 165, No. 6, pp. 681-683, June, 2018
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ivanova, A.S., Sitnikova, O.G., Popova, I.G. et al. Concentrations of Gaseous Transmitters during Catecholamine Damage to the Myocardium in Rats. Bull Exp Biol Med 165, 725–727 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-018-4251-2
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-018-4251-2