Abstract
This work originates from the need of getting a picture of the spot zone that is sharp enough to efficiently help us place tighter and more realistic constraints than we would usually do on dynamo models, in order to improve their predictive performance.
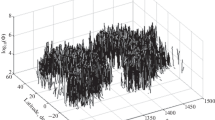
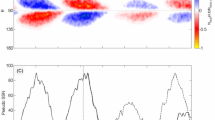
This paper questions the confidence in Maunder’s Butterfly Diagram (BD) as the fundamental tool for describing the magnetic flux large-scale distribution and presents a new version of the time-latitude diagram for cycles 21 through 23, where spot groups are given proportional relevance to their area. The diagram presented here confirms the active regions’ well-known tendency to repeatedly appear in a few photospheric regions (“activity nests”) tightly limited in latitude, active for a short time. Activity nests leave their signature in the BD, in the form of small portions (“knots”) characterized by the spotted area high density. The BD may be described as a cluster of knots. A knot may appear at either lower or higher latitudes than previous ones; accordingly, the spot mean latitude abruptly drifts equatorward or even poleward, even though the knot’s prevalent tendency is to appear at lower and lower latitudes.
A careful inspection of the BD suggests that its intricate fine structure may be (partially) disentangled by recognizing that, in any hemisphere, the activity is split into two or more distinct “activity waves” (out of phase compared to each other), drifting equatorward at a rate higher than the spot zone as a whole. Preliminary computations confirm this suggestion.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Antalová, A., Gnevishev, M.N.: Contr. Astron. Obs. Skalnaté Pleso 11, 63 (1983)
Bell, B.: Smithsonian Contrib. Astrophys. 5(3) (1960)
Berdyugina, S.V.: Highlights Astron. 14, 275 (2007)
Bumba, V., Howard, R.: Astrophys. J. 141, 1502 (1965)
Castenmiller, M.J.M., et al.: Sol. Phys. 105, 237 (1986)
Charbonneau, P.: Living Rev. Solar Phys. 2, 2 (2005). Online Article: http://www.livingreviews.org/lrsp-2005-2
Consolini, G., Tozzi, R., De Michelis, P.: Astron. Astrophys. 506, 1381 (2009)
Contarino, L., Romano, P., Ternullo, M., Zappalà, R.A., Zuccarello, F.: In: Proc. 1st Solar & Space Weather Euroconference ‘The Solar Cycle and Terrestrial Climate’, Tenerife, Spain (ESA SP-463) (2000)
Choudhuri, A.R.: Adv. Space Res. 41, 868 (2008)
Forgács-Dajka, E., et al.: Astron. Astrophys. 424, 311 (2004)
Gaizauskas, V., et al.: Astrophys. J. 265, 1056 (1983)
Gleissberg, W.: Sol. Phys. 4, 93 (1968)
Jiang, J., Wang, J.X.: Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 377, 711 (2007)
Kane, R.P.: Sol. Phys. 227, 155 (2005)
Godoli, G.: Sol. Phys. 9, 246 (1969)
Harvey, K.L., Zwann, C.: Sol. Phys. 148, 85 (1993)
Hathaway, D.H., et al.: Astrophys. J. 589, 665 (2003)
Howe, R., et al.: In: Brekke, P., et al. (eds.) Recent Insights into the Physics of the Sun and Heliosphere. IAU Symposium, vol. 203, p. 41 (2001)
Howe, R.: Solar interior rotation its variation. Living Rev. Solar Phys. 6, 1 (2009). URL (cited on September 2009): http://www.livingreviews.org/lrsp-2009-1
Kopecký, M.: Adv. Astron. Astrophys. 7, 57 (1970)
Krivova, N.A., Solanki, S.K.: Astron. Astrophys. 394, 701 (2002)
Major, B.: In: Forgács-Dajka, E., Petrovay, K., Erdélyi, R. (eds.) Publ. Astron. Dept. Eötvös University, vol. 14, p. 187 (2004)
Maunder, E.W.: Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 64, 760 (1904)
Maunder, E.W.: Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 82, 534 (1922)
Norton, A.A., Gilman, P.A.: Astrophys. J. 603, 348 (2004)
Ossendrijver, M.: Astron. Astrophys. Rev. 11, 287 (2003)
Petrovay, K., Szakály, G.: Sol. Phys. 185, 1 (1999)
Rabin, D., et al.: In: Cox, X., et al. (eds.) Solar Interior and Atmosphere, p. 781. The University of Arizona Press, Tucson (1991)
Rodonò, M.: Mem. Soc. Astron. Ital. 60, 587 (1989)
Schatten, K.H.: Sol. Phys. 125, 185 (1990)
Solanki, S.K., Inhester, B., Schüssler, M.: Rep. Progr. Phys. 69, 563 (2006)
Solanki, S.K., Wenzler, T., Schmitt, D.: Astron. Astrophys. 483, 623 (2008)
Ternullo, M.: Sol. Phys. 127, 29 (1990)
Ternullo, M.: Poster Papers presented at the Seventh European Meeting on Solar Physics, held 11–15 May, 1993 in Catania, Italy. G. Belvedere, et al. (eds.) Catania Astrophysical Observatory Special Publication, p. 35 (1994)
Ternullo, M.: Sol. Phys. 172, 37 (1997)
Ternullo, M.: Mem. Soc. Astron. Ital. 72, 565 (2001a)
Ternullo, M.: Mem. Soc. Astron. Ital. 72, 681 (2001b)
Ternullo, M., Bonanno, A.: In: Proceedings of LXXXVII Congr. Nazion. Soc. Ital. Fis., p. 185 (2001)
Ternullo, M.: Sol. Phys. 240, 153 (2007a)
Ternullo, M.: Mem. Soc. Astron. Ital. 78, 596 (2007b)
Ternullo, M.: Astron. Nachr. 328, 1023 (2007c)
Ternullo, M.: In: Electronic Proceedings—12th European Solar Physics Meeting, 8–12 September 2008, Freiburg, Germany: http://espm.kis.uni-freiburg.de (2008)
Ternullo, M.: Mem. Soc. Astron. Ital. (2009, in press)
Toomre, J., et al.: In: Sawaya-Lacoste (ed.) Proceedings of SOHO 12/GONG+2002 on Local and Global Helioseismology: The Present and Future, ESA SP-517, ESA Publication Division, Noordwijk, Netherlands (2003)
Van Driel-Gesztelyi, L., van der Zalm, E.B.J., Zwann, C.: In: Harvey, K.L. (ed.) The Solar Cycle, Asp Conference Series, vol. 27 (1992)
Vecchio, A., Carbone, V.: Astron. Astrophys. 502, 981 (2009)
Waldmeier, M.: Astron. Mitt Zürich 14, 470 (1939)
Waldmeier, M.: In: Proceedings of the Meeting on Sunspots, ed. by Comit. Naz. Manifestaz. Celebrat. IV Centen. Galileo G., Florence, p. 50 (1966)
Yallop, B.D., Hohenkerk, C.Y.: Sol. Phys. 68, 303 (1980)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ternullo, M. The butterfly diagram internal structure. Astrophys Space Sci 328, 301–305 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10509-010-0270-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10509-010-0270-9