Abstract
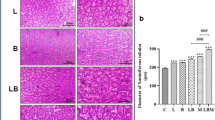
Immune stimulants are an alternative to antibiotic use and contribute to disease prevention in aquaculture. The effect of dietary administration of kappa carrageenan (Kc), extracted from the red algae Hypnea musciformis, in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) was assessed by monitoring weight gain after a 15-day feeding trial. Immunostimulation was inferred by the relative expression of transferrin, interleukin 1β (IL-1β), and growth hormone (GH) in the spleen after 24 h and 15 days of daily administration. The toxic activity of Kc was evaluated in brine shrimp (Artemia salina) nauplii. No significant toxic effects of Kc were observed in A. salina at any dose studied. A positive tendency in growth rate and fish survival values was observed when Kc was administered. Correspondingly, GH, transferrin and IL-1 β levels at day 15 post-treatment were higher in the spleens of fish fed with Kc at 5 g kg−1 relative to non-Kc-treated control fish. Feeding Kc extract from H. musciformis to the fish improved nonspecific immunity parameters and increased survival and growth, but further research, including longer-termed studies, should be conducted before recommendation of Kc supplementation in tilapia diets at commercial scale.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bagni M, Romano N, Finoia MG, Abelli L, Scapigliati G, Tiscar PG, Sarti M, Marino G (2005) Short- and long-term effects of a dietary yeast beta-glucan (Macrogard) and alginic acid (Ergosan) preparation on immune response in sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax). Fish Shellfish Immunol 18:311–325. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2004.08.003
Brudeseth BE, Wiulsrod R, Fredriksen BN, Lindmo K, Lokling K-E, Bordevik M, Steine N, Klevan A, Gravningen K (2013) Status and future perspectives of vaccines for industrialised fin-fish farming. Fish Shellfish Immunol 35:1759–1768. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2013.05.029
Cabello FC, Godfrey HP, Buschmann AH, Dolz HJ (2016) Aquaculture as yet another environmental gateway to the development and globalisation of antimicrobial resistance. Lancet Infect Dis 16:e127–e133. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1473-3099(16)00100-6
Camacho O, Montaña FJ (2012) Cultivo experimental en el mar del alga roja Hypnea Musciformis en el área de Santa Marta. Bol Invest Mar Cost INVEMAR 41:29–46
Cheng A-C, Chen Y-Y, Chen J-C (2008) Dietary administration of sodium alginate and kappa-carrageenan enhances the innate immune response of brown-marbled grouper Epinephelus fuscoguttatus and its resistance against Vibrio alginolyticus. Vet Immunol Immunopathol 121:206–215. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetimm.2007.09.011
Cheng W, Tsai RT, Chang CC (2012) Dietary sodium alginate administration enhances Mx gene expression of the tiger grouper, Epinephelus fuscoguttatus receiving poly I:C. Aquaculture 324–325:201–208. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2011.10.032
Cheng AC, Tu CW, Chen YY, Nan FH, Chen JC (2007) The immunostimulatory effects of sodium alginate and iota-carrageenan on orange-spotted grouper Epinephelus coicoides and its resistance against Vibrio alginolyticus. Fish Shellfish Immunol 22:197–205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2006.04.009
Corripio-Miyar Y, Bird S, Tsamopoulos K, Secombes CJ (2007) Cloning and expression analysis of two pro-inflammatory cytokines, IL-1β and IL-8, in haddock (Melanogrammus aeglefinus). Mol Immunol 44:1361–1373. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molimm.2006.05.010
da Silva Santos FM, da Silva AIM, Vieira CB, de Araujo MH, da Silva ALC, M das G C-d-C, de Souza BWS, de Souza Bezerra R (2017) Use of chitosan coating in increasing the shelf life of liquid smoked Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) fillet. J Food Sci Technol 54:1304–1311. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-017-2570-3
Dong HT, Techatanakitarnan C, Jindakittikul P, Thaiprayoon A, Taengphu S, Charoensapsri W, Khunrae P, Rattanarojpong T, Senapin S (2017) Aeromonas jandaei and Aeromonas veronii caused disease and mortality in Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus (L.). J Fish Dis 40:1395–1403. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfd.12617
