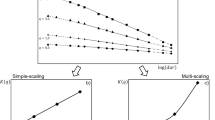
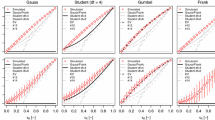
Abstract
Durations of rain events and drought events over a given region provide important information about the water resources of the region. Of particular interest is the shape of upper tails of the probability distributions of such durations. Recent research suggests that the underlying probability distributions of such durations have heavy tails of hyperbolic type, across a wide range of spatial scales from 2 km to 120 km. These findings are based on radar measurements of spatially averaged rain rate (SARR) over a tropical oceanic region. The present work performs a nonparametric inference on the Pareto tail-index of wet and dry durations at each of those spatial scales, based on the same data, and compares it with conclusions based on the classical Hill estimator. The results are compared and discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. J. Adler, R. E. Feldman, M. S. Taqqu (eds.): A Practical Guide to Heavy Tails. Statistical Techniques and Applications. Birkhäuser, Boston, 1998.
S. Cheng, J. Pan: Asymptotic expansions of estimators for the tail index with applications. Scand. J. Stat. 25 (1998), 717–728.
S. Cheng, L. Peng: Confidence intervals for the tail index. Bernoulli 7 (2001), 751–760.
L. de Haan, U. Stadtmüller: Generalized regular variation of second order. J. Austr. Math. Soc., Ser. A 61 (1996), 381–395.
C. De Michele, H. Pavlopoulos: The variance-scale plot of intermittent time series and the ranges of scales. Preprint of working paper. 2007.
P. Doukhan, G. Oppenheim, M. S. Taqqu (eds.): Theory and Applications of Long-Range Dependence. Birkhäuser, Boston, 2003.
P. Embrechts, C. Klüppelberg, T. Mikosch: Modelling Extremal Events for Insurance and Finance. Springer, Berlin, 1997.
E. Foufoula-Georgiou: On scaling theories of space-time rainfall: Some recent results and open problems. Stochastic Methods in Hydrology: Rainfall, Landforms and Floods. Advanced Series on Statistical Sciences and Applied Probability, Vol. 7 (O. E. Barndorff-Nielsen, V. K. Gupta, V. Perez-Abreu, E. C. Waymire, eds.). World Scientific, Singapore, 1998, pp. 129–171.
J. Gritsis: On the probability distribution of the duration of dry and wet spells in processes of spatially averaged rain rate. Master thesis. Department of Statistics, Athens University of Economics and Business, Athens, 1997.
V. K. Gupta: Emergence of statistical scaling in floods on channel networks from complex runoff dynamics. Chaos Solitons Fractals 19 (2004), 357–365.
V. K. Gupta, E. C. Waymire: Multiscaling properties of spatial rainfall and river flow distributions. J. Geophys. Res. 95 (1990), 1999–2009.
V. K. Gupta, E. C. Waymire: A statistical analysis of mesoscale rainfall as a random cascade. J. Appl. Meteorology 32 (1993), 251–267.
V. K. Gupta, E. C. Waymire: Spatial variability and scale invariance in hydrologic regionalization. In: Scale Dependence and Scale Invariance in Hydrology (G. Sposito, ed.). Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 1998, pp. 88–135.
E. Haeusler, J. Segers: Assessing confidence intervals for the tail index by Edgeworth expansions for the Hill estimator. Bernoulli 13 (2007), 175–194.
D. Heath, S. Resnick, G. Samorodnitsky: Heavy tails and long range dependence in on/off processes and associated fluid models. Math. Oper. Res. 23 (1998), 145–165.
J. Jurečková: Tests of tails based on extreme regression quantiles. Stat. Probab. Lett. 49 (2000), 53–61.
J. Jurečková: Statistical tests on tail index of a probability distribution. METRON—International Journal of Statistics LXI (2003), 151–190.
J. Jurečková, H. L. Koul, J. Picek: Testing the tail index in autoregressive models. Annals of the Institute of Statistical Mathematics. To appear. Published online: 10.1007/s10463-007-0155-z.
J. Jurečková, J. Picek: A class of tests on the tail index. Extremes 4 (2001), 165–183.
J. Jurečková, J. Picek: Estimates of the tail index based on nonparametric tests. Theory and Applications of Recent Robust Methods. Series: Statistics for Industry and Technology (M. Hubert, G. Pison, A. Struyf, S. Van Aelst, eds.). Birkhäuser, Basel, 2004, pp. 141–152.
