Abstract
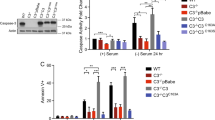
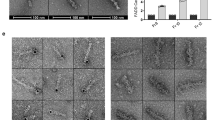
Caspase-8 can trigger cell death following prodomain-mediated recruitment to the ‘death-inducing signaling complex.’ The prodomain consists of two death effector domain (DED) motifs that undergo homotypic interactions within the cell. Aside from mediating recruitment of procaspase-8, the prodomains have also been implicated in regulating cell survival, proliferation, death, senescence, differentiation, and substrate attachment. Here, we perform the initial characterization of a novel isoform of caspase-8, designated caspase-8 isoform 6 (Casp-8.6), which encodes both prodomain DEDs followed by a unique C-terminal tail. Casp-8.6 is detected in cells of the hematopoietic compartment as well as several other tissues. When Casp-8.6 expression is reconstituted in caspase-8-deficient cells, Casp-8.6 does not significantly impact cellular proliferation, contrasting with our previous results using a domain-defined ‘DED-only’ construct that lacks the C-terminal tail. Like the DED-only construct, Casp-8.6 also robustly forms ‘death effector’ filaments, but in contrast to the DED construct, it does not exhibit a dependence upon intact microtubules to scaffold filament formation. Both types of death effector filaments promote apoptosis when expressed in the presence of full length caspase-8 (isoform 1). Together, the results implicate Casp-8.6 as a new physiological modulator of apoptosis.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pop C, Salvesen GS (2009) Human caspases: activation, specificity, and regulation. J Biol Chem 284(33):21777–21781
Mielgo A, Torres VA, Clair K, Barbero S, Stupack DG (2009) Paclitaxel promotes a caspase 8-mediated apoptosis through death effector domain association with microtubules. Oncogene 28(40):3551–3562
McDonald ER 3rd, El-Deiry WS (2004) Suppression of caspase-8- and -10-associated RING proteins results in sensitization to death ligands and inhibition of tumor cell growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101(16):6170–6175
Valmiki MG, Ramos JW (2009) Death effector domain-containing proteins. Cell Mol Life Sci 66(5):814–830
Finlay D, Vuori K (2007) Novel noncatalytic role for caspase-8 in promoting SRC-mediated adhesion and Erk signaling in neuroblastoma cells. Cancer Res 67(24):11704–11711
Mielgo A, Torres VA, Schmid MC, Graf R, Zeitlin SG, Lee P, Shields DJ, Barbero S, Jamora C, Stupack DG (2009) The death effector domains of caspase-8 induce terminal differentiation. PLoS One 4(11):e7879
Siegel RM, Martin DA, Zheng L, Ng SY, Bertin J, Cohen J, Lenardo MJ (1998) Death-effector filaments: novel cytoplasmic structures that recruit caspases and trigger apoptosis. J Cell Biol 141(5):1243–1253
Shikama Y, Shen L, Yonetani M, Miyauchi J, Miyashita T, Yamada M (2002) Death effector domain-only polypeptides of caspase-8 and -10 specifically inhibit death receptor-induced cell death. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 291(3):484–493
Xu Z, Tang K, Wang M, Rao Q, Liu B, Wang J (2009) A new caspase-8 isoform caspase-8 s increased sensitivity to apoptosis in Jurkat cells. J Biomed Biotechnol 2009:930462
Himeji D, Horiuchi T, Tsukamoto H, Hayashi K, Watanabe T, Harada M (2002) Characterization of caspase-8L: a novel isoform of caspase-8 that behaves as an inhibitor of the caspase cascade. Blood 99(11):4070–4078
Stupack DG, Teitz T, Potter MD, Mikolon D, Houghton PJ, Kidd VJ, Lahti JM, Cheresh DA (2006) Potentiation of neuroblastoma metastasis by loss of caspase-8. Nature 439(7072):95–99
Finlay D, Howes A, Vuori K (2009) Critical role for caspase-8 in epidermal growth factor signaling. Cancer Res 69(12):5023–5029
Stupack DG (2010) Caspase-8 as a therapeutic target in cancer. Cancer Lett. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2010.07.022
Salvesen GS, Riedl SJ (2009) Structure of the Fas/FADD complex: a conditional death domain complex mediating signaling by receptor clustering. Cell Cycle 8(17):2723–2727
Thierry F, Demeret C (2008) Direct activation of caspase 8 by the proapoptotic E2 protein of HPV18 independent of adaptor proteins. Cell Death Differ 15(9):1356–1363
Scott FL, Stec B, Pop C, Dobaczewska MK, Lee JJ, Monosov E, Robinson H, Salvesen GS, Schwarzenbacher R, Riedl SJ (2009) The Fas-FADD death domain complex structure unravels signalling by receptor clustering. Nature 457(7232):1019–1022. doi:10.1038/nature07606
Kheradmand F, Mattewal AS, Corry DB (2009) At last, an immune organ we can call our own? Am J Respir Crit Care Med 179(7):525–527
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yuan, R.T., Young, S., Liang, J. et al. Caspase-8 isoform 6 promotes death effector filament formation independent of microtubules. Apoptosis 17, 229–235 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-011-0677-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-011-0677-y