FAO (2014) The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture 2014
FUJIKI K, YANO T (1997) Effects of sodium alginate on the non-specific defence system of the common carp (Cyprinus carpio L.). Fish Shellfish Immunol 7:417–427. https://doi.org/10.1006/fsim.1997.0095
Ganz T, Nemeth E (2015) Iron homeostasis in host defence and inflammation. Nat Rev Immunol 15:500–510. https://doi.org/10.1038/nri3863
Gomaa HHA, Elshoubaky GA (2016) Antiviral activity of sulfated polysaccharides carrageenan from some marine seaweeds. Int J Curr Pharm Rev Res 7:34–42
Hai NV (2015) Research findings from the use of probiotics in tilapia aquaculture: a review. Fish Shellfish Immunol 45:592–597. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2015.05.026
Harwig J, Scott PM (1971) Brine shrimp (Artemia salina L.) larvae as a screening system for fungal toxins. Appl Microbiol 21:1011–1016
Huynh T-G, Shiu Y-L, Nguyen T-P, Truong Q-P, Chen J-C, Liu C-H (2017) Current applications, selection, and possible mechanisms of actions of synbiotics in improving the growth and health status in aquaculture: a review. Fish Shellfish Immunol 64:367–382. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2017.03.035
Ibrahem MD, Fathi M, Mesalhy S, Abd El-Aty AM (2010) Effect of dietary supplementation of inulin and vitamin C on the growth, hematology, innate immunity, and resistance of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Fish Shellfish Immunol 29:241–246. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2010.03.004
Kumar V, Kumar S, Pandey PK, Raman RP, Pani Prasad K, Roy S, Kumar A, Kumar K (2014) Growth and hemato-immunological response to dietary i-carrageenan in Labeo Rohita (Hamilton, 1822) juveniles. Isr J Aquacult Bamidgeh 66:1–2
Li P, Gatlin DM (2004) Dietary brewers yeast and the prebiotic Grobiotic™ AE influence growth performance, immune responses and resistance of hybrid striped bass (Morone chrysops x M. saxatilis) to Streptococcus iniae infection. Aquaculture 231:445–456. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2003.08.021
Liu X, Steele JC, Meng X-Z (2017) Usage, residue, and human health risk of antibiotics in Chinese aquaculture: a review. Environ Pollut 223:161–169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2017.01.003
Murthy HS (2017) Effect of dietary Administration of Carrageenan on growth, survival and feed utilization of common carp, Cyprinus carpio. JAMB 5. https://doi.org/10.15406/jamb.2016.05.00106
Ong ST, Shan Ho JZ, Ho B, Ding JL (2006) Iron-withholding strategy in innate immunity. Immunobiology 211:295–314. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.imbio.2006.02.004
Osman KM, Al-Maary KS, Mubarak AS, Dawoud TM, Moussa IMI, Ibrahim MDS, Hessain AM, Orabi A, Fawzy NM (2017) Characterization and susceptibility of streptococci and enterococci isolated from Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) showing septicaemia in aquaculture and wild sites in Egypt. BMC Vet Res 13:357. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12917-017-1289-8
Palstra AP, Kals J, Garcia AB, Dirks RP, Poelman M (2018) Immunomodulatory effects of dietary seaweeds in LPS challenged Atlantic salmon Salmo salar as determined by deep RNA sequencing of the head kidney transcriptome. Front Physiol 9:1–12. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2018.00625
Peixoto MJ, Salas-Leitón E, Pereira LF, Queiroz A, Magalhães F, Pereira R, Abreu H, Reis PA, Gonçalves JFM, Ozório RODA (2016) Role of dietary seaweed supplementation on growth performance, digestive capacity and immune and stress responsiveness in European seabass (Dicentrarchus labrax). Aquac Rep 3:189–197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aqrep.2016.03.005
Reverter M, Bontemps N, Lecchini D, Banaigs B, Sasal P (2014) Use of plant extracts in fish aquaculture as an alternative to chemotherapy: current status and future perspectives. Aquaculture 433:50–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2014.05.048
