Abstract
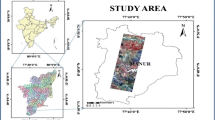
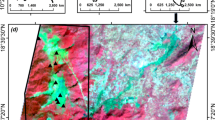
Hydromagnesite (HM for short) is a natural carbonate mineral that is widely distributed. It is a high-quality mineral raw material for preparing flame retardants, magnesium oxides, heavy/light basic magnesium carbonates, magnesium hydroxides, and other Mg products. The evaluation of HM resources is of great significance to the development and utilization of salt lake resources. Using remote sensing technology to observe HM resources in salt lake can overcome the shortcomings of traditional prospecting methods such as discontinuous spatial data, time and effort. In addition, spectral analysis is the basis of hyperspectral remote sensing, and more detailed analysis of the spectral characteristics of HM is still lacking; therefore, we measured the reflection spectral curve of HM samples in the area of Jiezechaka by ASD FieldSpec4 short-wave infrared spectrometer and determined the mineral composition and content of HM samples by X-ray diffraction. The analysis indicated three and seven absorption valleys with high and low absorption intensities, respectively, in the reflectance spectral curves of the HM samples in the Jiezechaka area. Then, on this basis, the Landsat8 OLI multispectral data and ZY1-02D AHSI hyperspectral data were used as the basic data of remote sensing inversion. As the ZY1-02D AHSI data have 166 bands, which is much more than Landsat8 OLI data, it has a stronger ability to characterize the spectral characteristics of HM and can better meet the requirements of remote sensing inversion. The end member spectra were selected based on PPI and SMACC methods, respectively. The HM information around Jiezechaka Salt Lake in Tibet was extracted by the mixture tuned matched filtering method, and the regional distribution map of HM was made. A confusion matrix operation was used to compare the determination results of the two types of data. Among them, based on Landsat8 data, PPI method was used to obtain end members, and the overall accuracy of HM extraction results was > 69%, and the kappa coefficient was 0.688. Based on Landsat8 data, SMACC method was used to obtain end members, and the overall accuracy of HM extraction results was > 67%, and the kappa coefficient was 0.667. Based on ZY1-02D AHSI data, PPI method was used to obtain end members, and the overall accuracy of HM extraction results was > 76%, and the kappa coefficient was 0.743. Based on ZY1-02D AHSI data, SMACC method was used to obtain end members, and the overall accuracy of HM extraction results was > 73%, and the kappa coefficient was 0.728. It shows that the end members selected by PPI method can better express HM information in the image. Finally, through the overlay analysis of the four results, we concluded that HM outcrops in the Jiezechaka area are mainly distributed in the northwestern and southeastern regions of the lake. This study provides a rapid assessment technique for measuring HM information from salt lakes.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
References
Abbey D, Gabor K, Schaefer NL, Ben K (2022) Rock alteration mapping in and around fossil shallow intrusions at Mt. Ruapehu New Zealand with laboratory and aerial hyperspectral imaging. J Volcanol Geotherm Res. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JVOLGEORES.2022.107700
Akao M, Marumo F, Iwai S (1974) The crystal structure of hydromagnesite. Acta Crystallogr B Struct Sci 30(11):2670–2672. https://doi.org/10.1107/S0567740874007771
Atay HY, Celik E (2010) Use of Turkish huntite/hydromagnesite mineral in plastic materials as a flame retardant. Polym Compos 31(10):1692–1700. https://doi.org/10.1002/pc.20959
Atay YH, Çirak M (2019) Separation of huntite and hydromagnesite from magnesite in combination of physicochemical treatment and size reduction—sciencedirect. Ain Shams Eng J 10(1):113–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asej.2018.05.003
Bai YL, Lv FJ, Su HB, Wu YX, Luan ZR (2023) Review of hyperspectral remote sensing altered mineral lnformation extractiion. Remote Sens Inf 38(01):1–10. https://doi.org/10.20091/j.cnki.1000-3177.2023.01.001. (in Chinese)
