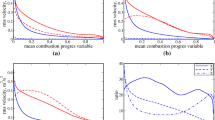
Abstract
Direct numerical simulations (DNS) of flame-vortex interaction are performed to study the effect of fuel composition on premixed flames wrinkling. Flame stretches are deduced from the DNS and compared with phenomenological functions from the literature for a range of vortex characteristics. Such functions, which are used as an input in most flamelet models for premixed combustion, depend on the turbulent scale parameters and the laminar flame properties. Therefore, all mixture related effects are supposed to be described by these latter quantities. However, such an assumption can be restrictive when considering various fuels and especially low Lewis number mixtures. In these conditions, thermo-diffusive instabilities can occur, leading to an increase of the flame wrinkling, which is not correctly described by common stretch models. To overcome this issue, DNS performed in this work integrate a description of chemistry processes through a new 4-steps kinetic scheme dedicated to the combustion of C H 4- H 2 and C 3 H 8- H 2 blends. It is shown that fuel composition effects can at first order be described through the mixture Lewis number, but also that the asymptotic behavior of current stretch functions are not relevant at large turbulent length scales. A new efficiency function for the flame stretch is thus finally proposed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lipatnikov, A., Chomiak, J.: Effects of premixed flames on turbulence and turbulent scalar transport. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 36, 1–102 (2010)
Driscoll, J.: Turbulent premixed combustion: Flamelet structure and its effect on turbulent burning velocities. Prog. Energy Combust Sci. 34(1), 91–134 (2008)
Peters, N.: Turbulent Combustion. Cambridge University Press (2000)
Damköhler, G.: Der einfluder turbulenz auf die flammengeschwindigkeit in gasgemischen. Z Elektrochem 46, 601–52 (1940)
Gülder, O., Smallwood, G., Wong, R., Snelling, D., Smith, R., Deschamps, B.: Flame front surface characteristics in turbulent premixed propane/air combustion. Combust. Flame 120, 407–16 (2000)
Chen, Y., Bilger, R.: Experimental investigation of three dimensional flame front structure in premixed turbulent combustion-i: Hydrocarbon air bunsen flames. Combust. Flame 131, 400–35 (2002)
Filatyev, S., Driscoll, J., Carter, C., Donbar, J.: Measured properties of turbulent premixed flames for model assessment, including burning velocities, stretch rates and surface densities. Combust. Flame 141, 1–21 (2005)
Kobayashi, H., Seyama, K., Hagiwara, H., Ogami, Y.: Burning velocity correlation of methane/air turbulent premixed flames at high pressure and high temperature. Proc. Combust Inst. 30, 82734 (2005)
Wu, M., Kwon, S., Driscoll, J., Faeth, G.: Turbulent premixed hydrogenair flames at high reynolds numbers. Combust. Sci. Technol. 73, 32750 (1990)
Driscoll, J., Gulati, A.: Measurement of various terms in the turbulent kinetic energy balance within a flame and comparison with theory. Combust. Flame 72, 131–52 (1988)
Cheng, R.: Velocity and scalar characteristics of premixed turbulent flames stabilized by weak swirl. Combust. Flame 101, 1–14 (1995)
Cho, P., Law, C., Hertzberg, J., Cheng, R.: Structure and propagation of turbulent premixed flames stabilized in a stagnation flow. Proc. Combust. Inst. 21, 1493–9 (1986)
Lawn, C., Schefer, R.: Scaling of premixed turbulent flames in the corrugated regime. Combust. Flame 146, 180–99 (2006)
Smith, K., Gouldin, F.: Turbulence effects on flame speed and flame structure. AIAA J 11(5), 1243–50 (1979)
Bradley, D., Haq, M., Hicks, R., Kitagawa, T., Lawes, M., Sheppard, C.: Turbulent burning velocity, burned gas distribution, and associated flame surface definition. Combust. Flame 133, 415–30 (2003)
Kido, H., Nakahar, M., Nakashima, K., Hashimoto, J.: Influence of local flame displacement velocity on turbulent burning velocity. Proc. Combust. Inst. 29, 1855–61 (2002)
