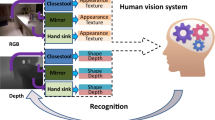
Abstract
Understanding the semantics of objects and scenes using multi-modal RGB-D sensors serves many robotics applications. Key challenges for accurate RGB-D image recognition are the scarcity of training data, variations due to viewpoint changes and the heterogeneous nature of the data. We address these problems and propose a generic deep learning framework based on a pre-trained convolutional neural network, as a feature extractor for both the colour and depth channels. We propose a rich multi-scale feature representation, referred to as convolutional hypercube pyramid (HP-CNN), that is able to encode discriminative information from the convolutional tensors at different levels of detail. We also present a technique to fuse the proposed HP-CNN with the activations of fully connected neurons based on an extreme learning machine classifier in a late fusion scheme which leads to a highly discriminative and compact representation. To further improve performance, we devise HP-CNN-T which is a view-invariant descriptor extracted from a multi-view 3D object pose (M3DOP) model. M3DOP is learned from over 140,000 RGB-D images that are synthetically generated by rendering CAD models from different viewpoints. Extensive evaluations on four RGB-D object and scene recognition datasets demonstrate that our HP-CNN and HP-CNN-T consistently outperforms state-of-the-art methods for several recognition tasks by a significant margin.









Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
In practice, we define the canonical view as the \(-\,27.5^{\circ }\) and \(20^{\circ }\) off the azimuth and elevation angles.
Available: http://rgbd-dataset.cs.washington.edu/.
References
Angeli, A., Filliat, D., Doncieux, S., & Meyer, J. A. (2008). Fast and incremental method for loop-closure detection using bags of visual words. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 24(5), 1027–1037.
Asif, U., Bennamoun, M., & Sohel, F. (2015). Discriminative feature learning for efficient rgb-d object recognition. In IEEE/RSJ international conference on intelligent robots and systems (IROS), 2015 (pp. 272–279). IEEE.
Asif, U., Bennamoun, M., & Sohel, F. (2015). Efficient RGB-D object categorization using cascaded ensembles of randomized decision trees. In Proceedings of ICRA, (pp. 1295–1302).
Azizpour, H., Razavian, A. S., Sullivan, J., Maki, A., & Carlsson, S. (2016). Factors of transferability for a generic convnet representation. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 38(9), 1790–1802. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2015.2500224.
Bai, J., Wu, Y., Zhang, J., & Chen, F. (2015). Subset based deep learning for RGB-D object recognition. Neurocomputing, 165, 280–292.
Bengio, Y. (2009). Learning deep architectures for AI. Foundations and Trends® in Machine Learning, 2(1), 1–127.
Bengio, Y., Lamblin, P., Popovici, D., & Larochelle, H. (2007). Greedy layer-wise training of deep networks. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 19, 153.
Bengio, Y., Courville, A., & Vincent, P. (2013). Representation learning: A review and new perspectives. IEEE PAMI, 35(8), 1798–1828.
Blum, M., Springenberg, J.T., Wulfing, J., & Riedmiller, M. (2012). A learned feature descriptor for object recognition in RGB-D data. In Proceedings of ICRA (pp. 1298–1303).
Bo, L., Ren, X., & Fox, D. (2011). Depth kernel descriptors for object recognition. In Proceedings of IROS (pp. 821–826).
Bo, L., Ren, X., & Fox, D. (2012). Unsupervised feature learning for rgb-d based object recognition. In Proceedings of ISER.
Browatzki, B., Fischer, J., Graf, B., Bulthoff, H., & Wallraven, C. (2011). Going into depth: Evaluating 2D and 3D cues for object classification on a new, large-scale object dataset. In IEEE international conference on computer vision workshops (ICCVW) (pp. 1189–1195).
Chatfield, K., Simonyan, K., Vedaldi, A., & Zisserman, A. (2014). Return of the devil in the details: Delving deep into convolutional nets. In Proceedings of BMVC. arXiv preprint arXiv:1405.3531.
