Abstract
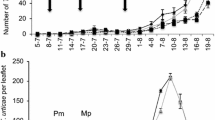
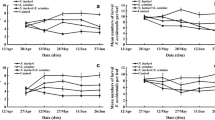
The compatibility of the selective insecticide spinosad (Conserve SC®), at rates recommended for thrips control in greenhouses, with release of the predatory mite Phytoseiulus persimilis Athias-Henriot (Acari: Phytoseiidae) to control spider mites, was investigated in a crop of ivy geranium Pelargonium peltatum, cultivar ‘Amethyst 96.’ Plants were inoculated with twospotted spider mites, Tetranychus urticae Koch (Acari: Tetranychidae), 2 weeks before treatments were applied. There were three treatment variables, each at two levels: predators (released or not), spray application (water or Conserve SC® at 2 ml/3.79 l), and timing of spray (1 day before or after predators were released). Twospotted spider mite populations then were sampled twice each week over a three-week period. The application or timing of spinosad had no effect on the ability of the predator to reduce the population of spider mites. Spider mite populations in the no-predator treatment continued to expand over the course of the experiment, while those in the predator-release treatment declined. We conclude that P. persimilis can be used in conjunction with spinosad on ivy geraniums without causing obvious detrimental effects to this predator or leading to a reduction in biological control.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
T. Burnett (1979) ArticleTitleAn acarine predator–prey population infesting roses Res. Population Ecol. 20 227–234
D.A. Chant (1961) ArticleTitleAn experiment in biological control of Tetranychus telarius (L.) (Acarina: Tetranychidae) in a greenhouse using the predacious mite Phytoseiulus persimilis Athias-Henriot (Phytoseiidae) Can. Entomol. 93 437–443
R.A. Cloyd C.S. Sadof (2000) ArticleTitleEffects of spinosad and acephate on western flower thrips inside and outside a greenhouse HortTechnology 10 359–362 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXivVegsrY%3D
K.W. Cote E.L. Edwin P.B. Schultz (2002) ArticleTitleCompatibility of acaricide residues with Phytoseiulus persimilistheir effects on Tetranychus urticae HortScience 37 906–909 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XovVCluro%3D
K.W. Cote P.B. Schultz E.E. Lewis (2004) ArticleTitleUsing acaricides in combination with Phytoseiulus persimis Athias-Henriot to suppress Tetranychus urticae Koch populations J. Entomol. Sci. 39 267–274 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2cXlvFOmtLY%3D
D.R. Gillespie D.A. Raworth (2004) Biological control of two-spotted spider mites on greenhouse vegetable crops Kevin M. Heinz Roy G. Driesche ParticleVan Michael P. Parrella (Eds) Biocontrol in Protected Culture Ball Publishing Batavia, IL 185–199
N. Gough (1991) ArticleTitleLong-term stability in the interaction between Tetranychus urticae and Phytoseiulus persimilis producing successful integrated control on roses in southeast Queensland Exp. Appl. Acarol. 12 83–101 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF01204402
H.J. Gould W.I. St. G. Light (1971) ArticleTitleBiological control of Tetranychus urticae on stock plants of ornamental ivy Plant Pathol. 20 18–20
R.A. Hamlen (1978) ArticleTitleBiological control of spider mites on greenhouse ornamentals using predaceous mites Proc. Florida State Hort. Soc. 91 247–249
S.A. Hassan P.A. Oomen (1985) Testing the side effects of pesticides on beneficial organisms by OILB Working Party N.W. Hussey N. Scopes (Eds) Biological Pest Control – The Glasshouse Experience Blandford Press PooleDorset, UK 145–152
S.A. Hassan P.A. Oomen W.P.J. Overmeer P. Plovoets J.N. Reboulet W. Rieckmann L. Samsoe-Peterson S.W. Shires A. Stäubli J. Stevenson J.J. Tuset G. Vanwetswinkel A.Q. Zon Particlevan (1985) ArticleTitleStandard methods to test the side-effects of pesticides on natural enemies of insects and mites developed by the IOBC/WPRS Working Group “Pesticides and Beneficial Organisms” OEPP/EPPO Bull. 15 IssueID2 213–256
