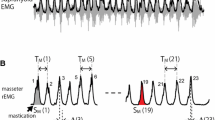
Reflection of the state of hunger in impulse activity of nose wing muscles and upper esophageal sphincter muscles was studied in chronic experiments on rabbits subjected to 24-h food deprivation in the absence of locomotion and during search behavior. In the absence of apparent behavioral activity, including sniffing, alai nasi muscles of hungry rabbits constantly generated bursts of action potentials synchronous with breathing, while upper esophageal sphincter muscles exhibited regular aperiodic low-amplitude impulse activity of tonic type. Latent form of food motivation was reflected in the structure of temporal organization of impulse activity of alai nasi muscles in the form of bimodal distribution of interpulse intervals and in temporal structure of impulse activity of upper esophageal sphincter muscles in the form of monomodal distribution. The latent form of food motivation was manifested in the structure of temporal organization of periods of the action potentials burst-like rhythm, generated by alai nasi muscles, in the form of monomodal distribution, characterized by a high degree of dispersion of respiratory cycle periods. In the absence of physical activity hungry animals sporadically exhibited sniffing activity, manifested in the change from the burst-like impulse activity of alai nasi muscles to the single-burst activity type with bimodal distribution of interpulse intervals and monomodal distribution of the burst-like action potentials rhythm periods, the maximum of which was shifted towards lower values, which was the cause of increased respiratory rate. At the same time, the monomodal temporal structure of impulse activity of the upper esophageal sphincter muscles was not changed. With increasing food motivation in the process of search behavior temporal structure of periods of the burst-like action potentials rhythm, generated by alai nasi muscles, became similar to that observed during sniffing, not accompanied by animal’s locomotion, which is typical for the increased respiratory rhythm frequency. Increased hunger motivation was reflected in the temporal structure of impulse activity of upper esophageal sphincter muscles in the form of a shift to lower values of the maximum of monomodal distribution of interpulse intervals on the histogram, resulting in higher impulse activity frequency. The simultaneous increase in the frequency of action potentials bursts generation by alai nasi muscles and regular impulse activity of upper esophageal sphincter muscles is a reliable criterion for enhanced food motivation during search behavior in rabbits.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bobrikov LV. Biomolecular and PBases of Neurosynergism. Moscow, 2005. Russian.
Kromin AA. Electrical and mechanical activity of the upper esophageal sphincter in rabbits. Fiziol. Zh. 1991; 37(3): 59-65. Russian.
Kromin AA, Zenina OY. Effects of electric stimulation of the hunger center in the lateral hypothalamus on slow electric activity and spike activity of fundal and antral stomach muscles in rabbits under conditions of hunger and satiation. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2013; 155(5):591-7.
Kromin AA, Ignatova YuP. Effect of neurostimlation of the hunger center in the lateral hypothalamus on impulse activity of the proper masticatory muscle in hungry and satiated rabbits. Trudy Nauch. Soveta po Eksperiment. Priklad. Fiziol. Moscow, 2009. Vol. 15. pp. 121-141. Russian.
Kromin AA, Chesnokova LN. Reflection of dominating food motivation in the structure of temporal organization of respiration during unproductive food-procurring behavior. Zh. Vyssh. Nervn. Deyat. 1990; 40(4):773-775. Russian.
Kromin AA, Ignatova YuP. Patent RF No. 52562. Electromyographical bipolar silver ball electrode. Byull. Izobr. No. 10 (April 10, 2006). Russian.
Sydakov KV. Dominant Motivation. Moscow, 2004. Russian.
Fabri KE. Basics of Zoopsychology. Moscow, 1999. Russian.
Shvyrkov VB. Introduction in Objective Psychology. Moscow, 1995. Russian.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Byulleten’ Eksperimental’noi Biologii i Meditsiny, Vol. 161, No. 3, pp. 300-307, March, 2016
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kromin, A.A., Dvoenko, E.E. & Zenina, O.Y. Reflection of the State of Hunger in Impulse Activity of Nose Wing Muscles and Upper Esophageal Sphincter during Search behavior in Rabbits. Bull Exp Biol Med 161, 327–333 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-016-3407-1
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-016-3407-1