Abstract
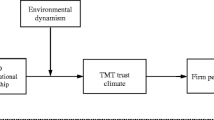
This study examines the inner influencing mechanism and boundary conditions of the association between CEO relationship-focused leadership behaviors and organizational performance. Using data from top managers, HR directors, and operational level employees at 286 companies in seven provinces of China, this paper finds that CEO relationship-focused leadership behaviors have a positive effect on organizational performance. Specifically, CEO relationship-focused leadership behaviors relate directly and positively to firm performance in organically-structured firms and indirectly and positively to firm performance in mechanistically-structured firms via the chain-mediating role of employee relations climate and employees’ attitudes. The findings offer theoretical contributions to the leadership and employee relations climate literature and provide practical value to Chinese enterprises.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ambrose, M. L., & Schminke, M. 2003. Organization structure as a moderator of the relationship between procedural justice, interactional justice, perceived organizational support, and supervisory trust. Journal of Applied Psychology, 88(2): 295–305.
Aryee, S., Sun, L. Y., Chen, Z. X. G., & Debrah, Y. A. 2008. Abusive supervision and contextual performance: The mediating role of emotional exhaustion and the moderating role of work unit structure. Management and Organization Review, 4(3): 393–411.
Barkema, H. G., Chen, X. P., George, G., Luo, Y., & Tsui, A. 2015. West meets East: New concepts and theories. Academy of Management Journal, 58(2): 460–479.
Bass, B. M. 1990. Handbook of leadership: A survey of theory and research. New York: Free Press.
Blau, P. M. 1964. Exchange and power in social life. New York: John Wiley.
Böhm, S. A., Dwertmann, D. J. G., Bruch, H., & Shamir, B. 2015. The missing link? Investigating organizational identity strength and transformational leadership climate as mechanisms that connect CEO charisma with firm performance. Leadership Quarterly, 26(2): 156–171.
Boone, C., & Van Witteloostijn, A. 2007. Individual-level heterogeneity and macro-level outcomes. Strategic Organization, 5: 259–270.
Carmeli, A., Gelbard, R., & Gefen, D. 2010. The importance of innovation leadership in cultivating strategic fit and enhancing firm performance. Leadership Quarterly, 21(3): 339–349.
Carmeli, A., Tishler, A., & Edmondson, A. C. 2012. CEO relational leadership and strategic decision quality in top management teams: The role of team trust and learning from failure. Strategic Organization, 10(1): 31–54.
Carter, S. M., & Greer, C. R. 2013. Strategic leadership values, styles, and organizational performance. Journal of Leadership and Organizational Studies, 20(4): 375–393.
Chen, X. P., & Farh, J. L. 1999. The effectiveness of transactional and transformational leader behaviors in Chinese organizations: Evidence from Taiwan. Chicago: Annual meeting of the Academy of Management.
Chen, Y., Tang, G., Jin, J., Xie, Q., & Li, J. 2014. CEOs’ transformational leadership and product innovation performance: The roles of corporate entrepreneurship and technology orientation. Journal of Product Innovation Management, 31(S1): 2–17.
Colbert, A. E., Kristof-Brown, A. L., & Barrick, M. R. 2008. CEO transformational leadership: The role of goal importance congruence in top management team. Academy of Management Journal, 51(1): 81–96.
Covin, J. G., & Slevin, D. P. 1988. The influence of organization structure on the utility of an entrepreneurial top management style. Journal of Management Studies, 25(3): 217–234.
Eisenbeiss, S. A., Van Knippenberg, D., & Fahrbach, C. M. 2015. Doing well by doing good? Analyzing the relationship between CEO ethical leadership and firm performance. Journal of Business Ethics, 128(3): 635–651.
Espedal, B., Kvitastein, O., & Grønhaug, K. 2012. When cooperation is the norm of appropriateness: How does CEO cooperative behavior affect organizational performance? British Journal of Management, 23(2): 257–271.
Farh, J. L., & Cheng, B. S. 2000. A cultural analysis of paternalistic leadership in Chinese organizations. In J. T. Li, A. S. Tsui, & E. Weldon (Eds.). Management and organizations in the Chinese context: 84–127. London: Palgrave Macmillan.
Farh, J. L., Zhong, C. B., & Organ, D. W. 2004. Organizational citizenship behavior in the People’s Republic of China. Organization Science, 15(2): 241–253.
Ferris, G. R., Arthur, M. M., Berkson, H. M., Kaplan, D. M., Harrell-Cook, G., & Frink, D. D. 1998. Toward a social context theory of the human resource management organization effectiveness relationship. Human Resource Management Review, 8(3): 235–264.
Fleishman, E. A. 1973. Twenty years of consideration and structure. In E. A. Fleishman, & J. G. Hunt (Eds.). Current developments in the study of leadership: 1–40. Carbondale: Southern Illinois University Press.