Cheng, Y., Zhao, X., Huang, K., & Tan, T. (2014). Semi-supervised learning for RGB-D object recognition. In Proceedings of ICPR (pp. 2377–2382).
Coates, A., Ng, A., & Lee, H. (2011). An analysis of single-layer networks in unsupervised feature learning. In Proceedings of AISTATS (pp. 215–223).
Deng, J., Dong, W., Socher, R., Li, L.J., Li, K., & Fei-Fei, L. (2009). Imagenet: A large-scale hierarchical image database. In IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, 2009, CVPR 2009 (pp. 248–255). IEEE.
Gupta, S., Girshick, R., Arbeláez, P., & Malik, J. (2014). Learning rich features from RGB-D images for object detection and segmentation. In Proceedings of ECCV (pp. 345–360).
Hariharan, B., Arbeláez, P., Girshick, R., & Malik, J. (2015). Hypercolumns for object segmentation and fine-grained localization. In Proceedings of CVPR.
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., & Sun, J. (2015). Spatial pyramid pooling in deep convolutional networks for visual recognition. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 37(9), 1904–1916.
Hinton, G., Osindero, S., & Teh, Y. (2006). A fast learning algorithm for deep belief nets. Neural Computation, 18(7), 1527–1554.
Hinton, G.E. (2012). A practical guide to training restricted boltzmann machines. In Neural networks: Tricks of the trade (pp. 599–619). Springer.
Huang, G. B., Zhu, Q. Y., & Siew, C. K. (2006). Extreme learning machine: Theory and applications. Neurocomputing, 70(1), 489–501.
Huang, G. B., Zhou, H., Ding, X., & Zhang, R. (2012). Extreme learning machine for regression and multiclass classification. IEEE Trans on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Part B: Cybernetics, 42(2), 513–529.
Jhuo, I.H., Gao, S., Zhuang, L., Lee, D., & Ma, Y. (2014). Unsupervised feature learning for RGB-D image classification. In Proceedings of ACCV (pp. 276–289).
Krizhevsky, A., Sutskever, I., & Hinton, G. (2012). Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of NIPS (pp. 1097–1105).
Lai, K., Bo, L., Ren, X., & Fox, D. (2011). A large-scale hierarchical multi-view RGB-D object dataset. In Proceedings of ICRA (pp. 1817–1824).
Lazebnik, S., Schmid, C., & Ponce, J. (2006). Beyond bags of features: Spatial pyramid matching for recognizing natural scene categories. In proceedings of CVPR (Vol. 2, pp. 2169–2178).
Le, Q.V., Karpenko, A., Ngiam, J., & Ng, A.Y. (2011). Ica with reconstruction cost for efficient overcomplete feature learning. In Advances in neural information processing systems (pp. 1017–1025).
Liao, Y., Kodagoda, S., Wang, Y., Shi, L., & Liu, Y. (2016). Understand scene categories by objects: A semantic regularized scene classifier using convolutional neural networks. In 2016 IEEE international conference on robotics and automation (ICRA) (pp. 2318–2325). IEEE.
Liu, L., Shen, C., & van den Hengel, A. (2015). The treasure beneath convolutional layers: Cross convolutional layer pooling for image classification. In Proceedings of CVPR.
Liu, W., Ji, R., & Li, S. (2015). Towards 3D object detection with bimodal deep boltzmann machines over RGBD imagery. In Proceedings of CVPR.
Lowe, D. G. (2004). Distinctive image features from scale-invariant keypoints. International Journal of Computer Vision, 60(2), 91–110.
Lowry, S., Snderhauf, N., Newman, P., Leonard, J. J., Cox, D., Corke, P., et al. (2016). Visual place recognition: A survey. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 32(1), 1–19. https://doi.org/10.1109/TRO.2015.2496823.
Phong, B. T. (1975). Illumination for computer generated pictures. Communications of the ACM, 18(6), 311–317.
Razavian, A.S., Azizpour, H., Sullivan, J., & Carlsson, S. (2014). CNN features off-the-shelf: An astounding baseline for recognition. In Proceedings of computer vision and pattern recognition workshops (CVPRW) (pp. 512–519).
