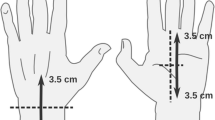
Abstract
Skin conductance responses (SCR) measure objective arousal in response to emotionally-relevant stimuli. Central nervous system influence on SCR is exerted differentially by the two hemispheres. Differences between SCR recordings from the left and right hands may therefore be expected. This study focused on emotionally expressive faces, known to be processed differently by the two hemispheres. Faces depicting neutral, happy, sad, angry, fearful or disgusted expressions were presented in two tasks, one with an explicit emotion judgment and the other with an age judgment. We found stronger responses to sad and happy faces compared with neutral from the left hand during the implicit task, and stronger responses to negative emotions compared with neutral from the right hand during the explicit task. Our results suggest that basic social stimuli generate distinct responses on the two hands, no doubt related to the lateralization of social function in the brain.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baron-Cohen, S., Golan, O., & Ashwin, E. (2009). Can emotion recognition be taught to children with autism spectrum conditions? Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. Series B, Biological Sciences, 364(1535), 3567–3574.
Bechara, A., Tranel, D., Damasio, H., Adolphs, R., Rockland, C., & Damasio, A. R. (1995). Double dissociation of conditioning and declarative knowledge relative to the amygdala and hippocampus in humans. Science, 269(5227), 1115–1118.
Blair, R. J., & Cipolotti, L. (2000). Impaired social response reversal. A case of ‘acquired sociopathy’. Brain: A Journal of Neurology, 123(Pt 6), 1122–1141.
Borod, J. C. (1992). Interhemispheric and intrahemispheric control of emotion: A focus on unilateral brain damage. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 60(3), 339–348.
Borod, J. C., Koff, E., Perlman Lorch, M., & Nicholas, M. (1986). The expression and perception of facial emotion in brain-damaged patients. Neuropsychologia, 24(2), 169–180.
Brand, G., Millot, J. L., & Biju, C. (2000). Comparison between monorhinal and birhinal olfactory stimulations in bilateral electrodermal recordings. Comptes rendus de l’Academie des sciences. Serie III, Sciences de la vie, 323(11), 959–965.
Britton, J. C., Phan, K. L., Taylor, S. F., Welsh, R. C., Berridge, K. C., & Liberzon, I. (2006). Neural correlates of social and nonsocial emotions: An fMRI study. Neuroimage, 31(1), 397–409.
Davidson, R. J., Ekman, P., Saron, C. D., Senulis, J. A., & Friesen, W. V. (1990). Approach-withdrawal and cerebral asymmetry: Emotional expression and brain physiology. I. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 58(2), 330–341.
Davidson, R. A., Fedio, P., Smith, B. D., Aureille, E., & Martin, A. (1992). Lateralized mediation of arousal and habituation: Differential bilateral electrodermal activity in unilateral temporal lobectomy patients. Neuropsychologia, 30(12), 1053–1063.
Gakhal, B., & Senior, C. (2008). Examining the influence of fame in the presence of beauty: An electrodermal ‘neuromarketing’ study. Journal of Consumer Behaviour, 7(4–5), 331–341.
Glascher, J., & Adolphs, R. (2003). Processing of the arousal of subliminal and supraliminal emotional stimuli by the human amygdala. The Journal of Neuroscience: The Official Journal of the Society for Neuroscience, 23(32), 10274–10282.
Gur, R. C., Sara, R., Hagendoorn, M., Marom, O., Hughett, P., Macy, L., et al. (2002). A method for obtaining 3-dimensional facial expressions and its standardization for use in neurocognitive studies. Journal of Neuroscience Methods, 115(2), 137–143.
Habel, U., Windischberger, C., Derntl, B., Robinson, S., Kryspin-Exner, I., Gur, R. C., et al. (2007). Amygdala activation and facial expressions: Explicit emotion discrimination versus implicit emotion processing. Neuropsychologia, 45(10), 2369–2377.
Hariri, A. R., Tessitore, A., Mattay, V. S., Fera, F., & Weinberger, D. R. (2002). The amygdala response to emotional stimuli: A comparison of faces and scenes. Neuroimage, 17(1), 317–323.
Heilman, K. M., Schwartz, H. D., & Watson, R. T. (1978). Hypoarousal in patients with the neglect syndrome and emotional indifference. Neurology, 28(3), 229–232.
Hempel, R. J., Tulen, J. H., van Beveren, N. J., van Steenis, H. G., Mulder, P. G., & Hengeveld, M. W. (2005). Physiological responsivity to emotional pictures in schizophrenia. Journal of Psychiatric Research, 39(5), 509–518.
