Abstract
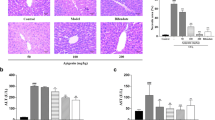
Microcystin-LR (MC-LR) produced by cyanobacteria in diverse water systems is a potent specific hepatotoxin and has been documented to induce various liver diseases via oxidative stress. However, the underlying mechanisms are largely unknown. In the current study, we investigated the molecular events involved in the oxidative liver injury by MC-LR. Our results demonstrated that MC-LR induced liver injury in mice through a series of steps that began with the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS), which stimulated the sustained activation of JNK and its downstream targets, AP-1 and Bid. Furthermore, the mitochondrial proteomic analysis indicated that JNK activation affected some crucial enzymes of energy metabolism, led to mitochondria dysfunction, which contributed to hepatocyte apoptosis and oxidative liver injury by MC-LR. Our results reveal significant insights into the mechanisms of liver injury induced by microcystins, and serve as a framework for deciphering the role of JNK in oxidative stress-associated liver diseases.








Similar content being viewed by others

References
Carmichael WW (1992) Cyanobacteria secondary metabolites-the cyanotoxins. J Appl Bacteriol 72:445–459
Carmichael WW (1997) The cyanotoxins. Adv Bot Res 27:211–256
Rao PV, Gupta N, Bhaskar AS et al (2002) Toxins and bioactive compounds from cyanobacteria and their implications on human health. J Environ Biol 23:215–224
Ueno Y, Nagata S, Tsutsumi T et al (1996) Detection of microcystins, a blue-green algal hepatotoxin, in drinking water sampled in Haimen and Fusui, endemic areas of primary liver cancer in China, by highly sensitive immunoassay. Carcinogenesis 17:1317–1326. doi:10.1093/carcin/17.6.1317
Probert CS, Robinson RJ, Jayanthi V et al (1995) Microcystin hepatitis. Arq Gastroenterol 32:199
Pouria S, Andrade A, Barbosa J et al (1998) Fatal microcystin intoxication in haemodialysis unit in Caruaru, Brazil. Lancet 352:21–26. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(97)12285-1
Chen T, Wang Q, Cui J et al (2005) Induction of apoptosis in mouse liver by microcystin-LR. Mol Cell Proteomics 4:958–974. doi:10.1074/mcp.M400185-MCP200
Weng D, Lu Y, Wei Y et al (2007) The role of ROS in microcystin-LR-induced hepatocyte apoptosis and liver injury in mice. Toxicology 232:15–23. doi:10.1016/j.tox.2006.12.010
Ding WX, Shen HM, Ong CN (2000) Critical role of reactive oxygen species and mitochondrial permeability transition in microcystin-induced rapid apoptosis in rat hepatocyte. Hepatology 32:547–555. doi:10.1053/jhep.2000.16183
Korenaga M, Wang T, Li Y et al (2005) Hepatitis C virus core protein inhibits mitochondrial electron transport and increases reactive oxygen species (ROS) production. J Biochem 280:37481–37488
Waris G, Huh KW, Siddiqui A (2001) Mitochondrially associated hepatitis B virus X protein constitutively activates transcription factors STAT-3 and NF-κB via oxidative stress. Mol Cell Biol 21:7721–7730. doi:10.1128/MCB.21.22.7721-7730.2001
Dey A, Cederbaum AI (2006) Alcohol and oxidative liver injury. Hepatology 43:63–74. doi:10.1002/hep.20957
Gawrieh S, Opara EC, Koch TR (2004) Oxidative stress in nonalcoholic fatty liver diseases: pathogenesis and antioxidant therapies. J Investig Med 52:506–514
Bouchard G, Yousef IM, Barriault C et al (2000) Role of glutathione and oxidative stress in phalloidin-induced cholestasis. J Hepatol 32:550–560. doi:10.1016/S0168-8278(00)80215-9
Stohs SJ (1990) Oxidative stress induced by 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD). Free Radic Biol Med 9:79–90. doi:10.1016/0891-5849(90)90052-K
Shen HM, Liu ZG (2006) JNK signaling pathway is a key modulator in cell death mediated by reactive oxygen and nitrogen species. Free Radic Biol Med 40:928–939. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2005.10.056
Kaneto H, Matsuoka T, Nakatani Y et al (2005) Oxidative stress, ER stress, and the JNK pathway in type 2 diabetes. J Mol Med 83:429–439. doi:10.1007/s00109-005-0640-x