Bhan SK, Krishnanunni K (1994) Applications of remote sensing techniques to geology. Proc Indian Acad Sci Sect C Eng Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02881136
Boardman JW, Kruscl FA, Green RO (1995) Mapping target signatures via partial unmixing of AVIRIS data. JPL Publication, La Cañada Flintridge
Boardman JW (1998) Leveraging the high dimensionality of aviris data for improved sub-pixel target unmixing and rejection of false positives: mixture tuned matched filtering. In: Summaries of the seventh Jpl airborne geoscience workshop. JPL Publication. nasa Jet Propulsion Lab
Braithwaite CJR, Zedef V (1996) Hydromagnesite stromatolites and sediments in an alkaline lake, Salda Golu, Turkey. J Sediment Res 66(5):991–1002. https://doi.org/10.1306/D426845F-2B26-11D7-8648000102C1865D
Chen F, Yu B, Li B (2018a) A practical trial of landslide detection from single-temporal landsat8 images using contour-based proposals and random forest: a case study of national Nepal. Landslides 15(3):453–464. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-017-0884-x
Chen J, Bing ZB, Mao ZX, Zhang CP, Bi ZW, Yang Z (2018b) Using geochemical data for prospecting target areas by the sequential maximum angle convex cone method in the Manzhouli area, China. Geochem J 52(1):13–27. https://doi.org/10.2343/geochemj.2.0493
Chu HF, Zhai ZM, Zhao YD, Li PX, Zhang LP (2007) A convex cone analysis method for endmember selection of multispectral and hyperspectral images. J Remote Sens 04:460–467 (in Chinese)
Clark NR, Swayze AG, Livo EK, Kokaly FR, Sutley JS, Dalton BJ, McDougal RR, Gent AC (2003) Imaging spectroscopy: earth and planetary remote sensing with the USGS Tetracorder and expert systems. J Geophys Res Planets 108(E12):5131. https://doi.org/10.1029/2002je001847
Dai JJ, Wang DH, Chen ZH (2017) Reflectance characteristics of rare earth elements solutions based on rare earth ore powder in South Jiangxi Province. Acta Geoscientica Sinica 38(04):523–528 (in Chinese)
Dai JJ, Wang DH, Dai HZ, Liu LJ, Ling TY (2018) Reflectance spectral characteristics of rocks and minerals in Jiajika Lithium Deposits in West Sichuan. Rock Miner Anal 37(05):507–517. https://doi.org/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201701110003. (in Chinese)
Dai JJ, Wang DH, Wang HY (2019) A review of the three type rare mineral resources survey in China using remote sensing. Acta Geol Sin 93(06):1270–1278. https://doi.org/10.19762/j.cnki.dizhixuebao.2019155. (in Chinese)
Dai JJ, Zhao LX, Jiang Q, Wang HY, Liu TY (2020) Review of thermal-infrared spectroscopy applied in geological ore exploration. Acta Geol Sin 94(08):2520–2533. https://doi.org/10.19762/j.cnki.dizhixuebao.2020172. (in Chinese)
Dai JJ, Zhao LX, Wang HY (2021) Thermal-infrared spectroscopy of garnet minerals. Spectrosc Spectr Anal 41(06):1764–1768. https://doi.org/10.3964/J.ISSN.1000-0593(2021)06-1764-05. (in Chinese)
Geng XX, Yang JM, Zhang YJ, Yao FJ (2008) Application of RS technology to geology and ore deposit research and the development prospect. Contrib Geol Miner Resour Res 2:89–93 (in Chinese)
Govil H, Gill N, Rajendran S, Santosh M, Kumar S (2018) Identification of new base metal mineralization in Kumaon Himalaya, lndia, using hyperspectral remote sensing and hydrothermal alteration. Ore Geol Rev 92:271–283. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oregeorev.2017.11.023
Green AA, Berman M, Switzer P, Craig DM (1988) A transformation for ordering multispectral data in terms of image quality with implications for noise removal. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 26(1):65–74. https://doi.org/10.1109/36.3001
Gruninger HJ, Ratkowski JA, Hoke LM (2004a) The sequential maximum angle convex cone (SMACC) endmember model. Spectr Sci 5425:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1117/12.543794
Hao Y, Zhang QM, Li GH, Zhu CC (2013) Synergistic lithium extraction from mixed brines of Jiezechaka and Longmucuo salt lakes in Tibet. Inorg Chem Ind 45(06):27–29 (in Chinese)
Hatjilazaridou K, Chalkiopoulou F, Grossou-Valta M (1998) Greek industrial minerals: current status and trends. Ind Miner 369:45–63