Hermans, E. J., & van Honk, J. (2006). Toward a framework for defective emotion processing in social phobia. Cognitive Neuropsychiatry, 11(3), 307–331.
Holloway, F. A., & Parsons, O. A. (1969). Unilateral brain damage and bilateral skin conductance levels in humans. Psychophysiology, 6(2), 138–148.
Hubert, B. E., Wicker, B., Monfardini, E., & Deruelle, C. (2009). Electrodermal reactivity to emotion processing in adults with autistic spectrum disorders. Autism: The International Journal of Research and Practice, 13(1), 9–19.
Kimura, Y., Yoshino, A., Takahashi, Y., & Nomura, S. (2004). Interhemispheric difference in emotional response without awareness. Physiology & Behavior, 82(4), 727–731.
Lane, R. D., Reiman, E. M., Bradley, M. M., Lang, P. J., Ahern, G. L., Davidson, R. J., et al. (1997). Neuroanatomical correlates of pleasant and unpleasant emotion. Neuropsychologia, 35(11), 1437–1444.
Lang, P. J., Greenwald, M. K., Bradley, M. M., & Hamm, A. O. (1993). Looking at pictures: affective, facial, visceral, and behavioral reactions. Psychophysiology, 30(3), 261–273.
Mangina, C. A., & Beuzeron-Mangina, J. H. (1996). Direct electrical stimulation of specific human brain structures and bilateral electrodermal activity. International Journal of Psychophysiology, 22(1), 1–8.
Morrow, L., Vrtunski, P. B., Kim, Y., & Boller, F. (1981). Arousal responses to emotional stimuli and laterality of lesion. Neuropsychologia, 19(1), 65–71.
Myslobodsky, M. S., & Rattok, J. (1977). Bilateral electrodermal activity in waking man. Acta Psychologica, 41(4), 273–282.
Petrovic, P., Kalisch, R., Pessiglione, M., Singer, T., & Dolan, R. J. (2008). Learning affective values for faces is expressed in amygdala and fusiform gyrus. Social Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience, 3(2), 109–118.
Roman, F., Garcia-Sanchez, F. A., Martinez-Selva, J. M., Gomez-Amor, J., & Carrillo, E. (1989). Sex differences and bilateral electrodermal activity: A replication. Pavlovian Journal of Biological Science, 24(4), 150–155.
Schulter, G., & Papousek, I. (1998). Bilateral electrodermal activity: Relationships to state and trait characteristics of hemisphere asymmetry. International Journal of Psychophysiology, 31(1), 1–12.
Snowden, J. S., Austin, N. A., Sembi, S., Thompson, J. C., Craufurd, D., & Neary, D. (2008). Emotion recognition in Huntington’s disease and frontotemporal dementia. Neuropsychologia, 46(11), 2638–2649.
Tranel, D., & Damasio, H. (1989). Intact electrodermal skin conductance responses after bilateral amygdala damage. Neuropsychologia, 27(4), 381–390.
Tranel, D., & Damasio, H. (1994). Neuroanatomical correlates of electrodermal skin conductance responses. Psychophysiology, 31(5), 427–438.
Tranel, D., Fowles, D. C., & Damasio, A. R. (1985). Electrodermal discrimination of familiar and unfamiliar faces: A methodology. Psychophysiology, 22(4), 403–408.
Tsunoda, T., Yoshino, A., Furusawa, T., Miyazaki, M., Takahashi, Y., & Nomura, S. (2008). Social anxiety predicts unconsciously provoked emotional responses to facial expression. Physiology & Behavior, 93(1–2), 172–176.
van Wingen, G. A., van Eijndhoven, P., Tendolkar, I., Buitelaar, J., Verkes, R. J., & Fernandez, G. (2010). Neural basis of emotion recognition deficits in first-episode major depression. Psychological Medicine, 41(7), 1–9.
Wang, G. H. (1964). The neural control of sweating. Madison: University of Wisconsin Press.
Zatorre, R. J., Jones-Gotman, M., Evans, A. C., & Meyer, E. (1992). Functional localization and lateralization of human olfactory cortex. Nature, 360(6402), 339–340.
Zoccolotti, P., Scabini, D., & Violani, C. (1982). Electrodermal responses in patients with unilateral brain damage. Journal of Clinical Neuropsychology, 4(2), 143–150.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Banks, S.J., Bellerose, J., Douglas, D. et al. Bilateral Skin Conductance Responses to Emotional Faces. Appl Psychophysiol Biofeedback 37, 145–152 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10484-011-9177-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10484-011-9177-7