Czaja MJ (2003) The future of GI and liver research: editorial perspectives III. JNK/AP-1 regulation of hepatocyte death. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 284:875–879
Lauricella M, Emanuele S, D’Anneo A et al (2006) JNK and AP-1 mediate apoptosis induced by bortezomib in HepG2 cells via FasL/caspase-8 and mitochondria-dependent pathways. Apoptosis 11:607–625. doi:10.1007/s10495-006-4689-y
Dirsch VM, Kischke SO, Estermeier M et al (2004) Apoptosis signaling triggered by the marine alkaloid ascididemin is routed via caspase-2 and JNK to mitochondria. Oncogene 23:1586–1593. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1207281
Deng Y, Ren X, Yang L et al (2003) A JNK-dependent pathway is required for TNFalpha-induced apoptosis. Cell 115:61–70. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(03)00757-8
Aoki H, Kang PM, Hampe J et al (2002) Direct activation of mitochondrial apoptosis machinery by c-Jun N-terminal kinase in adult cardiac myocytes. J Biochem 277:10244–10250
Tai DI, Tsai SL, Chen YM et al (2000) Activation of nuclear factor B in hepatitis C virus infection: implications for pathogenesis and hepatocarcinogenesis. Hepatology 31:656–664. doi:10.1002/hep.510310316
Feldmann G, Haouzi D, Moreau A et al (2000) Opening of the mitochondrial permeability transition pore causes matrix expansion and outer membrane rupture in Fas-mediated hepatic apoptosis in mice. Hepatology 31:674–683. doi:10.1002/hep.510310318
Masubuchi Y, Nakayama S, Horie T (2002) Role of mitochondrial permeability transition in diclofenac-induced hepatocyte injury in rats. Hepatology 35:544–551. doi:10.1053/jhep.2002.31871
Robert FS, David AB (2006) Mechanisms of liver injury: I. TNF-α-induced liver injury: role of IKK, JNK, and ROS pathways. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 290:583–589. doi:10.1152/ajpgi.00422.2005
Yongjun W, Rajat S, Jay HL et al (2006) Tumor necrosis factor-induced toxic liver injury results from JNK2-dependent activation of caspase-8 and the mitochondrial death pathway. J Biol Chem 281:15258–15267. doi:10.1074/jbc.M512953200
Katsunori Y, Koichi M, Shigeo M et al (2005) Transforming growth factor-β and platelet-derived growth factor signal via c-Jun N-Terminal Kinase-dependent smad2/3 phosphorylation in rat hepatic stellate cells after acute liver injury. Am J Pathol 166:1029–1039
Bennett B, Sasaki D, Murray B et al (2001) SP600125, an anthrapyrazolone inhibitor of Jun N-terminal kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:13681–13686. doi:10.1073/pnas.251194298
Komatsu M, Furukawa T, Ikeda R et al (2007) Involvement of mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathways in microcystin-LR-induced apoptosis after its selective uptake mediated by OATP1B1 and OATP1B3. Toxicol Sci 97:407–416. doi:10.1093/toxsci/kfm054
Ke Z, Lesleyann H, Clement I (2005) Up-regulation of c-Jun-NH2-kinase pathway contributes to the induction of mitochondria-mediated apoptosis by A-tocopheryl succinate in human prostate cancer cells. Mol Cancer Ther 4:43–50
Voisine C, Craig EA, Zufall N et al (1999) The protein import motor of mitochondria: unfolding and trapping of preproteins are distinct and separable functions of matrix hsp70. Cell 97:565–574. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80768-0
Jochimsen EM, Carmichael WW, An JS et al (1998) Liver failure and death after exposure to microcystins at a hemodialysis center in Brazil. N Engl J Med 338:873–878. doi:10.1056/NEJM199803263381304
Yu SZ, Chen G (1994) Blue-green algae toxins and liver cancer. Chin J Cancer Res 6:9–17. doi:10.1007/BF02672256
Yu SZ (1995) Primary prevention of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 10:674–682. doi:10.1111/j.1440-1746.1995.tb01370.x
Ding WX, Shen HM, Ong CN (2001) Pivotal role of mitochondrial Ca2+ in microcystin-induced mitochondrial permeability transition in rat hepatocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 285:1155–1161. doi:10.1006/bbrc.2001.5309