Hollingbery LA, Hull TR (2011) The thermal decomposition of natural mixtures of huntite and hydromagnesite. Thermochim Acta 528(2011):45–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tca.2011.11.002
Hosseinjani M, Tangestani HM (2011) Mapping alteration minerals using sub-pixel unmixing of ASTER data in the Sarduiyeh area, SE Kerman, Iran. Int J Digit Earth 4(6):487–504. https://doi.org/10.1080/17538947.2010.550937
Hu QF, Song LY, Hu XX (2005) Study on exploitation and utilization of basic magnesite. Inorg Chem Ind 11:44–46. https://doi.org/10.1088/1126-6708/2005/07/014. (in Chinese)
Jiang TM, Ji LM, Cheng HD, Li BK, Li G, Ma HZ, Zhang XY, Li CZ, Ma XH, Zhang PC (2021) Algae mineralization experiment and genetic analysis of hydromagnesite in Bangor Lake, Xizang (Tibet). Geol Rev 67(06):1709–1726. https://doi.org/10.16509/j.georeview.2021.09.011. (in Chinese)
Jiao LL, Zhao PC, Liu ZQ, Wu QS, Yan DQ, Li YL, Chen YN, Li JS (2022) Preparation of magnesium hydroxide flame retardant from hydromagnesite and enhance the flame retardant performance of EVA. Polymers 14(8):1567–1567. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14081567
Krishna G, Sahoo NR, Pradhan S, Ahmad T, Sahoo PM (2017) Hyperspectral satellite data analysis for pure pixels extraction and evaluation of advanced classifier algorithms for lulc classification. Earth Sci Inf 11(2):159–170. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12145-017-0324-4
Kruse FA (2000) The effects of spatial resolution, spectral resolution, and SNR on geologic mapping using hyperspectral data, northern Grapevine Mountains, Nevada. In: Proceedings of the 9th JPL airborne earth science workshop. Jet Propulsion Laboratory Publication, pp 1–9
Kumar C, Shetty A, Raval S, Sharma R, Ray C (2015) Lithological discrimination and mapping using ASTER SWIR data in the Udaipur area of Rajasthan, India. Procedia Earth Planet Sci 11:180–188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeps.2015.06.022
Latifovic R, Pouliot D, Campbell J (2018) Assessment of convolution neural networks for surficial geology mapping in the South Rae Geological Region, Northwest Territories, Canada. Remote Sens 10(2):307–307. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10020307
Li XH (2022) Genesis and prospecting criteria of Naqu Shui Magnesite Deposit in Tibet. China Well Rock Salt 53(04):21–24. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1001-0335.2022.04.007. (in Chinese)
Li QK, Chen GX, Luo L (2023) Mineral prospectivity mapping using attention-based convolutional neural network. Ore Geol Rev. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.OREGEOREV.2023.105381
Lin YJ, Zheng MP, Ye CY (2017) Hydromagnesite precipitation in the alkaline lake Dujiali, central Qinghai-Tibetan plateau: constraints on hydromagnesite precipitation from hydrochemistry and stable isotopes. Appl Geochem 78:139–148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2016.12.020
Lin YJ, Zheng MP, Ye CY, Power IM (2019) Rare earth element and strontium isotope geochemistry in Dujiali Lake, central Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, China: implications for the origin of hydromagnesite deposits. Geochemistry 79(2):337–346. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemer.2019.02.002
Liodakis S, Tsoukala M (2010) Environmental benefits of using magnesium carbonate minerals as new wildfire retardants instead of commercially available, phosphate-based compounds. Environ Geochem Health 32(5):391–399. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-009-9283-0
Liu YP, Dang B, Li Y, Ma HT (2015) Applications of Savitzky–Golay filter for seismic random noise reduction. Acta Geophys 64(1):101–124. https://doi.org/10.1515/acgeo-2015-0062
Liu DC, Yan BK, Qiu JT (2016) The application of airborne hyper-spectral remote sensing technology to mineral resources exploration. Acta Geoscientica Sinica 37(03):349–358 (in Chinese)
Liu HC, Ye FW, Zhang C, Tan HJ, Lu NC (2023) Mineral mapping based on spaceborne AHSl hyperspectral data in Kamusite Area of Xinjiang. World Nuclear Geosci 40(02):395–404 (in Chinese)
