Abstract
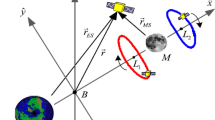
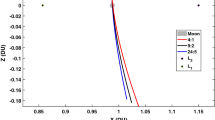
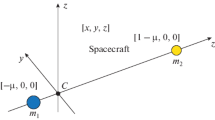
A convenient procedure for designing the direct transfer trajectory from lunar L2 point (LL2) halo orbit to a low lunar orbit (LLO) is presented in this paper. The trajectory characteristics are analyzed to support the manned lunar missions design aimed at lunar surface global access. The concise procedure is established based on the circular restricted three-body problem (CR3BP) model. An analytical algorithm is employed to estimate an initial maneuver vector for approaching the Moon in its close vicinity. An iteration process is adopted to generate favorable trajectory that satisfies the constraints at perilune. By introducing a number of intermediate coordinate frames, an algorithm to compute the arriving LLO inclination and right ascension of ascending node (RAAN) is proposed. The orbital inclination and RAAN in this paper are defined and established in the J2000 frame rather than in the synodical frame. Numerical results show that, regardless of value of out-of-plane amplitude (\(Az\)) of the halo orbit, the overall maneuver cost of the trajectory largely depends on departure position, and it has two minima around 0.65 km/s. Further study shows that the values of the arriving LLO inclination and RAAN largely depend on the choices of the departure time and the value of \(Az\). The periodicity, due to the natural motion of the Moon, is discovered to play a role in this time dependency. It is concluded that the fuel optimal trajectory permits access to almost any final lunar orbit, including a polar orbit, by means of varying the departure time and \(Az\) value.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alessi, E.M., Gómez, G., Masdemont, J.J.: Two-manoeuvres transfers between LEOs and Lissajous orbits in the Earth–Moon system. Adv. Space Res. 45(10), 1276–1291 (2010)
Baoyin, H.X., Mclnnes, C.R.: Trajectories to and from the Lagrange points and the primary body surfaces. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 29(4), 998–1003 (2006)
Farquhar, R.W.: The utilization of Halo orbits in advanced lunar operations. Technical Report X-551-70-449, Goddard Space Flight Center, Maryland (1971)
Gómez, G., Jorba, A., Masdemont, J.J., Simó, C.: Study of the transfer from the Earth to a halo orbit around the equilibrium point L1. Celest. Mech. Dyn. Astron. 56(4), 541–562 (1993)
Gordon, D.P.: Transfers to Earth Moon L2 halo orbits using lunar proximity and invariant manifold. MS Thesis, Purdue University (2008)
Howell, K.C., Breakwell, J.V.: Almost rectilinear halo orbits. Celest. Mech. Dyn. Astron. 32(1), 29–52 (1984)
Howell, K.C., Pernicka, H.J.: Numerical determination of Lissajous trajectories in the restricted three-body problem. Celest. Mech. Dyn. Astron. 41(1), 107–124 (1988)
Li, M.T., Zheng, J.H.: Impulsive lunar halo transfers using the stable manifolds and lunar fly-bys. Acta Astronaut. 66(9), 1481–1492 (2010)
Lian, Y.J., Gao, Y.D., Tang, G.J.: On equatorial inclination of parking orbits in transfers to lunar halo orbits. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 28(1–3), 210–222 (2015)
Merritt, P.D.: A differentially corrected halo transfer orbit. In: AIAA Paper 01-118, AIAA/AAS Aerospace Sciences Meeting and Exhibit, Reno, pp. 15–18 (1996)
Moore, A., Sina, O.B., Marsden, J.E.: Trajectory design combining invariant manifolds with discrete mechanics and optimal control. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 35(5), 1507–1525 (2012)
Nath, P., Ramanan, R.V.: Precise halo orbit design and optimal transfer to halo orbits from Earth using differential evolution. Adv. Space Res. 57(1), 202–217 (2016)
Parker, J.S., Born, J.H.: Direct lunar halo orbit transfers. J. Astronaut. Sci. 56(4), 441–476 (2008)
Qian, Y.J., Li, C.Y., Jing, W.X., Gao, C.S.: Sun–Earth–Moon autonomous orbit determination for quasi-periodic orbit about the translunar libration point and its observability analysis. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 28(1), 289–296 (2013)
Rausch, R.R.: Earth to halo orbit transfer trajectories. MS Thesis, Purdue University (2005)
Ren, Y., Shan, J.J.: A novel algorithm for generating libration point orbits about the collinear points. Celest. Mech. Dyn. Astron. 120(1), 57–75 (2014)
Renk, F., Hechler, M., Messerschmid, E.: Exploration mission in the Sun–Earth–Moon system: a detailed view on selected transfer problems. Acta Astronaut. 67(1–2), 82–96 (2010)
Rheinboldt, W.C.: Numerical continuation methods: a perspective. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 124(1), 229–244 (2000)
Richardson, D.L.: Analytic construction of periodic of orbits about the collinear points. Celest. Mech. Dyn. Astron. 22(3), 241–253 (1980)
Sun, Y., Zhang, J.: Error propagation characteristic analysis of halo orbit based on condition number of state transition matrix. Astrophys. Space Sci. 361(9), 297 (2016)
Acknowledgement
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant No. 11372345.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cao, P., He, B. & Li, H. Analysis of direct transfer trajectories from LL2 halo orbits to LLOs. Astrophys Space Sci 362, 153 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10509-017-3124-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10509-017-3124-x