Abstract
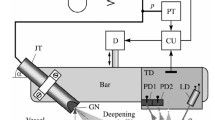
This paper presents an improved experimental setup for the contactless flow rate measurement in a weakly electrically conducting fluid on the base of Lorentz force velocimetry (LFV) and discusses the measurement results. The new setup embodies major improvements over the setup reported in Wegfraß et al. (Appl Phys Lett 100:194103, 2012). This measurement setup consists of a newly designed fluid channel with well defined flow profiles – a plug profile at the inlet and quasi parabolic profile at the outlet of the test section. Another improvement is the force measurement system which is based on electromagnetic force compensation (EMC). Furthermore an optimized Halbach array is used as a magnet system. The results of our measurements confirm the feasibility of LFV in a model fluid (salt water) with conductivities less than 10 Sm − 1 and demonstrate that the optimized magnet system increases the measurement signal. The used force measurement system had to be particularly calibrated for this purpose, so that in combination with the new magnet system design a three times higher signal resolution for the fluid velocity under laboratory conditions was achieved.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baker, R.C.: An Introductory Guide to Flow Measurement. Wiley, New York (2002)
Shercliff, J.A.: The Theory of Electromagnetic Flow-Measurement. Cambridge University Press, Cambrigde (1962)
Thess, A., Votyakov, E., Knaepen, B., Zikanov, O.: Theory of the Lorentz force flow meter. New J. Phys. 9, 299 (2007)
Minchenya, V., Karcher, C., Kolesnikov, Y., Thess, A.: Dry calibration of the Lorentz force flowmeter. Magnetohydrodynamics 45(4), 569 (2009)
Kolesnikov, Y., Karcher, C., Thess, A.: Lorentz force flowmeter for aluminum – laboratory experiments and plant tests. Met. Trans. B. 42B, 441–450 (2011)
Priede, J., Buchenau, D., Gerbeth, G.: Single-magnet rotary flowmeter for liquid metals. J. Appl. Phys. 110, 034512 (2011)
Wegfraß, A., Diethold, C., Werner, M., Fröhlich, T., Halbedel, B., Hilbrunner, F., Resagk, C., Thess, A.: A universal noncontact flowmeter for liquids. Appl. Phys. Lett. 100, 194103 (2012)
Wegfraß, A., Diethold, C., Werner, M., Resagk, C., Fröhlich, T., Halbedel, B., Thess, A.: Flow rate measurement of weakly conducting fluids using Lorentz force velocimetry. Meas. Sci. Technol. 23, 105307 (2012)
Werner, M., Halbedel, B.: Optimization of NdFeB magnet arrays for improvement of Lorentz force velocimetry. IEEE Trans. Magnet. 48, 11 (2012)
Werner, M., Halbedel, B.: Assembling and test of a Halbach array magnet system for Lorentz force velocimetry. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 19(Supplement 1–2), 145–148 (2012)
Diethold, C., Hilbrunner, F.: Force measurement system of low forces with high dead loads. Meas. Sci. Technol. 23, 074017 (2012)
Evaluation of measurement data - Guide to the expression of uncertainty in measurement. Joint Commitee for Guides in Metrology, JCGM 100 (2008)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Halbedel, B., Resagk, C., Wegfrass, A. et al. A Novel Contactless Flow Rate Measurement Device for Weakly Conducting Fluids Based on Lorentz Force Velocimetry. Flow Turbulence Combust 92, 361–369 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10494-013-9505-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10494-013-9505-5