Abstract
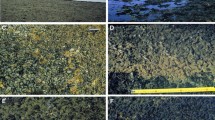
Benthic microbial mats are common in the alkaline hydromagnesite-magnesite playa lakes of Interior British Columbia. Four main zones are recognized based on mat morphology that can be related to the type and duration of wetting. From the basin margin toward the playa centre they are: (i) vegetated hummocky ground; (ii) polygonal hummocky ground; (iii) low-domal and stratiform mats, and (iv) laterally continuous and pustular mats. Mats in peripheral mudflats are commonly mineralized by hydromagnesite, mostly precipitated by capillary evaporation of shallow groundwaters. Mats forming in the ephemeral lake tend to have lower carbonate content.
Although widespread, the mats are poorly preserved in the Holocene sedimentary record. Underlying sediments are commonly weakly bedded, disturbed or massive. Desiccation, dehydration, wetting-drying cycles, and grazing by invertebrates cause fragmentation of mats at the surface, facilitating erosion. Cryogranulation, interstitial mineral precipitation, vesiculation, bioturbation, compaction, and volume changes associated with diagenesis, disrupt and destroy lamination in the upper few centimetres. Most surviving organic matter is lost by early microbial degradation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aldermann, 1965. Dolomitic sediments and their environment in the South-East of South Australia. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 29: 1355–1365.
Anderson, G. C., 1958. Some limnological features of a shallow saline meromictic lake. Limnol. Oceanogr. 3: 259–270.
Bauld, J., 1981a. Occurrence of benthic microbial mats in saline lakes. In W. D. Williams (ed.), Salt Lakes. Developments in Hydrobiology 5. Dr W. Junk Publishers, The Hague: 87–111. Reprinted from Hydrobiologia 81/82.
Bauld, J., 1981b. Geological role of cyanobacterial mats in sedimentary environments: a production and preservation of organic matter. J. Aust. Geol. Geophys. 6: 307–317.
Burne, R. V. & L. S. Moore, 1987. Microbialites: Organosedimentary deposits of benthic microbial communities. Palaios 2: 241–254.
Campbell, R. B. & H. W. Tipper, 1971. Geology of the Bonaparte Lake map area, British Columbia. Mem. Geol. Surv. Can. 363, 100 pp.
Casanova, J., 1986. East African Rift stromatolites. In: L. E. Frostick, R. W. Renaut, I. Reid & J. J. Tiercelin (eds), Sedimentation in the African Rifts. Spec. Publ. Geol. Soc. Lond. 25: 201–210.
Christ, C. L. & P. B. Hostetler, 1970. Studies in the system MgO-SiO2-CO2-H2O (II): The activity product constant of magnesite. Am. J. Sci. 286: 439–453.
Cook, R. U. & A. Warren, 1973. Geomorphology in deserts. Batsford, London, 394 pp.
Cohen, Y., R. W. Castenholz & H. O. Halvorson (eds), 1984. Microbial mats: Stromatolites. MBL Lectures in Biology Vol. 3, Liss, New York, 498 pp.
Cummings, J. M., 1940. Saline and hydromagnesite deposits of British Columbia. Bull. B. C. Dept. Mines 4, 160 pp.
De Deckker, P., 1983. Australian salt lakes: their history, chemistry and biota — a review. In U. T. Hammer (ed.), Saline Lakes Developments in Hydrobiology 16. Dr W. Junk Publishers, The Hague: 231–244. Reprinted from Hydrobiologia 105.
De Deckker, P., 1987. Biological and sedimentary facies of Australian salt lakes. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 62: 237–270.
Demicco, R. V. & E. Gierlowski-Kordesch, 1986. Facies sequences of a semi-arid closed basin: the Lower Jurassic East Berlin Formation of the Hartford Basin, New England, USA. Sedimentology 33: 107–118.
Fulton, R. J., 1984. Quaternary glaciation, Canadian Cordillera. In: R. J. Fulton (ed.), Quaternary stratigraphy of Canada — A Canadian contribution to I.G.C.P. Project 24. Pap. Geol. Surv. Can. 84-10: 39–47.