Safari R, Hoseinifar SH, Nejadmoghadam S, Jafar A (2016) Transciptomic study of mucosal immune, antioxidant and growth related genes and non-specific immune response of common carp (Cyprinus carpio) fed dietary Ferula (Ferula assafoetida). Fish Shellfish Immunol 55:242–248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2016.05.038
Salah AS, El Nahas AF, Mahmoud S (2017) Modulatory effect of different doses of beta-1,3/1,6-glucan on the expression of antioxidant, inflammatory, stress and immune-related genes of Oreochromis niloticus challenged with Streptococcus iniae. Fish Shellfish Immunol 70:204–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2017.09.008
Valente LMP, Gouveia A, Rema P, Matos J, Gomes EF, Pinto IS (2006) Evaluation of three seaweeds Gracilaria bursa-pastoris, Ulva rigida and Gracilaria cornea as dietary ingredients in European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) juveniles. Aquaculture 252:85–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2005.11.052
Vallejos-Vidal E, Reyes-López F, Teles M, MacKenzie S (2016) The response of fish to immunostimulant diets. Fish Shellfish Immunol 56:34–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2016.06.028
Vidal S, Tapia-Paniagua ST, Moriñigo JM, Lobo C, García de la Banda I, Balebona M d C, Moriñigo MÁ (2016) Effects on intestinal microbiota and immune genes of Solea senegalensis after suspension of the administration of Shewanella putrefaciens Pdp11. Fish Shellfish Immunol 58:274–283. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2016.09.010
Villamil L, Esguerra D (2017) Enterococcus , Myroides Y Exiguobacterium: génerosbacterianos con potencial probiótico para el cultivo de tilapia nilótica (Oreochromis niloticus) Enterococcus, Myroides, and Exiguobacterium. Bacterial Genus with Probiotic Potential for Nile Tilapia. Acta Biolo Colomb 22:331–339. https://doi.org/10.15446/abc.v22n3.59974
Villamil L, Reyes C, Martínez-Silva MA (2014) In vivo and in vitro assessment of lactobacillus acidophilus as probiotic for tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus, Perciformes: Cichlidae) culture improvement. Aquac Res 45:1116–1125. https://doi.org/10.1111/are.12051
Zhang Z, Yu A, Lan J, Zhang H, Hu M, Cheng J, Zhao L, Lin L, Wei S (2017) GapA, a potential vaccine candidate antigen against Streptococcus agalactiae in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Fish Shellfish Immunol 63:255–260. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2017.02.019
Zhao Z, Wang J, Han Y, Chen J, Liu G, Lu H, Yan B, Chen S (2017) Nutrients, heavy metals and microbial communities co-driven distribution of antibiotic resistance genes in adjacent environment of mariculture. Environ Pollut 220:909–918. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2016.10.075
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the Jorge Tadeo Lozano University, Santa Marta Campus, Santa Marta, Colombia, for providing the funding to carry out these experiments (grant: Effect of native bacteria and kappa carrageenan as immune modulators for Nile tilapia) and the members of GICMOA. We would also like to recognize the support of La Sabana University for data analysis. The authors acknowledge Dr. Michael Hume, Research Biologist, United States Department of Agriculture, Agricultural Research Service, for the contributions in the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical statements
Experiments were carried out according to the Laboratory Safety Manual of the participating institutions, Law 84 (National Congress of Colombia, 1989) and National Institutes of Health guide for the care and use of laboratory animals (NIH Publications No. 8023, revised 1978).
Additional information
Highlights
• Kappa carrageenan extracted from H. musciformis has immunomodulatory activity in tilapia.
• Dietary supplementation of Kappa carrageenan improves tilapia survival during a challenge with E. tarda.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Villamil, L., Infante Villamil, S., Rozo, G. et al. Effect of dietary administration of kappa carrageenan extracted from Hypnea musciformis on innate immune response, growth, and survival of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Aquacult Int 27, 53–62 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10499-018-0306-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10499-018-0306-7