Abstract
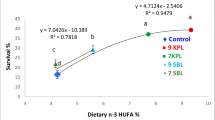
To investigate the dietary phosphatidylcholine (PC) requirements of red swamp crayfish (Procambarus clarkii), crayfish (initial body weight, 9.92 ± 0.32 g) were hand-fed six diets containing 0.6 (control group, PC1), 5.6 (PC2), 10.7 (PC3), 15.9 (PC4), 20.8 (PC5), and 26.2 (PC6) g/kg, respectively, for 8 weeks. Supplemental PC from 5.6 to 15.9 g/kg significantly improved survival (P < 0.05). The weight gain rate and specific growth rate of PC4 group were significantly higher than that of PC1 group (P < 0.05). The minimum value of feed conversion ratio was observed in crayfish fed with PC3 diet (P < 0.05). The maximum value of crude fat content of muscle was found in group PC4 (P < 0.05). The lipase activity in intestine and hepatopancreas and the activities of catalase and superoxide dismutase in hepatopancreas first increased and then decreased, which was highest in group PC4 (P < 0.05). The activities of aspartate aminotransferase and alanine aminotransferase in serum and malondialdehyde content in hepatopancreas first decreased and then increased, with the minimum values in group PC3 and group PC1, respectively. Total cholesterol content in hemolymph, hepatopancreas, and muscle increased significantly in groups PC4, PC3, and PC2, respectively, compared with group PC1 (P < 0.05). Free fatty acid content in muscle increased by 22.73% in group PC5 compared with group PC1 (P < 0.05). According to the regression analysis, the dietary phosphatidylcholine requirements for red swamp crayfish were 13.05~15.25 g/kg.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data are available from the corresponding author by request.
References
Adel M, Gholaghaie M, Khanjany P, Citarasu T (2017) Effect of dietary soybean lecithin on growth parameters, digestive enzyme activity, antioxidative status and mucosal immune responses of common carp (Cyprinus carpio). Aquacult Nutr 23:1145–1152. https://doi.org/10.1111/anu.12483
Chang G, Wu X, Cheng Y, Wang Z, Lu J (2011) Effects of phospholipid and highly unsaturated fatty acid on survival, weight gain, molting and biochemical composition of juvenile Chinese mitten crab, Eriocheir sinensis. J Fish Sci China 18:329–337. https://doi.org/10.16378/j.cnki.1003-1111.2020.05.016
Chowdhury DK, Sardar P, Kumar S, Varghese T, Singha KP, Maiti MK (2019) Phospholipid: an essential nutrient for fish larvae. J Experimental Zool India 22:1–5
Council NR (2011) Nutrient requirements of fish and shrimp. National academies press, Washington, DC
Coutteau P, Geurden I, Camara M, Bergot P, Sorgeloos P (1997) Review on the dietary effects of phospholipids in fish and crustacean larviculture. Aquaculture 155:149–164. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0044-8486(97)00125-7
Fisheries Bureau of Agriculture Ministry of China (2023) Fisheries production statistics for 2023. China Agricultural, Beijing
Gong H, Lawrence AL, Jiang D-H, Castille FL, Gatlin DM III (2000) Lipid nutrition of juvenile Litopenaeus vannamei: I. Dietary cholesterol and de-oiled soy lecithin requirements and their interaction. Aquaculture 190:305–324. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0044-8486(00)00414-2
Harada K (1987) Relationships between structure and feeding attraction activity of certain L-amino acids and lecithin in aquatic animals. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi 53:2243–2247. https://doi.org/10.2331/suisan.53.2243
Holme MH, Southgate PC, Zeng C (2007) Assessment of dietary lecithin and cholesterol requirements of mud crab, Scylla serrata, megalopa using semi-purified microbound diets. Aquacult Nutr 13:413–423. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2095.2007.00492.x
Hou Y, Yuan Y, Lu Y, Ma H, Sun P, Liang X, Huo Y, Zhou Q (2016) Dietary soy lecithin requirement of the juvenile swimming crab (Portunus Trituberculatus). J Fish China 40:1753–1764. https://doi.org/10.11964/jfc.20151210192
Hu Y, Tan B, Mai K, Ai Q, Zhang L, Zheng S (2011) Effects of dietary menhaden oil, soybean oil and soybean lecithin oil at different ratios on growth, body composition and blood chemistry of juvenile Litopenaeus vannamei. Aquacult Int 19:459–473. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10499-010-9361-4