Halpin, A. W. 1957. Manual for the leader behavior description questionnaire. Columbus: Bureau of Business Research, Ohio State University.
Hambrick, D. C. 2007. Upper echelons theory: An update. Academy of Management Review, 32(2): 334–343.
Hambrick, D. C., & Finkelstein, S. 1987. Managerial discretion: A bridge between polar views of organizational outcomes. Research in Organizational Behavior, 9: 369–406.
Hambrick, D. C., & Mason, P. A. 1984. Upper echelons: The organization as a reflection of its top managers. Academy of Management Review, 9(2): 193–206.
Hart, S. L., & Quinn, R. E. 1993. Roles executives play: CEOs, behavioral complexity, and firm performance. Human Relations, 46(5): 543–574.
Harter, J. K., Schmidt, F. L., & Hayes, T. L. 2002. Business-unit-level relationship between employee satisfaction, employee engagement, and business outcomes: A meta-analysis. Journal of Applied Psychology, 87(2): 268–279.
Hofstede, G. H. 2001. Culture’s consequences: Comparing values, behaviors, institutions and organizations across nations. Thousand Oaks: Sage.
James, L. R. 1982. Aggregation bias in estimates of perceptual agreement. Journal of Applied Psychology, 67(2): 219–229.
James, L. R., Demaree, R. G., & Wolf, G. 1984. Estimating within-group interrater reliability with and without response bias. Journal of Applied Psychology, 69: 85–98.
Jiang, K., Lepak, D. P., Hu, J., & Baer, J. C. 2012. How does human resource management influence organizational outcomes? A meta-analytic investigation of mediating mechanisms. Academy of Management Journal, 55(6), 1264–1294.
Jing, H. 2006. Study on the relationships among leadership style, market orientation and learning orientation. Science of Science and Management of S. & T., 27(7): 131–135.
Judge, T. A., Piccolo, R. F., & Ilies, R. 2004. The forgotten ones? The validity of consideration and initiating structure in leadership research. Journal of Applied Psychology, 89(1): 36–51.
Khandwalla, P. N. 1977. The design of organizations. New York: Harcourt, Brace, Jovanovich.
Kline, R. B. 2005. Principles and practice of structural equation modeling, 2nd ed. New York: Guilford.
Kozlowski, S. W., & Doherty, M. L. 1989. Integration of climate and leadership: Examination of a neglected issue. Journal of Applied Psychology, 74(4): 546–553.
Kuenzi, M., & Schminke, M. 2009. Assembling fragments into a lens: A review, critique, and proposed research agenda for the organizational work climate literature. Journal of Management, 35(3): 634–717.
Leung, K. 2012. Indigenous Chinese management research: Like it or not, we need it. Management and Organization Review, 8(1): 1–5.
Lin, Y., & Zhao, S. 2013. A study of network-building HR practices for TMT, strategic flexibility and firm performance: The moderating role of environmental uncertainty. Nankai Business Review, 16(2): 4–15.
Little, T. D., Cunningham, W. A., Shahar, G., & Widaman, K. F. 2002. To parcel or not to parcel: Exploring the question, weighing the merits. Structural Equation Modeling, 9: 151–173.
MacMahon, J. 1996. Employee relations in small firms in Ireland: An exploratory study of small manufacturing firms. Employee Relations, 18(5): 66–80.
Meyer, J. P., & Allen, N. J. 1997. Commitment in the workplace: Theory, research, and application. Thousand Oaks: Sage.
Muthén, L. K., & Muthén, B. O. 1998–2015. Mplus user’s guide, 7th ed. Los Angeles: Muthén & Muthén.
Ngo, H. Y., Lau, C. M., & Foley, S. 2008. Strategic human resource management, firm performance, and employee relations climate in China. Human Resource Management, 47(1): 73–90.
Northouse, P. G. 1997. Leadership: Theory and practice. Thousand Oaks: Sage.
Ostroff, C. 1992. The relationship between satisfaction, attitudes, and performance: An organizational level analysis. Journal of Applied Psychology, 77(6): 963–974.
Parthasarthy, R., & Sethi, S. P. 1993. Relating strategy and structure to flexible automation: A test of fit and performance implications. Strategic Management Journal, 14(7): 529–549.
Preacher, K. J., Rucker, D. D., & Hayes, A. F. 2007. Assessing moderated mediation hypotheses: Theory, methods, and prescriptions. Multivariate Behavioral Research, 42: 185–227.
Resick, C. J., Whitman, D. S., Weingarden, S. M., & Hiller, N. J. 2009. The bright-side and the dark-side of CEO personality: Examining core self-evaluations, narcissism, transformational leadership, and strategic influence. Journal of Applied Psychology, 94(6): 1365–1381.
