Abstract
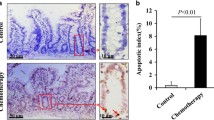
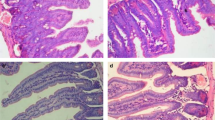
The purpose of the present study was to evaluate the effect of transforming-growth factor-alpha (TGF-α) on enterocyte apoptosis following methotrexate (MTX) induced intestinal mucositis in a rat and in Caco-2 cells. Non-pretreated and pretreated with MTX Caco-2 cells were incubated with increasing concentrations of TGF-α. Cell apoptosis was determined by FACS cytometry. Adult rats were divided into four groups: Control, Control-TGF-α, MTX, and MTX- TGF-α rats. Three days later rats were sacrificed. Enterocyte apoptosis were measured at sacrifice. RT-PCR and Western Blotting was used to determine the level of Bax and Bcl-2 mRNA and protein. Real time PCR was used to measure epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFr) expression along the villus-crypt axis. The in vitro experiment has shown that treatment with TGF-α of Caco-2 cells results in a significant inhibition of cell apoptosis in a dose-dependent manner. In vivo experiment, a decreased levels of apoptosis in MTX- TGF-α rats corresponded with the decrease in Bax and with the increase in Bcl-2 at both mRNA and protein levels. The inhibiting effect of TGF-α on enterocyte apoptosis was strongly correlated with EGFr expression along the villus-crypt axis. In conclusion, treatment with TGF-α inhibits enterocyte apoptosis following MTX- injury in the rat.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sonis ST, Elting LS, Keefe D et al (2004) Perspectives on cancer therapy-induced mucosal injury: pathogenesis, measurement, epidemiology, and consequences for patients. Cancer 100(9 Suppl):1995–2025. doi:10.1002/cncr.20162
Edward B, Rubenstein D, Peterson DE et al (2004) Clinical practice guidelines for the prevention and treatment of cancer therapy-induced oral and gastrointestinal mucositis. Cancer 100(9 Suppl):2026–2046. doi:10.1002/cncr.20163
Sonis ST (2004) The pathobiology of mucositis. Nat Rev Cancer 4:277–284. doi:10.1038/nrc1318
Gate L, Paul J, Ba GN et al (1999) Oxidative stress induced in pathologies: the role of antioxidants. Biomed Pharmacother 53:169–180. doi:10.1016/S0753-3322(99)80086-9
Verburg M, Renes IB, Meijer HP et al (2000) Selective sparing of goblet cells and paneth cells in the intestine of methotrexate-treated rats. Am J Physiol 279:G1037–G1047
Keefe DM, Brealey J, Goland GJ et al (2000) Chemotherapy for cancer causes apoptosis that precedes hypoplasia in crypts of the small intestine in humans. Gut 47:632–637. doi:10.1136/gut.47.5.632
Bowen JM, Gibson RJ, Cummins AG et al (2006) Intestinal mucositis: the role of the Bcl-2 family, p53 and caspases in chemotherapy-induced damage. Support Care Cancer 14:713–731. doi:10.1007/s00520-005-0004-7
Rosse T, Olivier R, Monney L et al (1998) Bcl-2 prolongs cell survival after Bax-induced release of cytochrome c. Nature 391:496–499. doi:10.1038/35160
Kurokawa MK, Lynch K, Podolsky DK (1987) Effects of growth factors on the intestinal epithelial line: transforming growth factor β inhibits proliferation and stimulates differentiation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 142:775–782. doi:10.1016/0006-291X(87)91481-1
Menard DP, Arsenalt P, Pothier P (1988) Biologic effects of ipidemal factor in human fetal jejuins. Gastroenterology 94:656–663
Booth D, Haley JD, Bruskin AM et al (2000) Transforming growth factor- β3 protects murine small intestinal crypt stem cells and animal survival after radiation, possibly by reducing stem cell cycling. Int J Cancer 86:53–59. doi :10.1002/(SICI)1097-0215(20000401)86:1<53::AID-IJC8>3.0.CO;2-Z
Hirano M, Iwakiri R, Fujimoto K et al (1995) Epidermal growth factor enhances repair of rat intestinal mucosa damaged by oral administration of methotrexate. J Gastroenterol 30:169–176. doi:10.1007/BF02348661
Howarth GS, Cool JC, Bourne AJ et al (1998) Insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) stimulates regrowth of the damaged intestine in rats, when administered following, but not concurrent with, methotrexate. Growth Factors 15:279–292
Yang H, Antony PA, Wildhaber BE et al (2004) Intestinal intraepithelial lymphocyte gamma delta-T cell-derived keratinocyte growth factor modulates epithelial growth in the mouse. J Immunol 172:4151–4158
Warner BW, VanderKolk WE, Can G (1997) Epidermal growth factor receptor expression following small bowel resection. J Surg Res 70:171–177. doi:10.1006/jsre.1997.5125
Sukhotnik I, Mogilner JG, Shaoul R et al (2008) Responsiveness of intestinal epithelial cell turnover to TGF-α after bowel resection in a rat is correlated with EGF receptor expression along the villus-crypt axis. Pediatr Surg Int 24:21–28. doi:10.1007/s00383-007-2038-z