Schwarz, M., Schulz, H., & Behnke, S. (2015). RGB-D object recognition and pose estimation based on pre-trained convolutional neural network features. In Proceedings of ICRA.
Silberman, N., & Fergus, R. (2011). Indoor scene segmentation using a structured light sensor. In 2011 IEEE international conference on computer vision workshops (ICCV workshops) (pp. 601–608). IEEE
Socher, R., Huval, B., Bath, B., Manning, C.D., & Ng, A. (2012). Convolutional-recursive deep learning for 3D object classification. In Proceedings of NIPS (pp. 665–673).
Song, S., Lichtenberg, S.P., & Xiao, J. (2015). Sun rgb-d: A rgb-d scene understanding benchmark suite. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (pp. 567–576).
Srivastava, N., Hinton, G., Krizhevsky, A., Sutskever, I., & Salakhutdinov, R. (2014). Dropout: A simple way to prevent neural networks from overfitting. The Journal of Machine Learning Research, 15(1), 1929–1958.
Su, H., Maji, S., Kalogerakis, E., & Learned-Miller, E. (2015). Multi-view convolutional neural networks for 3d shape recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision (pp. 945–953).
Torralba, A., Murphy, K.P., Freeman, W.T., & Rubin, M.A. (2003). Context-based vision system for place and object recognition. In Proceedings of ninth IEEE international conference on Computer vision, 2003 (pp. 273–280). IEEE.
Uzair, M., Mahmood, A., & Mian, A. (2015). Hyperspectral face recognition with spatiospectral information fusion and pls regression. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 24, 1127–1137. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2015.2393057.
Vedaldi, A., & Fulkerson, B. (2010). Vlfeat: An open and portable library of computer vision algorithms. In Proceedings of the international conference on multimedia (pp. 1469–1472). ACM.
Vedaldi, A., & Lenc, K. (2014). Matconvnet-convolutional neural networks for matlab. arXiv preprint arXiv:1412.4564.
Welsh, T., Ashikhmin, M., & Mueller, K. (2002). Transferring color to greyscale images. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 21(3), 277–280. https://doi.org/10.1145/566654.566576.
Wu, Z., Song, S., Khosla, A., Yu, F., Zhang, L., Tang, X., & Xiao, J. (2015). 3d shapenets: A deep representation for volumetric shapes. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (pp. 1912–1920).
Yang, J., Yu, K., Gong, Y., & Huang, T. (2009). Linear spatial pyramid matching using sparse coding for image classification. In IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, 2009, CVPR 2009 (pp. 1794–1801). IEEE
Yang, S., & Ramanan, D. (2015). Multi-scale recognition with DAG-CNNS. In Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision (pp. 1215–1223).
Zaki, H.F., Shafait, F., & Mian, A. (2015). Localized deep extreme learning machines for efficient RGB-D object recognition. In Proceedings of digital image computing: Techniques and applications (DICTA) (pp. 1–8). https://doi.org/10.1109/DICTA.2015.7371280.
Zaki, H.F.M., Shafait, F., & Mian, A. (2016). Convolutional hypercube pyramid for accurate RGB-D object category and instance recognition. In Proceedings of ICRA (to appear).
Zeiler, M.D., & Fergus, R. (2014). Visualizing and understanding convolutional networks. In Computer vision—ECCV 2014 (pp. 818–833). Springer.
Zhou, B., Lapedriza, A., Xiao, J., Torralba, A., & Oliva, A. (2014). Learning deep features for scene recognition using places database. In Proceedings of NIPS (pp. 487–495).
Acknowledgements
Funding was provided by Australian Research Council (Grant No. Australian Research Council (ARC) Discovery Project DP160101458).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zaki, H.F.M., Shafait, F. & Mian, A. Viewpoint invariant semantic object and scene categorization with RGB-D sensors. Auton Robot 43, 1005–1022 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10514-018-9776-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10514-018-9776-8