Lou W, Zhang DX, Bayless CR (2020) Review of mineral recognition and its future. Appl Geochem. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2020.104727
Lu L, Gong ZN, Liang YN, Liang S (2022) Retrieval of chlorophyll-a concentrations of class II water bodies of inland lakes and reservoirs based on ZY1-02D satellite hyperspectral data. Remote Sens 14(8):1842–1842. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14081842
Masoumi F, Eslamkish T, Honarmand M, Abkar AA (2017) Utilization of ASTER data and spectral analysis to discriminate hydrothermally altered areas over Rabor, South of Kerman, Iran. J Indian Soc Remote Sens 45(6):1039–1055. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12524-017-0662-1
Meer FD, Werff HMA, Ruitenbeek FJA, Checker CA, Bakker WH, Noomen MF, Meijde M, Carranza EJM (2012) Muili-and hyperspecral geologic remote sensing: a review. Int J Appl Earth Obs Geoinf 14(1):112–128
Naoto Y, Claas G, Jocelyn C (2017) Hyperspectral and multispectral data fusion: a comparative review of the recent literature. IEEE Geosci Remote Sens Mag 5(2):29–56
Othmane L, Ayoub A, Abdellah B, Tobbal MS, Zakaria A, Samir S (2021) Bentonite clay minerals mapping using ASTER and field mineralogical data: a case study from the eastern Rif belt, Morocco. Remote Sens Appl Soc Environ. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.RSASE.2021.100640
Ren HR, Chen Z, Wu YL, Yang MD, Chen J, Hu HS, Liu J (2014) Thermal characterization and kinetic analysis of nesquehonite, hydromagnesite, and brucite, using TG–DTG and DSC techniques. J Therm Anal Calorim 115(2):1949–1960. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-013-3372-0
Renaut RW (1993) Morphology, distribution, and preservation potential of microbial mats in the hydromagnesite–magnesite playas of the Cariboo Plateau, British Columbia, Canada. Hydrobiologia 267(1–3):75–98. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00018792
Savitzky A, Golay EJM (2002) Smoothing and differentiation of data by simplified least squares procedures. Anal Chem 36(8):1627–1639. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac60214a047
Shirmard H, Farahbakhsh E, Pour BA, Muslim MA, Müller DR, Chandra R (2020) Integration of selective dimensionality reduction techniques for mineral exploration using ASTER satellite data. Remote Sens 12(8):1261–1261. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12081261
Skliros V, Tsakiridis P, Perraki M (2020) A combined Raman, Fourier transform infrared, and X-ray diffraction study of thermally treated nesquehonite. J Raman Spectrosc 51(9):1445–1453. https://doi.org/10.1002/jrs.5768
Su YM, Pan CX, Wang GF (2010) Verification report of surface brine lithium, potassium and boron deposits in Jiezechaka Salt Lake Mining area, Ritu County, Tibet Autonomous Region (in Chinese)
Tian HS, Liu LX, Sun ZM, Zeng SL (2017) Thermal decomposition characteristics of hydromagnesite from Bangor Lake in Tibet. J Chin Ceram Soc 45(02):317–322. https://doi.org/10.14062/j.issn.0454-5648.2017.02.21. (in Chinese)
Tripathi KM, Govil H (2019) Evaluation of AVIRIS-NG hyperspectral images for mineral identification and mapping. Heliyon 5(11):e02931. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e02931
Wang AY, Wang AJ, Li LH (2011) Mapping mineralogical alteration using MNF transform and mineral in vegetated areas. Geol Explor 47(04):710–718 (in Chinese)
Wang YL, Liu JY, Shi TJ, Yang B, Li C, Xu H, Yin WZ (2020) Preparation, properties and phase transition of mesoporous hydromagnesite with various morphologies from natural magnesite. Powder Technol 364(c):822–830. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2020.01.090
Wang QQ, Dai SJ, Xi Y (2021) Preparation of magnesia from hydromagnesite ore by calcination. JOM 73(3):1–6. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11837-020-04555-0
Xi Y (2020) Study on purification of a low-grade hydromagnesite ore in Tibet area. Univ Sci Technol Liaoning. https://doi.org/10.26923/d.cnki.gasgc.2020.000087. (in Chinese)
Xu ZY, Chen SB, Zhu BX, Chen LW, Ye YH, Lu P (2022) Evaluating the capability of satellite hyperspectral imager, the ZY1–02D, for topsoil nitrogen content estimation and mapping of farmlands in black soil area, China. Remote Sens 14(4):1008–1008. https://doi.org/10.3390/RS14041008