Derynck R (1988) Transforming growth factor-α. Cell 54:593–595. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(88)80001-1
Alison MR, Sarraf CE (1994) The role of growth factors in intestinal cell proliferation. Cell Biol Int 18:1–10. doi:10.1006/cbir.1994.1001
Smith FP, Kisner DL, Widerlite L et al (1979) Chemotherapeutic alteration of small intestinal morphology and function: a progress report. J Clin Gastroenterol 1:203–207. doi:10.1097/00004836-197909000-00003
Chromszynski P (1993) A reagent for the single-step simultaneous isolation of RNA, DNA and proteins from cell and tissue samples. BioTechniques 15:532–536
Park PO, Haglund U, Bulkley GB et al (1990) The sequence of development of intestinal tissue injury after strangulation ischemia and reperfusion. Surgery 107:574–580
Delarco JE, Torado GJ (1978) Growth factors from murine sarcoma virus-transformed cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 75:4001–4005. doi:10.1073/pnas.75.8.4001
Malden LT, Novak U, Burgess AW (1989) Expression of transforming growth factor alpha messenger in the normal and neoplastic gastro-intestinal tract. Int J Cancer 43:380–384. doi:10.1002/ijc.2910430305
Goodlad RA, Wright NA (1995) Epidermal growth factor and transforming growth factor-alpha actions on the gut. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 7:928–932. doi:10.1097/00042737-199510000-00004
Koyama SY, Podolsky DK (1989) Different expression of transforming growth factors alpha and beta in rat intestinal epithelial cells. J Clin Invest 83:1768–1773. doi:10.1172/JCI114080
Podolsky DK (1994) Peptide growth factors in the gastrointestinal tract. In: Johnson LR (ed) Physiology of the gastrointestinal tract, 3rd edn. Raven Press, New York, pp 129–167
Hormi K, Lehy T (1996) Transforming growy factor-alpha in vivo stimulates epithelial cell proliferation in digestive tissues of suckling rats. Gut 39:532–538
Barnard JA, Polk WH, Moses HL et al (1991) Production of transforming growth factor-alpha by normal small intestine. Am J Physiol 261:994–1000
Konturek SJ, Brzozowski T, Maka J et al (1992) Transforming growth factor alpha and epidermal growth factor in protection and healing of gastric mucosal injury. Scand J Gastroenterol 27:649–655. doi:10.3109/00365529209000134
Dignass AU, Stow JL, Babyatsky MW (1996) Acute epithelial injury in the rat small intestine in vivo is associated with expanded expression of transforming growth factor alpha and beta. Gut 38:291–295. doi:10.1136/gut.38.5.687
Sonis ST, Costa JW Jr, Evitts SM et al (1992) Effect of epidermal growth factor on ulcerative mucositis in hamsters that receive cancer chemotherapy. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol 74:749–755. doi:10.1016/0030-4220(92)90402-C
Robinson BA, Clutterbuck RD, Millar JL et al (1985) Epidermal growth factor (hEGF) has no effect on murine intestine epithelial damage and regeneration after melphalan. Br J Cancer 52:733–737
Luck MS, Bass P (1993) Effect of epidermal growth factor on experimental colitis in the rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 264:984–990
Huang FS, Kemp CJ, Williams JL et al (2002) Role of epidermal growth factor and its receptor in chemotherapy-induced intestinal injury. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 282:G432–G442
De Jong KP, Stelleman R, Karrenbeld A et al (1998) Clinical relevance of transforming growth factor alpha, epidermal growth factor receptor, p53, and Ki67 in colorectal liver metastases and corresponding primary tumors. Hepatology 28:971–979. doi:10.1002/hep.510280411
Toschi L, Cappuzzo F (2007) Understanding the new genetics of responsiveness to epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Oncologist 12:211–220. doi:10.1634/theoncologist.12-2-211
Petschow BW, Carter DL, Hutton GD (1993) Influence of orally administered epidermal growth factor on normal and damaged intestinal mucosa in rats. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 17:49–58. doi:10.1097/00005176-199307000-00007
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a research grant from VFK Krebsforschung gGmbH in Berlin, Germany.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sukhotnik, I., Shteinberg, D., Ben Lulu, S. et al. Effect of transforming growth factor-alpha on enterocyte apoptosis is correlated with EGF receptor expression along the villus-crypt axis during methotrexate-induced intestinal mucositis in a rat. Apoptosis 13, 1344–1355 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-008-0258-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-008-0258-x