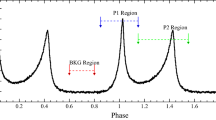
Abstract
The sharp drop in fluxes of the termination shock particles observed by Voyager 1 in the inner heliosheath at distance of about 122 au from the Sun can be explained by factors, which are not related to the heliopause crossing as is now commonly believed. It is shown that the region of the heliosheath occupied by the current sheet can be considered as a reservoir for suprathermal charged particles accelerated at the termination shock. When a spacecraft crosses the boundary of this region in the latitudinal direction, fluxes of the suprathermal particles can vary by several orders of magnitude.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Burlaga, L.F., Ness, N.F.: Astrophys. J. 795, L19 (2014)
Burlaga, L.F., Scudder, J.D., Klein, L.W., Isenberg, P.A.: J. Geophys. Res. 95, 2229 (1990)
Burlaga, L.F., Ness, N.F., Belcher, L.: Space Sci. Rev. 78, 33 (1996)
Burlaga, L.F., Ness, N.F., Acuña, M.H., Lepping, R.P., Connerney, J.E.P., Stone, E.C., McDonald, F.B.: Science 309, 2027 (2005)
Burlaga, L.F., Ness, N.F., Acuña, M.H., Lepping, R.P., Connerney, J.E.P., Richardson, J.D.: Nature 454, 75 (2008)
Burlaga, L.F., Ness, N.F., Stone, E.C.: Science 341, 147 (2013)
Chalov, S.V.: Planet. Space Sci. 41, 133 (1993)
Chalov, S.V., Malama, Y.G., Alexashov, D.B., Izmodenov, V.V.: Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 455, 431 (2016)
Decker, R.B.: Space Sci. Rev. 48, 195 (1988)
Decker, R.B., Krimigis, S.M., Roelof, E.C., Hill, M.E., Armstrong, T.P., Gloeckler, G., Hamilton, D.C., Lanzerotti, L.J.: Science 309, 2020 (2005)
Fahr, H.J., Scherer, K., Potgieter, M.S., Ferreira, S.E.S.: Astron. Astrophys. 486, L1 (2008)
Fisk, L.A., Gloeckler, G.: Astrophys. J. 776, 79 (2013)
Fisk, L.A., Gloeckler, G.: Astrophys. J. 789, 41 (2014)
Gurnett, D.A., Kurth, W.S., Burlaga, L.F., Ness, N.F.: Science 341, 1489 (2013)
Krimigis, S.M., Decker, R.B., Roelof, E.C., Hill, M.E., Armstrong, T.P., Gloeckler, G., Hamilton, D.C., Lanzerotti, L.J.: Science 341, 144 (2013)
Richardson, J.D., Kasper, J.C., Wang, C., Belcher, J.W., Lazarus, A.J.: Nature 454, 63 (2008)
Smith, E.: Adv. Space Res. 13(6), 5 (1993)
Stone, E.C., Cummings, A.C., McDonald, F.B., Heikkila, B.C., Lal, N., Webber, W.R.: Science 309, 2017 (2005)
Stone, E.C., Cummings, A.C., McDonald, F.B., Heikkila, B.C., Lal, N., Webber, W.R.: Nature 454, 71 (2008)
Stone, E.C., Cummings, A.C., McDonald, F.B., Heikkila, B.C., Lal, N., Webber, W.R.: Science 341, 150 (2013)
Webber, W.R., McDonald, F.B.: Geophys. Res. Lett. 40, 1665 (2013)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the RFBR in the frames of the project 16-01-00305.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chalov, S.V., Alexashov, D.B. Voyager 1 observations of the termination shock particles in the inner heliosheath at 122 au. Astrophys Space Sci 361, 219 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10509-016-2813-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10509-016-2813-1