Yamamoto GI, Kyono A, Sano Y, Matsushita Y, Yoneda Y (2021) In situ and ex situ studies on thermal decomposition process of hydromagnesite Mg5(CO3)4(OH)2·4H2O. J Therm Anal Calorim 144(3):1–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-020-09618-7
Yan RE, Xia ZK (1987) Discussion on hydromagnesite deposition and its forming environment in Pleistocene strata in Datong Basin, Shanxi Province. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Pekinensis 2:98–110. https://doi.org/10.13209/j.0479-8023.1987.030. (in Chinese)
Yang JZ, Zhao YL (2015) Technical features of remote sensing and its application in the geological survey and mineral resources survey. Miner Explor 6(05):529–534. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1674-7801.2015.05.006. (in Chinese)
Yang JF, Cui XF, Lu SW, Li QS (2005) Evolution of Jiezechaka lake and the climatic environment of the late pleistocence in Northwest Tibet. Xinjiang Geol 1:59–63. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1000-8845.2005.01.013. (in Chinese)
Yang JF, Wang YF, Zhao H, Bai CJ, Fang HB, Bai GD (2008) The records of shallow well in Lake Jiezechaka shoreline of Tibet and the lake evolution. J Lake Sci 20(01):83–87. https://doi.org/10.18307/2008.0112. (in Chinese)
Yang N, Zhang ZK, Yang JH, Hong ZL, Shi J (2021) A convolutional neural network of GoogLeNet applied in mineral prospectivity prediction based on multi-source geoinformation. Nat Resour Res 30(6):1–19. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11053-021-09934-1
Young GA (1915) Hydromagnesite deposits of Atlin, British Columbia. Geological Survey of Canada, 50–61
Zhang CJ, Zuo RG, Xiong YH (2021) Detection of the multivariate geochemical anomalies associated with mineralization using a deep convolutional neural network and a pixel-pair feature method. Appl Geochem. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.APGEOCHEM.2021.104994
Zhang Z, Chen C, Li YP (2022) Application of multi-source remote sensing data in rock and mineral identification in Karamaili area Xinjiang. Geol Rev 68(06):2365–2380. https://doi.org/10.16509/j.georeview.2022.06.085. (in Chinese)
Zhang ZX, Dai JJ, Wang XG, Hu ZH, Wan X, Peng Bo, Fu MH, Zhao LX (2023) Shortwave infrared characteristics of muscovite from giant Shimensi tungsten deposit in northern Jiangxi Province and implication to exploration. Miner Depos 42(01):116–127. https://doi.org/10.16111/j.0258-7106.2023.01.008. (in Chinese)
Zhao YS (2003) Principles and methods of remote sensing application analysis. Science Press, Beijing (in Chinese)
Zheng MP, Xiang J, Wei XJ, Zheng Y (1989) Salt lake on the Tibetan Plateau. Beijing Science & Technology Press, Beijing (in Chinese)
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank all editors and reviewers for their comments and suggestions.
Funding
This research was supported by the Research Projects of the Resource Dynamics and Resource Potential of the Jiezechaka and Longmucuo Salt Lakes in Tibet (HE2202), the China Geological Survey Project (DD20221684, DD20230054, DD20230033), the Basic Research Projects of the Institute of Mineral Resources, Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences (KK2102), and Scientific Investigation Project of Bulk Metal Resources in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau (2021QZKK0304).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
DJ conceived and supervised the study. ZY completed the field collection and content determination of the hydromagnesite samples; ZT completed the spectral determination and remote sensing determination and wrote the article. DJ and YC put forward revisions to the article.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, T., Dai, J., Zhao, Y. et al. MTMF Method for Hydromagnesite Determination Based on Landsat8 and ZY1-02D Data: A Case Study of the Jiezechaka Salt Lake in Tibet. Aquat Geochem (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10498-024-09428-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10498-024-09428-5