Abstract
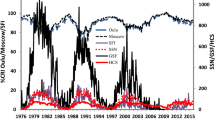
In the present paper a systematic study is carried out to validate the similarity or co-variability between daily terrestrial cosmic-ray intensity and three parameters of the solar corona evolution, i.e., the number of sunspots and flare index observed in the solar corona and the Ap index for regular magnetic field variations caused by regular solar radiation changes. The study is made for a period including three solar cycles starting with cycle 21 (year 1976) and ending on cycle 23 (year 2008). A cross-correlation analysis was used to establish patterns and dependence of the variables. This study focused on the time lag calculation for these variables and found a maximum of negative correlation over \(CC_{1}\approx 0.85\), \(CC_{2}\approx 0.75\) and \(CC_{3}\approx 0.63\) with an estimation of 181, 156 and 2 days of deviation between maximum/minimum of peaks for the intensity of cosmic rays related with sunspot number, flare index and Ap index regression, respectively.


Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Latitude 39.37∘ N, longitude 106.18∘ W, elevation 1612 m, rigidity (1965) 2.99 GV, standard atmospheric pressure: 672 mb.
Latitude 12.0∘ S, longitude 75.3∘ W, elevation 3350 m, rigidity (1965) 12.92 GV, standard atmospheric pressure: 704 mb.
Latitude 54.30∘ N, longitude 10.10∘ E, elevation 54 m, rigidity (1965) 2.36 GV, standard atmospheric pressure: 1006.6 mb.
Latitude 19.20∘ S, longitude 17.58∘ E, elevation 1240 m, rigidity (1965) 9.21 GV, standard atmospheric pressure: 880.0 mb.
References
Dorman, I., Dorman, L.: J. Geophys. Res. 72(5), 1513 (1967)
Mavromichalaki, H., Petropoulos, B.: Astrophys. Space Sci. 106(1), 61 (1984)
Mavromichalaki, H., Belehaki, A., Rafios, X.: Astron. Astrophys. 330, 764 (1998)
Mavromichalaki, H., Paouris, E., Karalidi, T.: Sol. Phys. 245(2), 369 (2007)
Mishra, M.: In: International Cosmic Ray Conference, vol. 2, p. 159 (2005)
Paouris, E., Mavromichalaki, H., Belov, A., Gushchina, R., Yanke, V.: Sol. Phys. 280(1), 255 (2012)
Popielawska, B.: Planet. Space Sci. 40(6), 811 (1992)
Popielawska, B.: J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 100(A4), 5883 (1995)
Schwabe, S.: Astron. Nachr. 21, 233 (1844)
Usoskin, I., Kananen, H., Mursula, K., Tanskanen, P., Kovaltsov, G.: J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 103(A5), 9567 (1998)
Van Allen, J.A.: Geophys. Res. Lett. 27(16), 2453 (2000)
Acknowledgements
Part of this work was supported by the Vicerrectoría de Investigación y Extensión of the Universidad Industrial de Santander, they provided a permanent sponsorship. DSP wants to thank the GIRG, Grupo Halley and Vicerrectoría Investigación y Extensión of Universidad Industrial de Santander for the hospitality during my post-doctoral fellowship. DSP also thanks Ángel G. Muñoz (IRI, Columbia University) for the comments, discussions and help in applying the technique to large amounts of datasets. The author also wants to thank an anonymous reviewer for the suggestion of some references to previous studies, and for the valuable comments and discussions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sierra-Porta, D. Cross correlation and time-lag between cosmic ray intensity and solar activity during solar cycles 21, 22 and 23. Astrophys Space Sci 363, 137 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10509-018-3360-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10509-018-3360-8