Abstract
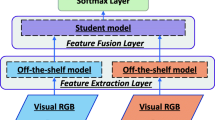
Most of the past deep learning methods which are proposed for RGB-D scene classification use global information and directly consider all pixels in the whole image for high-level tasks. Such methods cannot hold much information about local feature distributions, and simply concatenate RGB and depth features without exploring the correlation and complementarity between raw RGB and depth images. From the human vision perspective, we recognize the category of one unknown scene mainly relying on the object-level information in the scene which includes the appearance, texture, shape, and depth. The structural distribution of different objects is also taken into consideration. Based on this observation, constructing mid-level representations with discriminative object parts would generally be more attractive for scene analysis. In this paper, we propose a new Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs)-based local multi-modal feature learning framework (LM-CNN) for RGB-D scene classification. This method can effectively capture much of the local structure from the RGB-D scene images and automatically learn a fusion strategy for the object-level recognition step instead of simply training a classifier on top of features extracted from both modalities. The experimental results on two popular datasets, i.e., NYU v1 depth dataset and SUN RGB-D dataset, show that our method with local multi-modal CNNs outperforms state-of-the-art methods.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lu X, Li X, Mou L. Semi-supervised multitask learning for scene recognition. IEEE Trans Cybern 2015; 45(9):1967–1976.
Zhuo W, Salzmann M, He X, Liu M. 2017. Indoor scene parsing with instance segmentation, semantic labeling and support relationship inference. In: IEEE Conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, no. EPFL-CONF-227441.
Cong Y, Liu J, Yuan J, Luo J. Self-supervised online metric learning with low rank constraint for scene categorization. IEEE Trans Image Process 2013;22(8):3179–3191.
Lu X, Wang B, Zheng X, Li X. Exploring models and data for remote sensing image caption generation, IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing.
Yu J, Tao D, Rui Y, Cheng J. Pairwise constraints based multiview features fusion for scene classification. Pattern Recogn 2013;46(2):483–496.
Gao Y, Wang M, Tao D, Ji R, Dai Q. 3-D object retrieval and recognition with hypergraph analysis. IEEE Trans Image Process 2012;21(9):4290–4303.
Bian W, Tao D. Biased discriminant euclidean embedding for content-based image retrieval. IEEE Trans Image Process 2010;19(2):545–554.
Lu X, Chen Y, Li X. Hierarchical recurrent neural hashing for image retrieval with hierarchical convolutional features. IEEE Trans Image Process 2018;27(1):106–120.
Cheng G, Zhou P, Han J. Learning rotation-invariant convolutional neural networks for object detection in VHR optical remote sensing images. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 2016;54(12):7405–7415.
Cheng G, Li Z, Yao X, Guo L, Wei Z. Remote sensing image scene classification using bag of convolutional features. IEEE Geosci Remote Sens Lett 2017;14(10):1735–1739.
Wang P, Li W, Gao Z, Zhang Y, Tang C, Ogunbona P. Scene flow to action map: a new representation for RGB-D based action recognition with convolutional neural networks, IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.
Ma S, Bargal SA, Zhang J, Sigal L, Sclaroff S. Do less and achieve more: training CNNS for action recognition utilizing action images from the web. Pattern Recogn 2017;68:334–345.
Yang W, Jin L, Tao D, Xie Z, Feng Z. Dropsample: a new training method to enhance deep convolutional neural networks for large-scale unconstrained handwritten chinese character recognition. Pattern Recogn 2016;58:190–203.
Cheng G, Yang C, Yao X, Guo L, Han J. When deep learning meets metric learning: remote sensing image scene classification via learning discriminative cnns, IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing.
Luo Y, Wen Y, Tao D, Gui J, Xu C. Large margin multi-modal multi-task feature extraction for image classification. IEEE Trans Image Process 2016;25(1):414–427.
Montserrat DM, Lin Q, Allebach J, Delp EJ. Training object detection and recognition CNN models using data augmentation. Electron Imaging 2017;2017(10):27–36.
Li J, Zhang Z, He H. Hierarchical convolutional neural networks for EEG-based emotion recognition. Cognitive Computation 2017;10:1–13.
