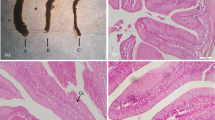
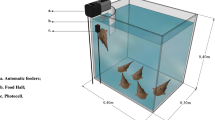
Abstract
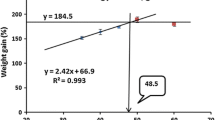
Juvenile Penaeus monodon weighing about 1.46 g were fed on a diet for 8 weeks at various daily feeding rates of 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 and 9 % of their body weight (BW), and the growth, feed utilization, blood parameters and non-specific immunity were determined. Forty shrimp per tank were distributed into 28 500-L fiberglass tanks, and they were fed four times 1 day. After the 56-day trial, survival was over 90 % and was not significantly affected by feeding rates. Final weight, weight gain and specific growth rates gradually increased with increasing feeding rate up to 8 % and then kept constant. Feed conversion rate (FCR: 1.08–2.20) from 9 % feeding rate treatment was significantly higher than that from 3 to 7 % feeding rate treatments (P < 0.05) but without difference to 8 % feeding rate treatment. Protein efficiency ratio linearly decreased with the increase in feeding rate. The apparent digestibility coefficients for dry matter, protein (APD) and energy (AED) of 3 % and 4 % feeding rate treatments were significantly lower than that of 5–9 % feeding rate treatments (P < 0.05). Activities of plasma glutamic oxaloacetic transaminase and glutamic pyruvic transaminase and concentrations of plasma cholesterol, triacylglycerol and low-density lipoprotein were increased with increasing feeding rate. Superoxide dismutase activities in hepatopancreas of shrimp from 3 to 5 % feeding rate treatments were significantly higher than that of shrimp from 7 to 9 % feeding rate treatments (P < 0.05) but without significant difference with 6 % feeding rate treatment. Nonlinear regression analysis of SGR indicated that the optimum feeding rate of juvenile P. monodon is 7.5 % BW/day.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdelghany AE, Ahmad MH (2002) Effects of feeding rates on growth and production of Nile tilapia, common carp and silver carp polycultured in fertilized ponds. Aquac Res 33:415–423
Allan GL, Moriarty DJW, Maguire GB (1995) Effects of pond preparation and feeding rate on production of Penaeus monodon Fabricius, water quality, bacteria and benthos in model farming ponds. Aquaculture 130:329–349
AOAC (Association of Official Analytical Chemists) (2001) Official methods of analysis, 15th edn. AOAC, Arlington
Bearnish FWH, Thomas E (1984) Effects of dietary protein and lipid on nitrogen losses in rainbow trout, Salmo gairdneri. Aquaculture 41:359–371
Brito R, Chimal MG, Gaxiola G, Rojas C (2000) Growth metabolic rate, and digestive enzyme activity in the white shrimp Litopenaeus setiferus early postlarvae fed different diets. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 255:21–36
Bureau DP, Hua K, Cho CY (2006) Effect of feeding level on growth and nutrient deposition in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss Walbaum) growing from 150 to 600 g. Aquac Res 37:1090–1098
Chien YH, Pan CH, Hunter B (2003) The resistance to physical stresses by Penaeus monodon juveniles fed diets supplemented with astaxanthin. Aquaculture 216:177–191
Cho SH, Lee SM, Park BH, Lee SM (2006) Effect of feeding ratio on growth and body composition of juvenile olive flounder Paralichthys olivaceus fed extruded pellets during the summer season. Aquaculture 251:78–84
Cui YB, Liu XF, Wang SM, Chen SL (1992) Grow and energy budget in young grass carp, Ctenopharyngodon idella Val., fed plant and animal diets. J Fish Biol 41:231–238
Duncan DB (1955) Multiple-range and multiple F tests. Biometrics 11:1–42
Elliott JM (1976) Body composition of brown trout (Salmo trutta L.) in relation to temperature and ration size. J Anim Ecol 45:273–289
Eroldoğan OT, Kumlu M, Aktaş M (2004) Optimum feeding rates for European sea bass Dicentrarchus labrax L. reared in seawater and freshwater. Aquaculture 231:501–515
Funge-Smith SJ, Briggs MRP (1998) Nutrient budgets in intensive shrimp ponds: implications for sustainability. Aquaculture 164:117–133
