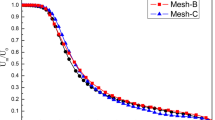
Abstract
Despite the large repository of experimental and computational studies on the topic of turbulent jets, inconclusive and conflicting estimates prevail in regard to certain terms in the turbulence energy budget and the dependence (or lack of dependence) of these and other flow physics on the jet Reynolds number. No comprehensive study exists which adequately addresses these inconsistencies. The purpose of this study is to resolve these contradictions and ascertain the true dependence of the flow statistics on the jet Reynolds number. This is accomplished through high fidelity Large Eddy Simulations (LES), which are performed for a single isothermal round jet at three different Reynolds numbers, encompassing nearly two orders of magnitude. In each case, results are compared to well-accepted experimental and computational studies, and excellent agreement is found with experimental quantities either directly acquired or computed directly from raw data. A separate discrete eddy simulation of the flow in the nozzle upstream of the jet inlet is performed and is found to be crucial in quantifying the flow physics in the near field (e.g., virtual origin). Results show a definite Reynolds number dependence for nearly all third order terms and this is non-negligible especially for the mean convection and production terms in the turbulent kinetic energy budget.





















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Corrsin, S.: Investigation of flow in an axially symmetrical heated jet of air. NACA-WR-W-9 (1943)
Corrsin, S., Kistler, A.L.: Free-stream boundaries of turbulent flows. NACA, Washington, DC (1955)
Corrsin, S.: On the spectrum of isotropic temperature fluctuations in an isotropic turbulence. J. Appl. Phys. 22, 469–473 (1951)
Wygnanski, I., Fiedler, H.: Some measurements in the self-preserving jet. J. Fluid Mech. 38, 577–612 (1969)
Panchapakesan, N., Lumley, J.: Turbulence measurements in axisymmetric jets of air and helium. Part 1. Air jet. J. Fluid Mech. 246, 197–223 (1993)
Hussein, H.J., Capp, S.P., George, W.K.: Velocity measurements in a high-Reynolds-number, momentum-conserving, axisymmetric, turbulent jet. J. Fluid Mech. 258, 31–75 (1994)
Wray, A.: A selection of test cases for the validation of large-eddy simulations of turbulent flows. AGARD Advisory Report. 345 (1998)
Wang, Z., He, P., Lv, Y., Zhou, J., Fan, J., Cen, K.: Direct numerical simulation of subsonic round turbulent jet. Flow Turbul. Combust. 84, 669–686 (2010)
Taub, G., Lee, H., Balachandar, S., Sherif, S.: A direct numerical simulation study of higher order statistics in a turbulent round jet. Phys. Fluids (1994-present) 25, 115102 (2013)
Zuckerman, N., Lior, N.: Jet impingement heat transfer: physics, correlations, and numerical modeling. Adv. Heat Transf. 39, 565–631 (2006)
Garimella, S.V., Rice, R.: Confined and submerged liquid jet impingement heat transfer. J. Heat Transf. 117, 871–877 (1995)
Wang, M., Freund, J.B., Lele, S.K.: Computational prediction of flow-generated sound. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 38, 483–512 (2006)
Wilcox, D.C.: Turbulence modeling for CFD. DCW Industries, La Canada (1998)
Launder, B.E., Sandham, N.D.: Closure Strategies for Turbulent and Transitional Flows. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2002)
Pope, S.B.: Turbulent Flows. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2000)
Sagaut, P.: Large Eddy Simulation for Incompressible Flows. Springer, Berlin (2002)
Dejoan, A., Leschziner, M.A.: Large eddy simulation of a plane turbulent wall jet. Phys. Fluids 17, 025102 (2005)
Bogey, C., Bailly, C.: Turbulence and energy budget in a self-preserving round jet: direct evaluation using large eddy simulation. J. Fluid Mech. 627, 129 (2009)
Bogey, C., Bailly, C.: A study of the influence of the reynolds number on jet self-similarity using Large-Eddy Simulation. In: Direct and Large-Eddy Simulation VII, pp 11–16 (2010)
Gohil, T.B., Saha, A.K., Muralidhar, K.: Large eddy simulation of a free circular jet. J. Fluids Eng. 136, 051205 (2014)
Lipari, G., Stansby, P.K.: Review of experimental data on incompressible turbulent round jets. Flow Turbul. Combust. 87, 79–114 (2011)
Brown, C., Bridges, J.: Small hot jet acoustic rig validation. NASA/TM-2006-214234 (2006)
Mazumdar, S., Landfried, D.T., Jana, A., Kimber, M.: Computational study of confined isothermal turbulent round jets. In: 15th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal hydraulics, Pisa (2013)
Kim, J., Choi, H.: Large eddy simulation of a circular jet: effect of inflow conditions on the near field. J. Fluid Mech. 620, 383 (2009)
Clément, A.: Coupling of two absorbing boundary conditions for 2D time-domain simulations of free surface gravity waves. J. Comput. Phys. 126, 139–151 (1996)
Lysenko, D.A., Ertesvåg, I.S., Rian, K.E.: Large-eddy simulation of the flow over a circular cylinder at Reynolds number 3900 using the OpenFOAM toolbox. Flow Turbul. Combust. 89, 491–518 (2012)
Lysenko, D.A., Ertesvåg, I.S., Rian, K.E.: Large-eddy simulation of the flow over a circular cylinder at Reynolds number 2 × 104. Flow Turbul. Combust. 92, 673–698 (2014)
Salkhordeh, S.: Large eddy simulations of isothermal and non-isothermal turbulent flows for high temperature gas cooled reactors. University of Pittsburgh (2016)