Riordan, C. M., Vandenberg, R. J., & Richardson, H. A. 2005. Employee involvement climate and organizational effectiveness. Human Resource Management, 44(4): 471–488.
Ryan, A., Schmit, M. J., & Johnson, R. 1996. Attitudes and effectiveness: Examining relations at an organizational level. Personnel Psychology, 49(4): 853–882.
Schleicher, D. J., Watt, J. D., & Greguras, G. J. 2004. Reexamining the job satisfaction-performance relationship: The complexity of attitudes. Journal of Applied Psychology, 89(1): 165–177.
Schumacker, R. E., & Lomax, R. G. 1996. A beginner’s guide to structural equation modeling. Mahwah: Lawrence Erlbaum.
Schuster, F. E. 1982. A tool for evaluating and controlling the management of human resources. Personnel Administrator, 27: 63–69.
Schuster, F. E. 1998. Employee-centered management: A strategy for high commitment and involvement. Westport: Quorum Books.
Slevin, D. P., & Covin, J. G. 1997. Strategy formation patterns, performance, and the significance of context. Journal of Management, 23(2): 189–209.
Song, L. J., Zhang, X., & Wu, J. B. 2014. A multilevel analysis of middle manager performance: The role of CEO and top manager leadership. Management and Organization Review, 10(2): 275–297.
Stogdill, R. M. 1950. Leadership, membership and organization. Psychological Bulletin, 47(1): 1–14.
Takeuchi, R., Chen, G., & Lepak, D. P. 2009. Through the looking glass of a social system: Cross-level effects of high-performance work systems on employees’ attitudes. Personnel Psychology, 62(1): 1–29.
Tsui, A. S., & Lau, C. M. 2002. Management of enterprises in the People’s republic of China. Boston: Kluwer Academic.
Tsui, A. S., Schoonhoven, C. B., Meyer, M. W., Lau, C. M., & Milkovich, G. T. 2004. Organization and management in the midst of societal transformation: The People’s Republic of China. Organization Science, 15(2): 133–144.
Waldman, D. A., Ramirez, G. G., House, R. J., & Puranam, P. 2001. Does leadership matter? CEO leadership attributes and profitability under condition of perceived environmental uncertainty. Academy of Management Journal, 44: 134–143.
Wang, D., Tsui, A. S., Zhang, Y., & Ma, L. 2003. Employment relationships and firm performance: Evidence from an emerging economy. Journal of Organizational Behavior, 24(5): 511–535.
Wang, H., Tsui, A. S., & Xin, K. R. 2011. CEO leadership behaviors, organizational performance, and employees’ attitudes. Leadership Quarterly, 22(1): 92–105.
Wang, H., Yi, R., & Tsui, A. S. 2006. CEO leadership behaviors and organizational performance in Chinese enterprises. Management World, 4: 87–96.
Wang, H., & Zhang, C. L. 2012. Leadership behaviors in the Chinese context: CEO leadership behaviors, empowering leadership, and leader-member exchange. Advances in Psychological Science, 20(10): 1519–1530.
Xi, M., & Zhao, S. M. 2013. Economic predicament and countermeasure in the transformation of labor relations: The case of manufacturing industry. East China Economic Management, 27(7): 116–120.
Xu, Y., & Zhao, S. 2011. An empirical study on the relationship of social exchange and economic exchange to affective commitment and turnover intention: Moderating role of leader-member exchange relationship. Science of Science and Management of S. & T., 32(11): 159–165.
Yang, K. S., Yu, A. B., & Yeh, M. H. 1989. Chinese individual modernity and traditionality: Construct definition and measurement. In K. S. Yang, & A. B. Yu (Eds.). Chinese psychology and behavior: 241–306. Taipei: Laureat.
Yukl, G. 2012. Effective leadership behavior: What we know and what questions need more attention. Academy of Management Perspectives, 26(4): 66–85.
Yukl, G., Gordon, A., & Taber, T. 2002. A hierarchical taxonomy of leadership behavior: Integrating a half century of behavior research. Journal of Leadership and Organizational Studies, 9(1): 15–32.
Zhang, W. H, & Wang, H. 2013. The triples of strategic leadership in the Chinese enterprises. Management World, (7): 94–112.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Senior Editor and two anonymous reviewers for their invaluable and insightful comments and suggestions on earlier versions of this manuscript. We also appreciate the feedback and help received from Betty S. Coffey at Walker College of Business, Appalachian State University. The National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 71332002 and No.71172063) supported this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xi, M., Zhao, S. & Xu, Q. The influence of CEO relationship-focused behaviors on firm performance: A chain-mediating role of employee relations climate and employees’ attitudes. Asia Pac J Manag 34, 173–192 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10490-016-9487-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10490-016-9487-7