Jafari F, Agh N, Noori F, Tokmachi A, Gisbert E (2018) Effects of dietary soybean lecithin on growth performance, blood chemistry and immunity in juvenile stellate sturgeon (Acipenser stellatus). Fish Shellfish Immunol 80:487–496. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2018.06.023
Ju ZY, Forster I, Dominy W, Lawrence A (2011) Classification and quantification of phospholipids and dietary effects on lipid composition in Pacific white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei. North Am J Aquaculture 73:221–229. https://doi.org/10.1080/15222055.2011.579035
Kumar V, Sinha AK, Romano N, Allen KM, Bowman BA, Thompson KR, Tidwell JH (2018) Metabolism and nutritive role of cholesterol in the growth, gonadal development, and reproduction of crustaceans. Rev Fish Sci Aquac 26:254–273. https://doi.org/10.1080/23308249.2018.1429384
Li X, Wang J, Han T, Hu S, Jiang Y, Wang C (2014) Effect of dietary phospholipids levels and sources on growth performance, fatty acid composition of the juvenile swimming crab, Portunus Trituberculatus. Aquaculture 430:166–172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2014.03.037
Li Y, Fan B, Huang Y, Wu D, Zhang M, Zhao Y (2018) Effects of dietary vitamin E on reproductive performance and antioxidant capacity of Macrobrachium nipponense female shrimp. Aquacult Nutr 24:1698–1708. https://doi.org/10.1111/anu.12804
Lin Z, Han F, Lu J, Guo J, Qi C, Wang C, Xiao S, Bu X, Wang X, Qin J (2020) Influence of dietary phospholipid on growth performance, body composition, antioxidant capacity and lipid metabolism of Chinese mitten crab, Eriocheir sinensis. Aquaculture 516:734653. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2019.734653
Lin Z, Wang X, Bu X, Jia Y, Shi Q, Du Z, Qin J, Chen L (2021) Dietary phosphatidylcholine affects growth performance, antioxidant capacity and lipid metabolism of Chinese mitten crab (Eriocheir sinensis). Aquaculture 541:736814. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2021.736814
Lin YH, Chen KH, Wu PC (2022) Effects of the diet based on soybean meal supplemented with soy lecithin on growth, biochemical parameters and digestibility of nutrients in grouper, Epinephelus lanceolatus. Aquac Res 53:700–706. https://doi.org/10.1111/are.15593
Lu J-f, Wan Q, Wu X-g, Yang X-z, Zhao W-x, Cheng Y-x (2009) A preliminary study on haemocytes and immune functions of the crayfish, Procambarus clarkii. J Fish China 33:1018–1025. https://doi.org/10.3724/SP.J.00001
Lu X, Peng D, Chen X, Wu F, Jiang M, Tian J, Liu W, Yu L, Wen H, Wei K (2020) Effects of dietary protein levels on growth, muscle composition, digestive enzymes activities, hemolymph biochemical indices and ovary development of pre-adult red swamp crayfish (Procambarus clarkii). Aquaculture Rep 18:100542. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aqrep.2020.100542
Niu J, Liu YJ, Tian LX, Mai KS, Lin HZ, Chen X, Yang HJ, Liang GY (2011) Influence of dietary phospholipids level on growth performance, body composition and lipid class of early postlarval Litopenaeus vannamei. Aquacult Nutr 17:e615–e621. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2095.2010.00807.x
Peng D, Chen X, Wen H, Wu F, Lu X, Tian J, Liu W, Jiang M, Yu L, Zhang L, Li S (2019) Effects of dietary lipid levels on growth performance, muscle composition, reproductive performance and hemolymph biochemical indices of Procambarus clarkii broodstock. J Fish China 43:2175–2185. https://doi.org/10.11964/jfc.20190911973
Ramesh S, Balasubramanian T (2005) Dietary value of different vegetable oil in black tiger shrimp Penaeus monodon in the presence and absence of soy lecithin supplementation: effect on growth, nutrient digestibility and body composition. Aquaculture 250:317–327. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2005.02.035
Saito H, Ishihara K (1997) Antioxidant activity and active sites of phospholipids as antioxidants. J Am Oil Chem Soc 74:1531–1536. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11746-997-0072-6