B. Kedem, L. S. Chiu: Are rain rate processes self similar? Water Resources Research 23 (1987), 1816–1818.
P. K. Kundu, T. L. Bell: A stochastic model of space-time variability of mesoscale rainfall: Statistics of spatial averages. Water Resources Research 39 (2003), 1328, doi:10.1029/2002WR001802.
S. Lovejoy, B. B. Mandelbrot: Fractal properties of rain and a fractal model. Tellus 37A (1985), 209–232.
S. Lovejoy, D. Schertzer: Generalized scale invariance in the atmosphere and fractal models of rain. Water Resources Research 21 (1985), 1233–1250.
S. Lovejoy, D. Schertzer: Multifractals and rain. New Uncertainty Concepts in Hydrology and Water Resources (Z. W. Kunzewicz, ed.). Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 1995.
S. B. Lowen, M. C. Teich: Fractal renewal processes generate 1/f noise. Phys. Rev. E 47 (1993), 992–1001.
S. B. Lowen, M. C. Teich: Fractal-Based Point Processes. Wiley Series in Probability and Statistics. John Wiley & Sons, Hoboken, 2005.
B. B. Mandelbrot: The Fractal Geometry of Nature. W. H. Freeman, San Francisco, 1982.
D. Marsan, S. Lovejoy, D. Schertzer: Causal space-time multifractal processes: Predictability and forecasting of rain fields. J. Geophys. Res. 101(D21) (1996), 26333–26346.
T. Over, V. K. Gupta: Statistical analysis of meso-scale rainfall: Dependence of a random cascade generator on large-scale forcing. J. Appl. Meteor. 33 (1994), 1526–1542.
T. Over, V. K. Gupta: A space-time theory of mesoscale rainfall using random cascades. J. Geophys. Res. 101 (1996), 26319–26331.
H. Pavlopoulos, J. Gritsis: Wet and dry epoch durations of spatially averaged rain rate, their probability distributions and scaling properties. Environ. Ecol. Stat. 6 (1999), 351–380.
H. Pavlopoulos, V. K. Gupta: On the intermittence of rainfields: A space-time approach. Technical Report No. 143. Department of Statistics, Athens University of Economics, Athens, 2001.
H. Pavlopoulos, V. K. Gupta: Scale invariance of regional wet and dry durations of rain fields: A diagnostic study. J. Geophys. Res. 108(D8) (2003), 8387, doi:10.1029/2002JD002763.
J. Picek: Confidence intervals of the tail index. In: Proceedings in Computational Statistics (A. Rizzi, M. Vichi, eds.). Physica, Heidelberg, 2006, pp. 1301–1308.
J. Picek, J. Jurečková: A class of tests on the tail index using the modified extreme regression quantiles. ROBUST’2000 (J. Antoch, G. Dohnal, eds.). Union of Czech Mathematicians and Physicists, Prague, 2001, pp. 217–226.
F. Schmitt, S. Svannistsem, A. Barbosa: Modeling of rainfall time series using two-state renewal processes and multifractals. J. Geophys. Res. 103(D18) (1998), 181–194.
D. A. Short, P. A. Kucera, B. S. Ferrier, J. C. Gerlach, S. A. Rutledge, O. W. Thiele: Shipboard radar rainfall patterns within the TOGA/COARE IFA. Bull. Am. Meteor. Soc. 78 (1997), 2817–2836.
M. S. Taqqu, J. B. Levy: Using renewal processes to generate long-range dependence and high variability. Dependence in Probability and Statistics (E. Eberlein, M. S. Taqqu, eds.). Birkhäuser, 1986, pp. 73–89.
Y. Tessier, S. Lovejoy, D. Schertzer: Universal multifractals: Theory and observations of rain and clouds. J. Appl. Meteor. 32 (1993), 223–250.
W. Willinger, M. S. Taqqu, R. Sherman, D. V. Wilson: Self-similarity through high variability: Statistical analysis of Ethernet LAN traffic at the source level (Extended Version). IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking 5 (1997), 71–86.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The authors express sincere thanks to the Mathematisches Forschungsinstitut Oberwolfach (MFO) for facilitating their collaboration under a “Research in Pairs” project hosted at MFO during March 5–25, 2006. The research of the second and third authors was supported by the project LC06024.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pavlopoulos, H., Picek, J. & Jurečková, J. Heavy tailed durations of regional rainfall. Appl Math 53, 249–265 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10492-008-0008-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10492-008-0008-y