Huang JS, Chen G, Zhang JD, Shi G, Tang BG, Zhou H, Pan CH (2010) Effect of ration level on growth and energy budget of Trachinotus ovatus juvenile. J Guangdong Ocean Univ 30(1):18–22
Liñán-Cabello MA, Paniagua-Michel J, Zenteno-Savín T (2003) Carotenoids and retinal levels in captive and wild shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei. Aquacult Nutr 9(6):383–389
Mihelakakis A, Tsolkas C, Yoshimatsu T (2002) Optimization of feeding rate for hatchery-produced juvenile gilthead sea bream Sparus aurata. J World Aquac Soc 33:169–175
Ng WK, Lu KS, Hashim R, Ali A (2000) Effects of feeding rate on growth, feed utilization and body composition of tropical bagrid catfish. Aquac Int 8:19–29
Niu J, Lin HZ, Jiang SG, Chen X, Wu KC, Liu YJ, Wang S, Tian LX (2013) Comparison of effect of chitin, chitosan, chitosan oligosaccharide and N-acetyl-d-glucosamine on growth performance, antioxidant defenses and oxidative stress status of Penaeus monodon. Aquaculture 372–375:1–8
Pan CH, Chien YH, Hunter B (2003) The resistance to ammonia stress of Penaeus monodon Fabricius juvenile fed diets supplemented with astaxanthin. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 297:107–118
Partridge GJ, Jenkins GI (2002) The effect of salinity on growth and survival of juvenile black bream (Acanthopagrus butcheri). Aquaculture 210:219–230
Prior RL, Cao G (1999) In vivo total antioxidant capacity: comparison of different analytical methods. Free Radical Bio Med 27:1173–1181
Rabe J, Brown JA (2000) A pulse feeding strategy for rearing larval fish: an experiment with yellowtail flounder. Aquaculture 191:289–302
Refstie S, Helland SJ, Storebakken T (1997) Adaptation to soybean meal in diets for rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Aquaculture 153:263–272
Shimeno S, Shikata T, Hosokawa H, Masumoto T, Kheyyali D (1997) Metabolic responses to feeding rates in common carp, Cyprinus carpio. Aquaculture 151:371–377
Smith DM, Burford MA, Tabrett SJ, Irvin SJ, Ward L (2002) The effect of feeding frequency on water quality and growth of the black tiger shrimp (Penaeus monodon). Aquaculture 207:125–136
Tacon AGJ (1996) Nutritional studies in crustaceans and the problems of applying research findings to practical farming systems. Aquacult Nutr 2:165–174
Van Ham EH, Berntssen MHG, Imsland AK, Parpoura AC, Wendelaar Bonga SE, Stefansson SO (2003) The influence of temperature and ration on growth, feed conversion, body composition and nutrient retention of juvenile turbot (Scophthalmus maximus). Aquaculture 217:547–558
Xie SQ, Cui YB, Yang YX, Liu JK (1997) Energy budget of Nile tilapia (oreochromis niloticus) in relation size. Aquaculture 154:57–68
Zeitoun IH, Ullrey DE, Magee WT, Gill JL, Bergen WG (1976) Quantifying nutrient requirements of fish. J Fish Res Board Can 33:167–172
Zhou QC, Zheng SX, Ye YW, Feng Y, Qi XJ (2004) Effcet of feeding ratio on growth, feed utilization and body composition of shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei Boone. Mar Sci Bull 23(1):64–68
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by Project of Science and Technology of Guangdong Province (2012A031100006 and 2013B090600045) and Project of Science and Technology of Guangzhou City (2012J2200065), and Fund of National Modern Industrial Technology System of Shrimp (nycytx-46), and Hainan Natural Science Foundation (312088), and National Key Technology R&D Program of China (2012BAC07B05). The authors thank the participants who gave their time to the trial. Jin Niu, Yong-Jian Liu, Li-Xia Tian and Hei-Zhao Lin designed the study. Yun-Qiang Zhang, Xu Chen and Zhong Huang carried out the rearing work. Jun Wang, Yun Wang and Chuan-Peng Zhou helped analyze the samples. Jin Niu analyzed the results and wrote the paper with contributions from the other authors. There are no conflicts of interest.
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Niu, J., Chen, X., Zhang, YQ. et al. The effect of different feeding rates on growth, feed efficiency and immunity of juvenile Penaeus monodon . Aquacult Int 24, 101–114 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10499-015-9911-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10499-015-9911-x