Salkhordeh, S., Mazumdar, S., Landfried, D.T., Jana, A., Kimber, M.L.: LES of an isothermal high reynolds number turbulent round jet. In: 2014 22nd International Conference on Nuclear Engineering, pp. V004T10A48–VT10A48. American Society of Mechanical Engineers (2014)
Vuorinen, V., Keskinen, J.-P., Duwig, C., Boersma, B.: On the implementation of low-dissipative Runge–Kutta projection methods for time dependent flows using OpenFOAM®;. Comput. Fluids 93, 153–163 (2014)
Issa, R.I., Gosman, A., Watkins, A.: The computation of compressible and incompressible recirculating flows by a non-iterative implicit scheme. J. Comput. Phys. 62, 66–82 (1986)
Geurts, B.: Elements of Direct and Large-Eddy Simulation. RT Edwards, Philadelphia (2004)
Lysenko, D.A., Ertesvåg, I.S., Rian, K.E.: Modeling of turbulent separated flows using OpenFOAM. Comput. Fluids 80, 408–422 (2013)
Salkhordeh, S., Clifford, C., Jana, A., Kimber, M.L.: Large Eddy simulations of scaled HTGR lower plenum for assessment of turbulent mixing. Nucl. Eng. Des. 334, 24–41 (2018)
Smagorinsky, J.: General circulation experiments with the primitive equations. I. The basic experiment*. Mon. Weather Rev. 91, 99–164 (1963)
Bogey, C., Bailly, C.: Large eddy simulations of round free jets using explicit filtering with/without dynamic Smagorinsky model. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 27, 603–610 (2006)
Le Ribault, C., Sarkar, S., Stanley, S.A.: Large eddy simulation of a plane jet. Phys. Fluids 11, 3069 (1999)
Fureby, C., Tabor, G., Weller, H., Gosman, A.: A comparative study of subgrid scale models in homogeneous isotropic turbulence. Phys. Fluids (1994-present) 9, 1416–1429 (1997)
Lilly, D.: A proposed modification of the Germano subgrid-scale closure method. Phys. Fluids A: Fluid Dyn. (1989–1993) 4, 633–635 (1992)
Bogey, C., Marsden, O.: Numerical modelling of jets exiting from the ASME and conical nozzles. In: 53rd AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting, p. 0510 (2015)
George, W.K.: The self-preservation of turbulent flows and its relation to initial conditions and coherent structures. In: Advances in Turbulence, pp. 39–73 (1989)
George, W.K.: Asymptotic effect of initial and upstream conditions on turbulence. J. Fluids Eng. 134, 061203 (2012)
Mi, J., Nobes, D.S., Nathan, G.: Influence of jet exit conditions on the passive scalar field of an axisymmetric free jet. J. Fluid Mech. 432, 91–125 (2001)
Xu, G., Antonia, R.: Effect of different initial conditions on a turbulent round free jet. Exp. Fluids 33, 677–683 (2002)
Ricou, F.P., Spalding, D.: Measurements of entrainment by axisymmetrical turbulent jets. J. Fluid Mech. 11, 21–32 (1961)
Boersma, B.J., Brethouwer, G., Nieuwstadt, F.T.M.: A numerical investigation on the effect of the inflow conditions on the self-similar region of a round jet. Phys. Fluids 10, 899 (1998)
Dahm, W.J., Dimotakis, P.E.: Mixing at large Schmidt number in the self-similar far field of turbulent jets. J. Fluid Mech. 217, 299–330 (1990)
Kwon, S.J., Seo, I.W.: Reynolds number effects on the behavior of a non-buoyant round jet. Exp. Fluids 38, 801–812 (2005)
Bogey, C., Bailly, C.: Large eddy simulations of transitional round jets: influence of the Reynolds number on flow development and energy dissipation. Phys. Fluids 18, 065101 (2006)
Fellouah, H., Ball, C.G., Pollard, A.: Reynolds number effects within the development region of a turbulent round free jet. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 52, 3943–3954 (2009)
Mi, J., Xu, M., Zhou, T.: Reynolds number influence on statistical behaviors of turbulence in a circular free jet. Phys. Fluids (1994-present) 25, 075101 (2013)
Salkhordeh, S., Kimber, M.: Effect of inflow condition on near-field prediction of Large Eddy Simulations of isothermal and non-isothermal turbulent jets. APS Meeting Abstracts, 2017APS..DFDL31012S (2017)
Han, Y.O., George, W.K., Hjarne, J.: Effect of a contraction on turbulence. Part 1. Experiment. Spectrum 1, 11 (2005)
Spalart, P.R.: Detached-eddy simulation. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 41, 181–202 (2009)
Geurts, B.J, Fröhlich, J.: A framework for predicting accuracy limitations in large-eddy simulation. Phys. Fluids (1994-present) 14, L41–L44 (2002)
Shiri, A., George, W.K., Naughton, J.W.: Experimental study of the far field of incompressible swirling jets. AIAA J. 46, 2002–2009 (2008)
Acknowledgements
This research was performed using funding received from the United States Department of Energy Office of Nuclear Energy’s Nuclear Energy University Programs. The authors are also grateful for the National Science Foundation’s eXtreme Science and Engineering Discovery Environment (XSEDE) supercomputing resources used for most of the computational work required for this study. Additional resources available through the Institute for Scientific Computation at Texas A&M University also made this work possible.
Funding
This research was performed using funding received from the United States Department of Energy Office of Nuclear Energy’s Nuclear Energy University Programs.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Salkhordeh, S., Mazumdar, S., Jana, A. et al. Reynolds Number Dependence of Higher Order Statistics for Round Turbulent Jets Using Large Eddy Simulations. Flow Turbulence Combust 102, 559–587 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10494-018-9971-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10494-018-9971-x