Shepherd, I., Cheng, R.: The burning rate of premixed flames in moderate and intense turbulence. Combust. Flame 127, 2066–75 (2001)
Bradley, D., Lau, A., Lawes, M.: Flame stretch rate as a determinant of turbulent burning velocity. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond., 338–359 (1992)
Kobayashi, H., Nakashima, T., Tamura, T., Maruta, K., Niioka, T.: Turbulence measurements and observations of turbulent premixed flames at elevated pressures up to 3.0 mpa. Combust. Flame 108, 104–117 (1997)
Ziegler, M.: Untersuchungen zur ausbreitung stationairer, turbulenter vormischflammen unter besonderer beruicksichtigung bevorzugter diffusion. PhD thesis, University of Karlsruhe (1998)
Zimont, V.: Gas premixed combustion at high turbulence. turbulent flame closure combustion model. Exp. Thermal Fluid Sci. 21, 179–86 (2000)
Gülder, O.: Turbulent premixed flame propagation models for different combustion regimes. In: Twenty-third Symposium (International) on Combustion. The Combustion Institute, pp. 743–750 (1990)
Peters, N.: The turbulent burning velocity for large-scale and small-scale turbulence. J. Fluid. Mech. 384, 107–132 (1999)
Lee, T., North, G., Santavicca, D.: Surface properties of turbulent premixed propane/air flames at various lewis numbers. Combust. Flame 93, 445–456 (1993)
Wu, M., Kwon, S., Driscoll, J., Faeth, G.: Preferential diffusion effects on the surface structure of turbulent premixed hydrogen/air flames. Combust. Sci. Technol. 78, 69–96 (1991)
Goix, P., Shepherd, I.: Lewis number effects in turbulent premixed flame structure. Combust. Sci. Technol. 91, 191–206 (1993)
Lipatnikov, A., Chomiak, J.: Molecular transport effects on turbulent flame propagation and structure. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 13, 1–73 (2005)
Eickhoff, H.: Analysis of the turbulent burning velocity. Combust. Flame 128, 347–350 (2002)
Lee, J. G., Lee, T.-W., Nyet, D. A., Santavicca, D. A.: Lewis number effects on premixed flames interacting with turbulent karman vortex streets. Combust. Flame 100, 161–168 (1995)
Baritaud, T., Duclos, J.-M., Fusco, A.: Modelling turbulent combustion and pollutant formation in stratified charge si engine. In: 26th Symposium International on Combustion, pp. 2627–35 (1996)
Colin, O., Benkenida, A., Angelberger, C.: A 3d modeling of mixing and ignition and combustion phenomena in highly stratified gasoline engines. Oil Gas Sci. Technol., 47–62 (2003)
Dahms, R., Drake, M., Fansler, T. D., Kuo, T.-W., Peters, N.: Understanding ignition processes in spray-guided gasoline engines using high-speed imaging and the extended spark-ignition model sparkcimm. Part b: Importance of molecular fuel properties in early flame front propagation. Combust. Flame 158(11), 2245–60 (2011)
Karpov, V., Lipatnikov, A., Zimont, V.: A test of an engineering model of premixed turbulent combustion. Proc. Combust. Inst. 26, 249–57 (1996)
Hawkes, E., Cant, R.: A flame surface density approach to large-eddy simulation of premixed turbulent combustion. Proc. Combus.t Inst. 28, 51–58 (2000)
Richard, S., Colin, O., Vermorel, O., Benkenida, A., Angelberger, C., Veynante, D.: Towards large eddy simulation of combustion in spark ignition engines. Proc. Combust. Inst. 31, 3059–66 (2007)
Fiorina, B., Vicquelin, R., Auzillon, P., Darabiha, N., Gicquel, O., Veynante, D.: A filtered tabulated chemistry model for les of premixed combustion. Combust. Flame 157, 465–75 (2010)
Weller, H. G., Tabor, G., Gosman, A. D., Fureby, C.: Application of a flame-wrinkling les combustion model to a turbulent mixing layer. Proc. Comb. Inst. 27(1), 899–907 (1998)
Colin, O., Ducros, F., Veynante, D., Poinsot, T.: A thickened flame model for large eddy simulations of turbulent premixed combustion. Phys. Fluids 12(7), 1843–1863 (2002)
Richard, S., Bougrine, S., Font, G., Lafossas, F.-A., Berr, F. L.: On the reduction of a 3d cfd combustion model to build a physical 0d model for simulating heat release and knock and pollutants in si engines. Oil Gas Sci. Technol. 64, 223–242 (2009)