Feng S, Wang Y, Song K, Wang D, Yu G. Detecting multiple coexisting emotions in microblogs with convolutional neural networks. Cognitive Computation 2017;10:1–20.
Deng J, Dong W, Socher R, Li L-J, Li K, Fei-Fei L. Imagenet: a large-scale hierarchical image database. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition; 2009. p. 248– 255.
Wan L, Zeiler M, Zhang S, Cun YL, Fergus R. Regularization of neural networks using dropconnect. In: International Conference on Machine Learning; 2013. p. 1058–1066.
Zhou B, Lapedriza A, Xiao J, Torralba A, Oliva A. Learning deep features for scene recognition using places database. In: Neural Information Processing Systems; 2014. p. 487–495.
Krizhevsky A, Sutskever I, Hinton GE. Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. In: Neural Information Processing Systems; 2012. p. 1097–1105.
Han J, Shao L, Xu D, Shotton J. Enhanced computer vision with Microsoft Kinect sensor: a review. IEEE Trans Cybern 2013;43(5):1318–1334.
Cai Z, Han J, Liu L, Shao L. RGB-D datasets using Microsoft Kinect or similar sensors: a survey. Multimed Tools Appl 2017;76(3):4313–4355.
Zrira N, Khan HA, Bouyakhf EH. Discriminative deep belief network for indoor environment classification using global visual features. Cognitive Computation 2017;10:1–17.
Feichtenhofer C, Pinz A, Wildes RP. Temporal residual networks for dynamic scene recognition. In: IEEE Conference on computer vision and pattern recognition; 2017.
Gong Y, Wang L, Guo R, Lazebnik S. Multi-scale orderless pooling of deep convolutional activation features. In: European Conference on Computer Vision; 2014. p. 392–407.
Yoo D, Park S, Lee J-Y, Kweon IS. Fisher kernel for deep neural activations, arXiv:1412.1628.
Liao Y, Kodagoda S, Wang Y, Shi L, Liu Y. Understand scene categories by objects: a semantic regularized scene classifier using convolutional neural networks. In: IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation; 2016. p. 2318–2325.
Gupta S, Arbeláez P, Girshick R, Malik J. Indoor scene understanding with RGB-D images: bottom-up segmentation, object detection and semantic segmentation. Int J Comput Vis 2015;112(2):133–149.
Arbelaez P, Maire M, Fowlkes C, Malik J. Contour detection and hierarchical image segmentation. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 2011;33(5):898–916.
Bo L, Ren X, Fox D. Unsupervised feature learning for RGB-D based object recognition. In: Experimental Robotics; 2013. p. 387–402.
Lai K, Bo L, Ren X, Fox D. A large-scale hierarchical multi-view RGB-D object dataset. In: IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA); 2011. p. 1817–1824.
Socher R, Huval B, Bath B, Manning C, Ng AY. Convolutional-recursive deep learning for 3D object classification. In: Neural Information Processing Systems; 2012. p. 665–673.
Socher R, Lin CC, Manning C, Ng AY. Parsing natural scenes and natural language with recursive neural networks. In: International Conference on Machine Learning; 2011. p. 129–136.
Cai Z, Shao L. RGB-D data fusion in complex space. In: IEEE International Conference on Image Processing. Beijing; 2017. p. 1965–1969.
Song S, Xiao J. Deep sliding shapes for amodal 3D object detection in RGB-D images.
Krause A, Perona P, Gomes RG. Discriminative clustering by regularized information maximization. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; 2010. p. 775–783.
Wang X, Yang M, Zhu S, Lin Y. Regionlets for generic object detection. In: IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision; 2013. p. 17–24.
Uijlings JR, van de Sande KE, Gevers T, Smeulders AW. Selective search for object recognition. Int J Comput Vis 2013;104(2):154–171.
Lu X, Zhang W, Li X. A hybrid sparsity and distance-based discrimination detector for hyperspectral images. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 2018;56(3):1704–1717.
