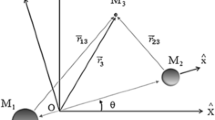
Abstract
Techniques associated with stable manifold and lunar flyby have been applied to the construction of optimal transfers to Earth-Moon \(L_{1} /L_{2}\) libration point orbits. Compared with traditional design methods and to reduce maneuver cost, the design process presents a detailed analysis on the effect of lunar proximity with multiple constraints. An accurate and fast design strategy for seeking an insertion point and modifying the stable manifold to satisfy these constraints is proposed. Combined this strategy with the differential correction algorithm, the optimal transfer trajectory can be determined from a low-Earth orbit to a halo orbit around the \(L_{1} /L_{2}\) libration point within a little computational time. Different amplitudes and insertion points of halo orbit in conjunction with various constraint conditions about lunar flyby are considered to deeply examine the efficiency and reliability of the design algorithm. Preliminary results indicate that the required mission cost has a significant correlation with lunar proximity constraints, and demonstrate that the method of constructing impulsive lunar halo transfer trajectories with multiple constraints is feasible.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alessi, E.M., Gómez, G., Masdemont, J.J.: Two-maneuvers transfers between LEOs and Lissajous orbits in the Earth-Moon system. Adv. Space Res. 45, 1276–1291 (2010)
Belbruno, E., Miller, J.: A ballistic lunar capture trajectory for the Japanese spacecraft Hiten. Technical Report 312/90.4-1731-EAB, Jet Propulsion Laboratory (1990)
Broschart, S., Chung, M., Hatch, S., Ma, J., Sweetser, T., Weinstein-Weiss, S., Angelopoulos, V.: Preliminary trajectory design for the ARTEMIS Lunar Mission. In: Astrodynamics Specialist Conference, Number AAS 09-382, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, August 9–13 (2009)
Breakwell, J.V., Kamel, A.A., Ratner, M.J.: Station-keeping for a translunar communication station. Celest. Mech. 10, 357–373 (1974)
Breakwell, J.V., Brown, J.V.: The halo family of 3-dimensional periodic orbits in the Earth-Moon restricted 3-body problem. Celest. Mech. 20, 389–404 (1979)
Bihan, B.L., Kokou, P., Lizy-Destrez, S.: Computing an optimized trajectory between Earth and an EML2 halo orbit. In: AIAA Guidance, Navigation, and Control Conference. National Harbor, Maryland (2014)
Davis, K.E., Anderson, R.L., Scheeres, D.J., Born, G.H.: The use of invariant manifolds for transfers between unstable periodic orbits of different energies. Celest. Mech. Dyn. Astron. 107, 471–485 (2010)
Farquhar, R.W.: The utilization of halo orbits in advanced lunar operations. Technical report NASA TN D-6365 (1971)
Farquhar, R.W., Kamel, A.A.: Quasi-periodic orbits about the translunar libration point. Celest. Mech. 7(4), 458–473 (1973)
Farquhar, R.W., Dunham, D.W., Yanping, Guo, McAdams, J.V.: Utilization of libration points for human exploration in the Sun-Earth-Moon system and beyond. Acta Astronaut. 55, 687–700 (2004)
Folta, D.C., Pavlak, T.A., Haapala, A.F., Howell, K.C.: Preliminary design considerations for access and operations in Earth-Moon \(L_{1}/L_{2}\) orbits. In: Paper AAS 13-339, Proceedings of the AAS/AIAA Space Flight Mechanics Meeting, Kauai, Hawaii (2013)
Gómez, G., Jorba, A., Masdemont, J., Simò, C.: Study of the transfer from the Earth to a halo orbit around the equilibrium point \(L_{1}\). Celest. Mech. Dyn. Astron. 56(4), 541–562 (1993)
Gordon, D.P.: Transfers to Earth-Moon L2 halo orbits using lunar proximity and invariant manifolds. M.S. Thesis, Purdue Univ. (2008)