Bougrine, S., Richard, S., Veynante, D.: On the combination of complex chemistry with a 0-d coherent flame model to account for the fuel properties in spark ignition engines simulations: Application to methane-air-diluents mixtures, thirty-third international symposium on combustion. Proc. Combust. Inst. 33, 3123–30 (2011)
Candel, S., Poinsot, T.: Flame stretch and the balance equation for the flame surface area. Combust. Sci. Tech. 70, 1–15 (1990)
Matalon, M.: On flame stretch. Combust. Sci. Technol. 31, 169–181 (1983)
Poinsot, T., Veynante, D., Candel, S.: Diagram of premixed turbulent combustion based on direct simulation. In: Proceedings of the 23rd Symposium (International) on Combustion. The Combustion Institute, pp. 561–606 (1990)
Meneveau, C., Poinsot, T.: Stretching and quenching of flamelets in premixed turbulent combustion. Combust. Flame, 311–32 (1991)
Charlette, F., Meneveau, C., Veynante, D.: A power-law flame wrinkling model for les of premixed turbulent combustion. Combust. Flame 131, 159–180 (2002)
Aluri, N. K., Muppala, S., Dinkelacker, F.: Substantiating a fractal-based algebraic reaction closure of premixed turbulent combustion for high pressure and the lewis number effects. Combust. Flame 145, 663–674 (2006)
Law, C., Jomaas, G., Bechtold, J.: Cellular instabilities of expanding hydrogen/propane spherical flames at elevated pressure: Theory and experiment. Proc. Combust. Inst. 30, 159–67 (2005)
Muppala, S., Nakahara, M., Aluri, N., Kido, H., Wena, J., Papalexandris, M.: Experimental and analytical investigation of the turbulent burning velocity of two-component fuel mixtures of hydrogen, methane and propane. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 34, 9258–65 (2009)
Dinkelacker, F., Manickam, B., Muppala, S.: Modelling and simulation of lean premixed turbulent methane/hydrogen/air flames with an effective lewis number approach. Combust. Flame 158, 1742–49 (2011)
Smith, G., Golden, D., Frenklach, M., Moriarty, N., Eiteneer, B., Goldenberg, M., Bowman, C., Hanson, R., Song, S., Gardiner, W., Lissianski, V., Qin, Z.: Gri mech. http://www.me.berkeley.edu/grimech (2000)
Qin, Z., Lissianski, V., Yang, H., Gardiner, W., Davis, S., Wang, H.: Combustion chemistry of propane: a case study of detailed reaction mechanism optimization. Proc. Comb. Inst. 28, 1663–69 (2000)
Conaire, M., Curran, H., Simmie, J., Pitz, W., Westbrook, C.: A comprehensive modeling study of hydrogen oxidation. Int. J. Chem. Kin. 36(11), 603–622 (2004)
Clarke, A., Stone, R., Beckwith, P.: Measuring the laminar burning velocity of methane/diluent/air mixtures within a constant-volume combustion bomb in a micro-gravity environment. J. Inst. Energy 68, 13036 (1995)
Poinsot, T., Veynante, D.: Theoretical and Numerical Combustion. Edwards (2001)
Jones, W., Lindset, R.: Global reaction schemes for hydrocarbon combustion. Combust. Flame 73, 233–49 (1988)
Williams, F: Combustion Therory 2nd edn (1985)
Ribert, G., Gicquel, O., Darabiha, N., Veynante, D.: Tabulation of complex chemistry based on self-similar behaviour of laminar premixed flames. Combust. Flame 146(4), 649–64 (2006)
Moureau, V., Lartigue, G., Sommerer, Y., Angelberger, C., Colin, O., Poinsot, T.: Numerical methods for unsteady compressible multi-component reacting flows on fixed and moving grids. J. Comput. Phys. 202(2), 710–736 (2005)
Paul, R., Bray, K.: Study of premixed turbulent combustion including landau-darrieus instability effects. Symp. Int. Combust. 26(1), 259–266 (1996)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bougrine, S., Richard, S., Colin, O. et al. Fuel Composition Effects on Flame Stretch in Turbulent Premixed Combustion: Numerical Analysis of Flame-Vortex Interaction and Formulation of a New Efficiency Function. Flow Turbulence Combust 93, 259–281 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10494-014-9546-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10494-014-9546-4