Siva P, Xiang T. Weakly supervised object detector learning with model drift detection. In: International Conference on Computer Vision; 2011. p. 343–350.
Deselaers T, Alexe B, Ferrari V. Localizing objects while learning their appearance. In: European Conference on Computer Vision; 2010. p. 452–466.
Lu X, Zheng X, Yuan Y. Remote sensing scene classification by unsupervised representation learning. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 2017;55(9):5148–5157.
Cheng M.-M., Zhang Z, Lin W.-Y., Torr P. Bing: binarized normed gradients for objectness estimation at 300fps. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition; 2014. p. 3286–3293.
Arbeláez P, Pont-Tuset J, Barron J, Marques F, Malik J. Multiscale combinatorial grouping. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition; 2014. p. 328–335.
Zitnick CL, Dollár P. Edge boxes: Locating object proposals from edges. In: European Conference on Computer Vision; 2014. p. 391–405.
Gu C, Lim JJ, Arbeláez P, Malik J. Recognition using regions. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition; 2009. p. 1030–1037.
Carreira J, Sminchisescu C. Constrained parametric min-cuts for automatic object segmentation. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition; 2010. p. 3241–3248.
Hosang J, Benenson R, Schiele B. How good are detection proposals, really?, arXiv:1406.6962.
Jia Y, Shelhamer E, Donahue J, Long J, Girshick R, Guadarrama S, Darrell T. Caffe: Convolutional architecture for fast feature embedding. In: International Conference on Multimedia; 2014. p. 675–678.
Schölkopf B, Platt JC, Shawe-Taylor J, Smola AJ, Williamson RC. Estimating the support of a high-dimensional distribution. Neural Comput 2001;13(7):1443–1471.
Vapnik V. 2013. The nature of statistical learning theory.
Gupta S, Girshick R, Arbeláez P, Malik J. Learning rich features from RGB-D images for object detection and segmentation. In: Europen Conference on Computer Vision; 2014. p. 345–360.
Yang J, Yu K, Gong Y, Huang T. Linear spatial pyramid matching using sparse coding for image classification. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition; 2009. p. 1794–1801.
Arandjelovic R, Zisserman A. All about VLAD. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition; 2013. p. 1578–1585.
Jégou H, Douze M, Schmid C, Pérez P. Aggregating local descriptors into a compact image representation. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition; 2010. p. 3304–3311.
Silberman N, Fergus R. Indoor scene segmentation using a structured light sensor. In: IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops (ICCV Workshops); 2011. p. 601–608.
Song S, Lichtenberg SP, Xiao J. Sun rgb-d: A RGB-D scene understanding benchmark suite. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition; 2015. p. 567–576.
Oliva A, Torralba A. Modeling the shape of the scene: a holistic representation of the spatial envelope. Int J Comput Vis 2001;42(3):145–175.
Simonyan K, Zisserman A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition, arXiv:1409.1556.
Le QV, Karpenko A, Ngiam J, Ng AY. ICA with reconstruction cost for efficient overcomplete feature learning. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; 2011. p. 1017–1025.
Wang J, Yang J, Yu K, Lv F, Huang T, Gong Y. Locality-constrained linear coding for image classification. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition; 2010. p. 3360–3367.
Jin L, Gao S, Li Z, Tang J. Hand-crafted features or machine learnt features? Together they improve RGB-D object recognition. In: International Symposium on Multimedia; 2014. p. 311–319.
Wang A, Cai J, Lu J, Cham TJ. Modality and component aware feature fusion for RGB-D scene classification. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition; 2016. p. 5995–6004.
Szegedy C, Liu W, Jia Y, Sermanet P, Reed S, Anguelov D, Erhan D, Vanhoucke V, Rabinovich A. Going deeper with convolutions. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition; 2015. p. 1–9.
Liu L, Wang L, Liu X. In defense of soft-assignment coding. In: IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision; 2011. p. 2486–2493.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cai, Z., Shao, L. RGB-D Scene Classification via Multi-modal Feature Learning. Cogn Comput 11, 825–840 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12559-018-9580-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12559-018-9580-y