Sink TD, Lochmann RT (2014) The effects of soybean lecithin supplementation to a practical diet formulation on juvenile channel catfish, Ictalurus punctatus: growth, survival, hematology, innate immune activity, and lipid biochemistry. J World Aquac Soc 45:163–172. https://doi.org/10.1111/jwas.12108
Teshima S-i, Kanazawa A (1979) Lipid transport mechanism in the prawn. Bull Jpn Soc Sci Fish 45:1341–1346. https://doi.org/10.2331/suisan.45.1341
Teshima S, Kanazawa A, Kakuta Y (1986) Effects of dietary phospholipids on growth and body composition of the juvenile prawn. Jpn Soc Sci Fish 52:155–158. https://doi.org/10.2331/suisan.52.155
Tian J, Wen H, Lu X, Liu W, Wu F, Yang C-G, Jiang M, Yu L-J (2018) Dietary phosphatidylcholine impacts on growth performance and lipid metabolism in adult genetically improved farmed Tilapia (GIFT) strain of Nile tilapia Oreochromis Niloticus. Br J Nutr 119:12–21. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0007114517003063
Tocher DR, Bendiksen EÅ, Campbell PJ, Bell JG (2008) The role of phospholipids in nutrition and metabolism of teleost fish. Aquaculture 280:21–34
Wang J, Han T, Li X, Hu S, Jiang Y, Wang C (2016) Effects of dietary phosphatidylcholine (PC) levels on the growth, molt performance and fatty acid composition of juvenile swimming crab, Portunus Trituberculatus. Anim Feed Sci Technol 216:225–233. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anifeedsci.2016.03.023
Wang J, Yang M, Li X, Wang C, Han T (2018) Dietary phospholipids requirement of the early juvenile (C1) swimming crab, Portunus Trituberculatus. Aquac Res 49:415–421. https://doi.org/10.1111/are.13471
Wang S, Han Z, Turchini GM, Wang X, Fang Z, Chen N, Xie R, Zhang H, Li S (2021) Effects of dietary phospholipids on growth performance, digestive enzymes activity and intestinal health of largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides) larvae. Front Immunol 12:827946–827946. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2021.827946
Wu F, Gu Z, Yu XC, Tian L J (2021) Effect of lipid sources on growth performance, muscle composition, haemolymph biochemical indices and digestive enzyme activities of red swamp crayfish (Procambarus clarkii). Aquacult Nutr 27:1996–2006. https://doi.org/10.1111/anu.13335
Xu H, Wang J, Han T, Li X, Zheng P, Yin F, Wang C (2019) Effects of dietary phospholipids levels on growth performance, lipid metabolism, and antioxidant capacity of the early juvenile green mud crab, Scylla paramamosain (Estampador). Aquac Res 50:513–520. https://doi.org/10.1111/are.13922
Xu L, Tian J, Wen H, Wu F, Zhang W, Gao W, Chen X (2021) Dietary calcium requirement of red swamp crayfish (Procambarus clarkii). Aquacult Nutr 27:153–162. https://doi.org/10.1111/anu.13173
Xu L, Chen X, Wen H, Wu F, Zhang W, Gao W, Tian J (2022) Dietary phosphorus requirement of red swamp crayfish (Procambarus clarkii). Aquac Res 53:1293–1303. https://doi.org/10.1111/are.15663
Zhang W, Wang F, Tan B, Dong X, Zhang H, Chi S, Liu H, Zhang S, Yang Q (2019) Effect of the dietary phosphatidylcholine at different growth stages of Pacific white shrimps, Litopenaeus vannamei. Aquacult Nutr 25:555–566. https://doi.org/10.1111/anu.12857
Funding
This study was supported by the R&D Program of Hubei in Characteristic Freshwater Products Industry Chain, and the Open Project of Key Lab of Freshwater Biodiversity Conservation Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs of China (LFBC1106).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Juan Tian, Jie Li, and Hongwei Liang designed the research; Wenfu Xiao, Liangzi Xu, Mingzhu Li, Lixue Dong, and Weihua Gao conducted the experiments and analyzed the data; Wenfu Xiao, Liangzi Xu, and Juan Tian wrote this paper; all the authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Gavin Burnell
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Tian, J., Xiao, W., Zhang, J. et al. Dietary phosphatidylcholine requirements of red swamp crayfish (Procambarus clarkii). Aquacult Int (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10499-024-01458-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10499-024-01458-8