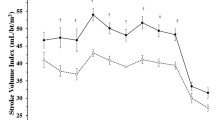
The study examined the effect of α1-adrenoceptor stimulation with methoxamine on chronotropic function of isolated heart perfused ex vivo according to Langendorff and cardiac chronotropy in vivo. Stimulation of α1-adrenoceptors in isolated heart induced gradually developing bradycardia, which progressed during several minutes. Similar stimulation in vivo produced a short-term bradycardia probably terminated by the compensatory influences in the whole organism. Comparison of the data obtained in both experimental paradigms during α1-adrenoceptor stimulation revealed unidirectional changes in cardiac chronotropy characterized with time-related peculiarities.
Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
16 March 2021
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-021-05110-w
References
Zefirov TL, Ziyatdinova NI, Gainullin AA, Zefirov AL. Blockade of hyperpolarization-activated channels modifies the effect of beta-adrenoceptor stimulation. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2002;133(5):425-427.
Zefirov TL, Ziatdinova NI, Khisamieva LI, Zefirov AL. Comparative analysis of the impact of α1-and α2-adrenoreceptor blockade on cardiac function in rats during postnatal ontogeny. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2011;151(6):664-666.
Bisognano JD, Weinberger HD, Bohlmeyer TJ, Pende A, Raynolds MV, Sastravaha A, Roden R, Asano K, Blaxall BC, Wu SC, Communal C, Singh K, Colucci W, Bristow MR, Port DJ. Myocardial-directed overexpression of the human beta(1)-adrenergic receptor in transgenic mice. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol 2000;32(5):817-830.
Jensen BC, O’Connell TD, Simpson PC. Alpha-1-adrenergic receptors: targets for agonist drugs to treat heart failure. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2011;51(4):518-528.
Lakatta EG, Maltsev VA, Vinogradova TM. A coupled SYSTEM of intracellular Ca2+ clocks and surface membrane voltage clocks controls the timekeeping mechanism of the heart’s pacemaker. Circ. Res. 2010;106(4):659-673.
Myslivecek J, Nováková M, Klein M. Receptor subtype abundance as a tool for effective intracellular signalling. Cardiovasc. Hematol. Disord. Drug Targets. 2008;8(1):66-79.
Salameh A, Krautblatter S, Baessler S, Karl S, Rojas Gomez D, Dhein S, Pfeiffer D. Signal transduction and transcriptional control of cardiac connexin 43 up-regulation after alpha 1-adre noceptor stimulation. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2008. Vol. 326(1):315-322.
Shannon R, Chaudhry M. Effect of alpha1-adrenergic receptors in cardiac pathophysiology. Am Heart J. 2006;152(5):842-850.
Simpson P. Lessons from knockouts: the alpha1-Ars. The Adrenergic Receptors in the 21st Century. Perez DM, eds. Totowa, 2006):207-240.
Steinfath M, Chen YY, Lavický J, Magnussen O, Nose M, Rosswag S, Schmitz W, Scholz H. Cardiac alpha 1-adrenoceptor densities in different mammalian species. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1992;107(1):185-188.
Triposkiadis F, Karayannis G, Giamouzis G, Skoularigis J, Louridas G, Butler J. The sympathetic nervous system in heart failure physiology, pathophysiology, and clinical implications. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2009;54(19):1747-1762.
Zhu WZ, Wang SQ, Chakir K, Yang D, Zhang T, Brown JH, Devic E, Kobilka BK, Cheng H, Xiao RP. Linkage of beta1-adrenergic stimulation to apoptotic heart cell death through protein kinase A-independent activation of Ca2+/calmodulin kinase II. J. Clin. Invest. 2003;111(5):617-625.
Ziyatdinova NI, Dementieva RE, Fashutdinov LI, Zefirov TL. Blockade of different subtypes of α(1)-adrenoceptors produces opposite effect on heart chronotropy in newborn rats. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2012;154(2):184-185.
Ziyatdinova NI, Zefirov AL, Zefirov TL. Age-related peculiarities of the effect of alpha-adrenoreceptor blockade on cardiac function in rats. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2002;133(6):532-534.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Byulleten’ Eksperimental’noi Biologii i Meditsiny, Vol. 162, No. 7, pp. 7-10, July 2016
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zefirov, T.L., Khabibrakhmanov, I.I., Ziyatdinova, N.I. et al. Peculiar Aspects in Influence of α1-Adrenoceptor Stimulation on Isolated Rat Heart. Bull Exp Biol Med 162, 4–6 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-016-3530-z
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-016-3530-z