Ding WX, Shen HM, Ong CN (2002) Calpain activation after mitochondrial permeability transition in microcystin-induced cell death in rat hepatocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 291:321–331. doi:10.1006/bbrc.2002.6453
Lemasters JJ, Nieminen AL, Qian T et al (1998) The mitochondrial permeability transition in cell death: a common mechanism in necrosis, apoptosis and autophagy. Biochim Biophys Acta 1366:177–196. doi:10.1016/S0005-2728(98)00112-1
Kamata H, Honda S, Maeda S et al (2005) Reactive oxygen species promote TNFα-induced death and sustained JNK activation by inhibiting MAP kinase phosphatases. Cell 120:649–661. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2004.12.041
Ward M, Rehm M, Duessmann H et al (2006) Real time single cell analysis of bid cleavage and bid translocation during caspase-dependent and neuronal caspase-independent apoptosis. J Biol Chem 281:5837–5844. doi:10.1074/jbc.M511562200
Pei Y, Xing D, Gao X et al (2007) Real-time monitoring full length bid interacting with Bax during TNF-alpha-induced apoptosis. Apoptosis 12:1681–1690. doi:10.1007/s10495-007-0091-7
Behrens A, Sibilia M, Wagner EF (1999) Amino-terminal phosphorylation of c-Jun regulates stress-induced apoptosis and cellular proliferation. Nat Genet 21:326–329. doi:10.1038/6854
Puthalakath H, Strasser A (2002) Keeping killers on a tight leash: transcriptional and post-translational control of the pro-apoptotic activity of BH3-only proteins. Cell Death Differ 9:505–512. doi:10.1038/sj.cdd.4400998
Yin KJ, Lee JM, Chen SD et al (2002) Amyloid-beta induces Smac release via AP-1/Bim activation in cerebral endothelial cells. J Neurosci 22:9764–9770
Harris CA, Johnson EM Jr (2001) BH3-only Bcl-2 family members are coordinately regulated by the JNK pathway and require Bax to induce apoptosis in neurons. J Biol Chem 276:37754–37760
Kuwana T, Bouchier-Hayes L, Chipuk JE et al (2005) BH3 domains of BH3-only proteins differentially regulate Bax-mediated mitochondrial membrane permeabilization both directly and indirectly. Mol Cell 7:525–535. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2005.02.003
Francisconi S, Codenotti M, Toninelli GF et al (2006) Mitochondrial dysfunction and increased sensitivity to excitotoxicity in mice deficient in DNA mismatch repair. J Neurochem 98:223–233. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.2006.03864.x
Ross CD, Godfrey DA (1985) Distributions of aspartate aminotransferase and malate dehydrogenase activities in rat retinal layers. J Histochem Cytochem 33:624–630
Igbavboa U, Zwizinski CW, Pfeiffer DR (1989) Release of mitochondrial matrix proteins through a Ca21-requiring, cyclosporin-sensitive pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 161:619–625. doi:10.1016/0006-291X(89)92644-2
Gurvitz A, Hamilton B, Ruis H et al (2001) Peroxisomal degradation of trans-unsaturated fatty acids in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem 276:895–903. doi:10.1074/jbc.M003305200
Decaux JF, Robin D, Robin P et al (1988) Intramitochondrial factors controlling hepatic fatty acid oxidation at weaning in the rat. FEBS Lett 232:156–158. doi:10.1016/0014-5793(88)80407-1
Acknowledgements
We thank Prof. Ning Su from the School of Basic Medical Sciences, Southeast University, for excellent technical assistance. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Project No. 30571538), the Key Project of Chinese Ministry of Education (No. 107049), the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (No. BK2006120), and the National Basic Research Program of China (No.2006CB910103). The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Yinna Wei and Dan Weng equally contributed to this work.
D. Owen Young—An international exchange student from USA.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wei, Y., Weng, D., Li, F. et al. Involvement of JNK regulation in oxidative stress-mediated murine liver injury by microcystin-LR. Apoptosis 13, 1031–1042 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-008-0237-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-008-0237-2