Gerdes, G. & W. E. Krumbein, 1987. Biolaminated deposits. Lectures Notes in Earth Sciences 9. Springer, Berlin, 183 pp.
Golubic, S., 1991. Modern stromatolites: A review. In R. Riding (ed.), Calcareous algae and stromatolites. Springer, Berlin: 541–561.
Grant, B., 1987. Magnesite, brucite and hydromagnesite occurrences in British Columbia. Open File Rep. B.C. Geol. Surv. Branch 1987-13, 68 pp.
Halley, R. B., 1976. Textural variation within Great Salt Lake algal mounds. In: M. R. Walter (ed.), Stromatolites. Elsevier, Amsterdam: 435–446.
Hallsworth, E. G., G. K. Robertson & F. R. Gibbons, 1955. Studies in pedogenesis in New South Wales, VII: The ‘gilgai’ soils. J. Soil Sci. 6: 1–31.
Hammer, U. T., 1986. Saline lake ecosystems of the world. Dr W. Junk Publishers, Dordrecht, 616 pp.
Hardie, L. A., J. P. Smoot & H. P. Eugster, 1978. Saline lakes and their deposits: a sedimentological approach. In: A. Matter & M. E. Tucker (eds), Modern and ancient lake sediments. Blackwell, Oxford: 7–41.
Irion, G. & G. Müller, 1968. Huntite, dolomite, magnesite and polyhalite of Recent age from Toz Gölü, Turkey. Nature 220: 130–131.
Kelts, K. & K. J. Hsü, 1978. Freshwater carbonate sedimentation. In A. Lerman (ed.), Lakes: chemistry, geology, physics. Springer, New York; 295–323.
Kempe, S., J. Kazmierczak, G. Landmann, T. Konuk, A. Reimer & A. Lipp, 1991. Largest known microbialites discovered in Lake Van, Turkey. Nature 349: 605–608.
Kennard, J. M. & N. P. James, 1986. Thrombolites and stromatolites: two distinct types of microbial structures. Palaios 1: 492–503.
Langmuir, D., 1965. Stability of carbonates in the system MgO-CO2-H2O. J. Geol. 73: 730–754.
Last, W. M. & P. De Deckker, 1990. Modern and Holocene carbonate sedimentology of two saline volcanic maar lakes., southern Australia. Sedimentology 37: 967–981.
Mackay, J. R., 1980. The origins of hummocks, western Arctic coast, Canada. Can. J. Earth Sci. 17: 996–1006.
Mathews, W. H., 1989. Neogene Chilcotin basalts in southcentral British Columbia: Geology, ages and geomorphic history. Can. J. Earth Sci. 26: 969–982.
McIntyre, D. S., 1958. Soil splash and the formation of surface crusts by raindrop impact. Soil Sci. 85: 261–266.
Molnar, B., 1990. Modern lacustrine carbonate (calcite, dolomite, magnesite) formation and environments in the Hungary. Abstr. (Pap.) 13 Int. Sedimentol. Congr., Nottingham, U.K.: 363–364.
Monger, J. W. H., 1989. Overview of Cordilleran geology. In: B. D. Rickets (ed.), Western Canada Sedimentary Basin — a case history. Canadian Society of Petroleum Geologists, Calgary: 9–32.
Moss, B. & J. Moss, 1969. Aspects of the limnology of an endorheic African lake (Lake Chilwa, Malawi). Ecology 50: 109–118.
Motts, W. (ed.), 1970. Geology and hydrology of selected playas in Western United States. U.S. Air Force Cambridge Research Laboratories, Bedford, Massachussetts, Final Scientific Report (Part II), AFCRL-69–0214, 288 pp.
Müller, G., G. Irion & U. Förstner, 1972. Formation and diagenesis of inorganic Ca-Mg carbonates in lacustrine environments. Naturwissenschaften 59: 158–164.
Osborne, R. H, G. R. Licari & M. H. Link, 1982. Modern lacustrine stromatolites, Walker Lake, Nevada. Sed. Geol. 32: 39–61.