A. Kropczynska A. Pilko A. Witul Al. Mabrouk Asshleb (1999) ArticleTitleControl of two-spotted spider mite with Amblyseius californicus on croton IOBC/WPRS Bull. 22 IssueID1 133–136
R.K. Lindquist M.L. Wolgamott (1980) ArticleTitleToxicity of acephate to Phytoseiulus persimilis and Tetranychus urticae Environ. Entomol. 9 389–392 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL3MXhtVCr
P.A. Oomen (1988) ArticleTitleGuideline for the evaluation of side-effects of pestcides on Phytoseilus persimilis OEPP/EPPO Bull. 11 IssueID4 51–64
P.A. Oomen G. Romeijn G.L. Wiegers (1991) ArticleTitleSide effects of 100 pesticides on the predatory mite Phytoseiulus persimiliscollected and evaluated according to the EPPO guideline OEPP/EPPO Bull. 21 IssueID4 701–712
G.P. Opit D.C. Margolies J.R. Nechols (2003) ArticleTitleWithin-plant distribution of twospotted spider miteTetranychus urticae Koch (Acari: Tetranychidae), on ivy geranium: development of a presence–absence sampling plan J. Econ. Entomol. 96 482–488 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD2c7gsVGlsg%3D%3D Occurrence Handle14994819
G.P. Opit J.R. Nechols D.C. Margolies (2004) ArticleTitleBiological control of twospotted spider mites, Tetranychus urticae Koch (Acari: Tetranychidae), using Phytoseiulus persimilis Athias-Henriot (Acari: Phytoseidae) on ivy geranium: assessment of predator release ratios Biol. Control 29 445–452 Occurrence Handle10.1016/j.biocontrol.2003.08.007
P.D. Pratt B.A. Croft (2000) ArticleTitleToxicity of pesticides registered for use in landscape nurseries to the acarine biological control agentNeoseiulus fallacies J. Environ. Hort. 18 197–201
K.L. Robb M.P. Parrella (1999) Western flower thrips, a serious pest of floricultural crops B.L. Parker M. Skinner T. Lewis (Eds) Toward Understanding the Thysanoptera General technical report NE-147 USDA Forest Service Radnot, Pennsylvania, USA 343–358
L. Samsoe-Peterson (1983) ArticleTitleLaboratory method for testing side effects of pesticides on juvenile stages of the predatory mitePhytoseiulus persimilis (AcarinaPhytoseiidae) based on detached bean leaves Entomophaga 28 167–178
InstitutionalAuthorNameSAS (2001) SAS/STAT Software Version 8.1 SAS Institute Inc. Cary, NC
S.P. Simmonds (1972) ArticleTitleObservations on the control of Tetranychus urticae on roses by Phytoseiulus persimilis Plant Pathol. 21 163–165
J.D. Stark J.E. Banks (2003) ArticleTitlePopulation-level effects of pesticides and other toxicants on arthropods Annu. Rev. Entomol. 48 505–519 Occurrence Handle10.1146/annurev.ento.48.091801.112621 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXnvVyksA%3D%3D Occurrence Handle12221038
J.D. Stark P.C. Jepson D.F. Mayer (1995) ArticleTitleLimitations to use of topical toxicity data for predictions of pesticide side effects in the field J. Econ. Entomol. 88 1081–1088 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2MXovFSqurY%3D
G. Sterk G. Vanwetswinkel (1988) ArticleTitleA semi-field method for testing the side-effects on the predatory mite Phytoseiulus persimilis A.H. (PhytoseiidaeAcari) IOBC/WPRS Bull. 11 IssueID4 135–136
T. Williams J. Valle E. Viñuela (2003) ArticleTitleIs the naturally derived insecticide spinosad compatitible with insect natural enemies? Biocontrol Sci. Technol. 13 459–475 Occurrence Handle10.1080/0958315031000140956
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Holt, K.M., Opit, G.P., Nechols, J.R. et al. Testing for Non-target Effects of Spinosad on Twospotted Spider Mites and their Predator Phytoseiulus persimilis under Greenhouse Conditions. Exp Appl Acarol 38, 141–149 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10493-006-0018-y
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10493-006-0018-y