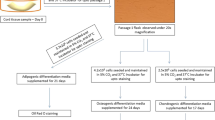
Extraembryonic tissues, in particular, umbilical cord stroma are promising sources of multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells for regenerative medicine. In recent years, methods for isolation of mesenchymal stromal cells from different compartments of the umbilical cords based on enzymatic disaggregation of the tissue or on tissue explants have been proposed. Here we propose a protocol of isolation of multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells from the whole umbilical cord that combines the advantages of each approach and ensures sufficient cell yield for further experimental and clinical applications. A combination of short-term incubation of tissue fragments on cold collagenase solution followed by their culturing in the form of explants significantly increased the yield of cells with high proliferative activity, typical pluripotent mesenchymal stromal cell phenotype, and preserved differentiation capacity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
V. Aguilera, L. Briceno, H. Contreras, et al., PLoS One, 9, No. 11, doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0111025 (2014).
B. An, S. Na, S. Lee, et al., Cell Tissue Res, 359, No. 3, 767-777 (2014).
T. Bakhshi, R. C. Zabriskie, S. Bodie, et al., Transfusion, 48, No. 12, 2638-2644 (2008).
M. E. Bernardo and W. E. Fibbe, Cell Stem Cells, 13, No. 4, 392-402 (2013).
A. Can and S. Karahuseyinoglu, Stem Cells, 25, No. 11, 2886-2895 (2007).
K. C. Chao, K. F. Chao, Y. S. Fu, and S. H. Liu, PLoS One, 3, No. 1, doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0001451 (2008).
M. S. Choudhery, M. Badowski, A. Muise, and D. T. Harris, Cytotherapy, 15, No. 3, 330-343 (2013).
M. C. Corotchi, M. A. Popa, A. Remes, et al., Stem Cell Res. Ther., 4, No. 4, 81 (2013).
A. M. DiMarino, A. I. Caplan, and T. L. Bonfield, Front. Immunol., 4, 201 (2013).
D. C. Ding, Y. H. Chang, W. C. Shyu, and S. Z. Lin, Cell Transplant., 24, No. 3, 339-347 (2015).
J. Dittmer and B. Leyh, J. Clin. Oncol., 44, No. 6, 1789-1798 (2014).
J. D. Glenn and K. A. Whartenby, World J. Stem Cells, 6, No. 5, 526-539 (2014).
J. U. Hsieh, H. W. Wang, S. J. Chang, et al., PLoS One, 8, No. 8, doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0072604 (2013).
S. Kern, H. Eichler, J. Stoeve, et al., Stem Cells, 24, No. 5, 1294-1301 (2006).
D. W. Kim, M. Staples, K. Shinozuka, et al., Int. J. Mol. Sci., 14, No. 6, 11,692-11,712 (2013).
N. Kim and S. G. Cho, Korean. J. Intern. Med., 28, No. 4, 387-402 (2013).
C. Leite, N. T. Silva, S. Mendes, et al., PLoS One, 9, No. 10, doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0111059 (2014).
E. Martin-Rendon, D. Sweeney, J. Girdlestone, et al., Vox Sang., 95, No. 2, 137-148 (2008).
M. B. Murphy, K. Moncivais, and A. I. Caplan, Exp. Mol. Med., 45, No. 2, e54 (2013).
T. Nagamura-Inoue and H. He, World J. Stem Cells, 6, No. 2, 195-202 (2014).
T. Pereira, G. Ivanova, A. R. Caseiro, et al., PLoS One, 9, No. 11, doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0113769 (2014).
W. C. Pereira, I. Khushnooma, M. Madkaikar, and K. Ghosh, J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med., 2, No. 7, 394-399 (2008).
Y. A. Romanov, A. N. Darevskaya, N. V. Merzlikina, and L. B. Buravkova, Bull. Exp. Biol. Med., 140, No. 1, 138-143 (2005).
Y. A. Romanov, V. A. Svintsitskaya, and V. N. Smirnov, Stem Cells, 21, No. 1, 105-110 (2003).
P. Salehinejad, N. B. Alitheen, A. M. Ali, et al., In vitro Cell Dev. Biol. Anim., 48, No. 2, 75-83 (2012).
M. T. Sutton and T. L. Bonfield, Stem Cells Int., doi: 10.1155/2014/516278 (2014).
N. Tsagias, I. Koliakos, V. Karagiannis, et al., Transfus. Med., 21, No. 4, 253-261 (2011).
N. Watson, R. Divers, R. Kedar, et al., Cytotherapy, 17, No. 1, 18-24 (2015).
S. M. Watt, F. Gullo, M. van der Garde, et al., Br. Med. Bull., 108, 25-53 (2013).
J. H. Yoon, E. Y. Roh, S. Shin, et al., Biomed. Res. Int., doi: 10.1155/2013/428726 (2013).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Kletochnye Tekhnologii v Biologii i Meditsine, No. 3, pp. 174-180, July, 2015
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Romanov, Y.A., Balashova, E.E., Volgina, N.E. et al. Optimized Protocol for Isolation of Multipotent Mesenchymal Stromal Cells from Human Umbilical Cord. Bull Exp Biol Med 160, 148–154 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-015-3116-1
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-015-3116-1