Howell, K.C., Ozimek, M.T.: Low-thrust transfers in the Earth-Moon system including applications to libration point orbit. In: Paper AAS 07-343, Proceedings of the AAS/AIAA Astrodynamics Specialist Conference, Mackinac Island, MI (2007)
Kakoi, M., Howell, K.C., Folta, D.: Access to Mars from Earth-Moon libration point orbits: manifold and direct options. Acta Astronaut. 102, 269–286 (2014)
Koon, W.S., Lo, M.W., Marsden, J.E., Ross, S.D.: Dynamical Systems, the Three-Body Problem and Space Mission Design. Marsden Books, Wellington (2005)
Lo, M.W., Ross, S.D.: The lunar L1 gateway: portal to the stars and beyond. In: Proceeding of the AIAA Space 2001 Conference, Albuquerque (2001)
Li, M.T., Zheng, J.H.: Indirect transfer to the Earth-Moon L1 libration point. Celest. Mech. Dyn. Astron. 108(2), 203–213 (2010a)
Li, M.T., Zheng, J.H.: Impulsive lunar halo transfers using the stable manifolds and lunar flybys. Acta Astronaut. 66, 1481–1492 (2010b)
Mingotti, G., Topputo, F., Bernelli-Zazzera, F.: Combined optimal low thrust and stable manifold trajectories to the Earth-Moon Halo orbits. AIP Conf. Proc. 886, 100–110 (2007)
Mingotti, G., Topputo, F., Bernelli-Zazzera, F.: Optimal low-thrust invariant manifold trajectories via attainable sets. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 34, 1644–1655 (2011)
Pergola, P., Alessi, E.M.: Libration point orbit characterization in the Earth-Moon system. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 426, 1212–1222 (2012)
Parker, J.S.: Families of low-energy lunar halo transfers. In: AAS/AIAA Spaceflight Dynamics Conference, AAS 06-132 (2006)
Parker, J.S., Born, G.H.: Direct lunar halo transfers. In: AAS/AIAA Spaceflight Mechanics Conference, AAS 07-229 (2007)
Parker, J.S., Anderson, R.L.: Low-Energy Lunar Trajectory Design, 1st edn. JPL Deep-Space Communications and Navigation Series. Wiley, New York (2014)
Qi, R., Xu, S.J.: Optimal low-thrust transfers to lunar L1 halo orbit using variable specific impulse engine. J. Aerosp. Eng. 28(4), 1–13 (2014)
Rausch, R.R.: Earth to halo orbit transfer trajectories. M.S. Thesis, Purdue Univ. (2005)
Renk, F., Hechler, M., Messerschmid, E.: Exploration missions in the Sun-Earth-Moon system: a detailed view on selected transfer problems. Acta Astronaut. 67, 82–96 (2010)
Szebehely, V.: Theory of Orbits: The Restricted Problem of Three Bodies. Academic Press, New York (1967)
Vaquero, M., Howell, K.C.: Leveraging resonant-orbit manifolds to design transfers between libration-point orbits. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 37(4), 1144–1157 (2014)
Woodard, M., Folta, D., Woodfork, D.A.RT.EM.I.: The first mission to lunar libration orbits. In: 21st International Symposium on Space Flight Dynamics, Toulouse, France (2009)
Xu, M., Tan, T., Xu, S.: Research on the transfers to Halo orbits from the view of invariant manifolds. Phys. Mech. Astron. 55(4), 671–683 (2012)
Zanzottera, A., Mingotti, G., Castelli, R., Dellnitz, M.: Intersecting invariant manifolds in spatial restricted three-body problems: design and optimization of Earth-to-halo transfers in the Sun-Earth-Moon scenario. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 17(2), 832–843 (2012)
Acknowledgements
The research presented in this paper was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 11572037 and Grant No. 11290150). The authors thank the Editor and all the reviewers for their insightful suggestions. Their comments have greatly improved the quality of this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zeng, H., Zhang, J. Design of impulsive Earth-Moon Halo transfers: lunar proximity and direct options. Astrophys Space Sci 361, 328 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10509-016-2888-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10509-016-2888-8