Park, R. K., 1977. The preservation potential of some recent stromatolites. Sedimentology 24: 485–506.
Popov, V. S. & Sadykov, T. S., 1987. Magnesium carbonate deposits of the Lake Beshkod region (Western Uzbekistan). Lithol. Mineral. Res. 21: 394–400.
Pueyo-Mur, J. J., 1978. La precipitación evaporitica actual en las lagunas saladas del área: Bujaraloz, Sástago, Caspe, Alcañiz y Calanda (provincias de Zaragoza y Teruel). Rev. Inst. Inv. Geol. Disputación Prov. Barcelona 33: 5–56.
Pueyo-Mur, J. J. & M. Ingles-Urpinell, 1987. Magnesite formation in recent playa lakes, Los Menegros, Spain. In: J. D. Marshall (ed.), Diagenesis of sedimentary sequences. Spec. Publ. Geol. Soc. Lond. 36: 119–122.
Reinecke, L., 1920. Mineral deposits between Lillooet and Prince George, British Columbia. Mem. Geol. Surv. Can., 118.
Renaut, R. W., 1990. Recent carbonate sedimentation and brine evolution in the saline lake basins of the Cariboo Plateau, British Columbia, Canada. In F. A. Comín & T. G. Northcote (eds), Saline Lakes. Developments in Hydrobiology 59. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht: 67–81. Reprinted from Hydrobiologia 197.
Renaut, R. W. & P. R. Long, 1987. Freeze-out precipitation of salts in saline lakes — examples from Western Canada. In: G. L. Strathdee, M. O. Klein & L. A. Melis (eds), Crystallization and precipitation. Pergamon, Oxford: 33–42.
Renaut, R. W. & P. R. Long, 1989. Sedimentology of the saline lakes of the Cariboo Plateau, Interior British Columbia. Sed. Geol. 64: 239–264.
Renaut, R. W. & W. A. S. Sarjeant, 1991. Salt tracks — evidence for animal activities in saline mudflats and their palacolimnological implications. Prog. Abstr., Sedimentary and Paleolimnological Records of Saline Lakes Conf., Saskatoon, Canada: 40.
Renaut, R. W. & D. Stead, 1991a. Recent magnesite-hydromagnesite sedimentation in playa basins of the Cariboo Plateau, British Columbia. Pap. B.C. Geol. Surv. Branch 1991-1: 279–288.
Renaut, R. W. & D. Stead, 1991b. Carbonate-evaporite sedimentation at Clinton Lake, British Columbia. Prog. Abstr., Sedimentary and Paleolimnological Records of Saline Lakes Conf., Saskatoon, Canada: 41.
Renaut, R. W., D. Stead & R. B. Owen, in press. The saline lakes of the Fraser Plateau, British Columbia, Canada. In E. Gierlowski-Kordesch & K. Kelts (eds), Global geological record of lake basins, Vol. 1. Cambridge University Press.
Riding, R., 1991. Classification of microbial carbonates. In R. Riding (ed.), Calcareous algae and stromatolites. Springer, Berlin: 21–51.
Rollins, L., 1988. PCWATEQ: A simple, interactive PC version of the water chemistry analysis program WATEQF.
Rosen, M. R., D. E. Miser & J. K. Warren, 1988. Sedimentology, mineralogy and isotopic analysis of Pellet Lake, Coorong region, South Australia. Sedimentology 35: 105–122.
Scudder, G. G. E., 1969. The fauna of saline lakes on the Fraser Plateau in British Columbia. Verh. int. Ver. Limnol. 17: 430–439.
Smith, A. M. & T. R. Mason, 1991. Pleistocene, multiple-growth, lacustrine oncoids from the Poacher's Point Formation, Etosha Pan, northern Namibia. Sedimentology 38: 591–600.
Smoot, J. P. & T. K. Lowenstein, 1991. Depositional environments of non-marine evaporites. In J. L. Melvin (ed.), Evaporites, petroleum and mineral resources. Elsevier. Amsterdam: 189–347.
