Abstract
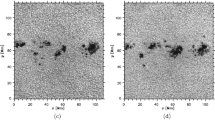
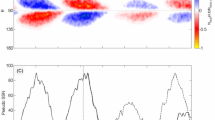
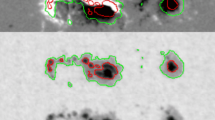
Patterns in the properties of bipolar active regions are determined throughout Cycle 21. Active regions that emerged on the visible hemisphere were identified on NSO/KP full-disk magnetograms during 29 solar rotations selected from 1975 through 1986. The bipolar active regions are included only once in this sampling; their properties are derived at the time of maximum development. In order to study an unbiased sample over the entire range of areas larger than 2.5 square degrees (or 373 Mm2), their counts are corrected for size-dependent effects that reduce the chance of their identifications.
The size distribution of bipolar active regions is a well-defined function that decreases with increasing size. Except for the smallest regions, the shape of the size distribution is independent of the phase of a cycle, only the scaling factor varies. The shape of the size distribution function for bipoles emerging within existing sunspot regions is virtually the same as that for bipoles emerging outside existing regions. Over the cycle, at least 44% of the regions larger than 3.5 square degrees emerge within existing sunspot regions. Hence, the rate at which new regions emerge is much higher within the boundaries of existing sunspot regions than it is in the activity belts outside existing regions. For regions emerging outside of existing sunspot regions, this rate increases by a factor of 3.5 from cycle minimum to maximum, while for new bipoles within existing active regions, the emergence rate varies with a significantly lower magnitude.
Through the cycle, for regions in all size bins, the emergence frequencies appear to vary in phase. The frequencies increase by a factor of more than 8 from minimum to maximum for regions larger than 3.5 square degrees, but no more than 4.7 for the smaller regions. Short-term variations in the emergence frequency of regions do not necessarily occur simultaneously for regions of all sizes, implying that the size distribution is variable on time scales of less than six rotations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bogdan, T. J., Gilman, P. A., Lerche, L., and Howard, R.: 1988,Astrophys. J. 327, 451.
Brouwer, M. P. and Zwaan, C.: 1990,Solar Phys. 129, 221.
Castenmiller, M. J. M., Zwaan, C., and van der Zalm, E. B. J.: 1986,Solar Phys. 105, 237.
DeVore, C. R., Sheeley, N. R., Jr., Boris, J. P., Young, T. R., Jr., and Harvey, K. L.: 1985,Solar Phys. 102, 41.
Dodson, H. W. and Hedeman, E. R.: 1972, in M. Dryer (ed.),Solar Terrestrial Physics, Part 1, p. 151.
Gaizauskas, V., Harvey, K. L., Harvey, J. W., and Zwaan, C.: 1983,Astrophys. J. 265, 1065.
Harvey, K. L.: 1984, inProceedings of the Fourth European Meeting on Solar Physics - ‘The Hydromagnetics of the Sun’, held in Noordwijkerhout, The Netherlands, 1–3 October, 1984, ESA SP-220, p. 235.
Harvey, K. L.: 1992, in R. F. Donnelly (ed.),Proceedings of the SOLER22 Workshop, held in Boulder, Colorado, 3–7 June, 1991, p. 113.
Harvey, K. L.: 1993a, ‘Magnetic Bipoles on the Sun’, Thesis Utrecht University, Chapter 3.
Harvey, K. L.: 1993b, in preparation.
Harvey, K. L.: 1993c, in preparation.
Howard, R. F.: 1989,Solar Phys. 123, 271.
Howard, R. F.: 1991a,Solar Phys. 132, 271.
Howard, R. F.: 1991b,Solar Phys. 132, 271.
Howard, R. F.: 1991c,Solar Phys. 135, 271.
Howard, R., Gilman, P. A., and Gilman, P. I.: 1984,Astrophys. J. 283, 373.
Kopecký, M.: 1977,Bull. Astron. Inst. Czech. 28, 168.
Ligget, M. and Zirin, H.: 1985,Solar Phys. 97, 51.
Livingston, W. C., Harvey, J., Slaughter, C., and Trumbo, D.: 1976,Appl. Optics 15, 40.
Ringnes, T. S.: 1981, Institute of Theoretical Astrophysics, Blindern, Oslo, Report No. 52.
Schrijver, C. J.: 1988,Astron. Astrophys. 189, 163.
Tang, F., Howard, R., and Adkins, J. M.: 1984,Solar Phys. 91, 75.
van Driel-Gesztelyi, L., van der Zalm, E. B. J., and Zwaan, C.: 1992, in K. L. Harvey (ed;),The Solar Cycle, ASP Conference Series, Vol. 127, p. 89.
Wang, Y.-M. and Sheeley, N. R., Jr.: 1989,Solar Phys. 124, 81.
Zwaan, C.: 1978,Solar Phys. 60, 213.
Zwaan, C.: 1992, in J. H. Thomas and N. W. Weiss (eds;),Sunspots: Theory and Observations, Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, Holland, p. 75.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Harvey, K.L., Zwaan, C. Properties and emergence patterns of bipolar active regions. Sol Phys 148, 85–118 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00675537
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00675537