Smoot, J. P. & P. E. Olsen, 1985. Massive mudstones in basin analysis and paleoclimatic interpretation of the Newark Supergroup. Circ. U.S. Geol. Surv. 946: 4–10.
Southgate, P. N., I. B. Lambert, T. H. Donnelly, R. Henry, H. Etminan & G. Weste, 1989. Depositional environments and diagenesis in Lake Parakeelya: a Cambrian alkaline playa from the Officer Basin, South Australia. Sedimentology 36: 1091–1112.
Springer, M. E., 1958. Desert pavement and vesicular layer of some desert soils in the desert of the Lahortan Basin, Nevada. Proc. Soil. Sci. Soc. Am. 22: 63–66.
Surdam, R. C. & C. A. Wolfbauer, 1975. The Green River Formation — a playa-lake complex. Bull. Geol. Soc. Am. 86: 335–345.
Surdam, R. C. & J. L. Wray, 1976. Lacustrine stromatolites, Eocene Green River Formation, Wyoming. In: M. R. Walter (ed.), Stromatolites. Elsevier, Amsterdam: 535–541.
Thompson, J. B. & F. G. Ferris, 1990. Cyanobacterial precipitation of gypsum, calcite and magnesite from natural lake water. Geology 18: 995–998.
Topping, M. S. & C. G. E. Scudder, 1977. Some physical and chemical features of saline lakes in central British Columbia. Syesis 10: 145–166.
Truc, G., 1978. Lacustrine sedimentation in an evaporitic environment: the Ludian (Palaeogene) of the Mormoiron basin, southeastern France. In: A. Matter & M. E. Tucker (eds), Modern and ancient lake sediments. Blackwell, Oxford: 189–203.
Tufnell, L., 1975. Hummocky microrelief in the Moor House area of the Northern Pennines, England. Biul. Pergyl. 24: 353–368.
Valentine, K. W. G. & A. Schori, 1980. Soils of the Lac La Hache-Clinton area, British Columbia. B.C. Soil Surv. Rep. 25, 118 pp.
Van Houten, F. B., 1980. Late Triassic part of Newark Supergroup, Delaware River section, west-central New Jersey. In: W. Manspeizer (ed.), Field studies of New Jersey geology and guide to field trips. 52nd Annual Meeting, New York State Geological Association, New York: 264–276.
Verger, F., 1964. Mottureaux et gilgais. Annal. Géogr. 73: 413–430.
von der Borch, C. C., 1965. The distribution and preliminary geochemistry of modern carbonate sediments of the Coorong area, South Australia. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 29: 781–799.
von der Borch, C. C., 1976. Stratigraphy of stromatolite occurrences in carbonate lakes of the Coorong Lagoon area, South Australia. In: M. R. Walter (ed.), Stromatolites. Elsevier, Amsterdam: 413–420.
von der Borch, C. C., B. Bolton & J. K. Warren, 1977. Environmental setting and microstructure of subfossil lithified stromatolites associated with evaporites, Marion Lake, South Australia. Sedimentology 24: 693–708.
Walter, M. R. (ed.), 1976. Stromatolites. Elsevier, Amsterdam, 790 pp.
Walter, M. R., S. Golubic & W. V. Preiss, 1973. Recent stromatolites from hydromagnesite and aragonite depositing lakes near Coorong Lagoon, South Australia. J. Sed. Petrol. 43: 1021–1030.
Warren, J. K., 1990. Sedimentology and mineralogy of dolomitic Coorong lakes, South Australia. J. Sed. Petrol. 60: 843–858.
White, A. H. & B. C. Youngs, 1980. Cambrian alkali playa-acustrine sequences in the northeastern Officer Basin, South Australia. J. Sed. Petrol. 50: 1279–1286.
Williams, P. J. & M. W. Smith, 1989. The frozen earth: Fundamentals of geocryology. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 306 pp.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Renaut, R.W. Morphology, distribution, and preservation potential of microbial mats in the hydromagnesite-magnesite playas of the Cariboo Plateau, British Columbia, Canada. Hydrobiologia 267, 75–98 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00018792
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00018792