Abstract
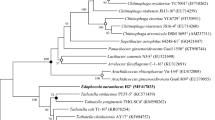
A Gram-stain-negative bacterium, H13-6T, was isolated from a microbial fermentation bed material collected from a pig farm located in Yan’an, Shaanxi, China. Phylogenetic analysis based on 16S rRNA gene sequences showed that strain H13-6T was affiliated with the genus Xanthomonas and showed highest similarity to strain Xanthomonas maliensis M97T (98.38%), Xanthomonas prunicola CFBP 8353T (98.26%) and Xanthomonas oryzae ATCC 35933T (98.11%). The pairwise ortho Average Nucleotide Identity values and the digital DNA-DNA hybridization values between strain H13-6T and the other Xanthomonas species were all below their respective cut-offs. Two genes encoding for chitinase were found and the strain showed a strong chitin-degrading activity. The major fatty acids were Iso-C15:0 (55.9%), Antesio-C15:0 (7.4%) and Iso-C11:0 (5.5%) and the major polar lipids were diphosphatidylglycerol, phosphatidyglycerol and phosphatidylethanolamine. Based on the phenotypic properties and phylogenetic distinctiveness, Xanthomonas chitinilytica was proposed as a novel species of the genus Xanthomonas, with strain H13-6T (= CGMCC 1.61317T = NBRC 115641T) as type strain.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
This Whole Genome Shotgun project of strain H13-6T has been deposited at DDBJ/ENA/GenBank under the accession JAPCHY000000000. The version described in this paper is version JAPCHY000000000.1. The GenBank/EMBL/DDBJ accession numbers for 16S rRNA gene sequence is ON115013. The type strain H13-6T was deposited at the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Centre (CGMCC 1.61317T) and Biological Resource Center, NITE (NBRC 115641T).
References
Bankevich A, Nurk S, Antipov D, Gurevich AA, Dvorkin M, Kulikov AS, Lesin VM, Nikolenko SI, Pham S, Prjibelski AD, Pyshkin AV, Sirotkin AV, Vyahhi N, Tesler G, Alekseyev MA, Pevzner PA (2012) SPAdes: a new genome assembly algorithm and its applications to single-cell sequencing. J Comput Biol 19:455–477
Bansal K, Kaur A, Midha S, Kumar S, Korpole S, Patil PB (2021) Xanthomonas sontii sp. nov., a non-pathogenic bacterium isolated from healthy basmati rice (Oryza sativa) seeds from India. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 114:1935–1947
Blin K, Shaw S, Kloosterman AM, Charlop-Powers Z, Van Wezel GP, Medema MH, Weber T (2021) antiSMASH 6.0: improving cluster detection and comparison capabilities. Nucleic Acids Res 49:W29–W35
Dowson DW (1939) On the systematic position and generic names of the Gram negative bacterial plant pathogens. Zentralblatt Für Bakteriologie U.s.w. 100:17
Essakhi S, Cesbron S, Fischer-Le Saux M, Bonneau S, Jacques MA, Manceau C (2015) Phylogenetic and variable-number tandem-repeat analyses identify nonpathogenic Xanthomonas arboricola lineages lacking the canonical type III secretion system. Appl Environ Microbiol 81:5395–5410
Felsenstein J (1981) Evolutionary trees from DNA sequences: a maximum likelihood approach. J Mol Evolut 17:368–376
Felsenstein J (1985) Confidence limits on phylogenies—an approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 39:783–791
Fitch WM (1971) Toward defining course of evolution - minimum change for a specific tree topology. Syst Zool 20:406
Galperin MY, Makarova KS, Wolf YI, Koonin EV (2014) Expanded microbial genome coverage and improved protein family annotation in the COG database. Nucleic Acids Res 43:D261–D269
Goris J, Konstantinidis KT, Klappenbach JA, Coenye T, Vandamme P, Tiedje JM (2007) DNA-DNA hybridization values and their relationship to whole-genome sequence similarities. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:81–91
Hauben L, Vauterin L, Swings J, Moore ER (1997) Comparison of 16S ribosomal DNA sequences of all Xanthomonas species. Int J Syst Bacteriol 47:328–335
Jain C, Rodriguez RL, Phillippy AM, Konstantinidis KT, Aluru S (2018) High throughput ANI analysis of 90K prokaryotic genomes reveals clear species boundaries. Nat Commun 9:5114
Kanehisa M, Sato Y, Kawashima M (2021) KEGG mapping tools for uncovering hidden features in biological data. Protein Sci 31:47–53
Kim J, Na S-I, Kim D, Chun J (2021) UBCG2: up-to-date bacterial core genes and pipeline for phylogenomic analysis. J Microbiol 59:609–615
Kotb E, Alabdalall AH, Alghamdi AI, Ababutain IM, Aldakeel SA, Al-Zuwaid SK, Algarudi BM, Algarudi SM, Ahmed AA, Albarrag AM (2023) Screening for chitin degrading bacteria in the environment of Saudi Arabia and characterization of the most potent chitinase from Streptomyces variabilis Am 1. Sci Rep 13:11723
Kovacs N (1956) Identification of Pseudomonas pyocyanea by the oxidase reaction. Nature 178:703–703
Kumar S, Stecher G, Tamura K (2016) MEGA7: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol Biol Evol 33:1870–1874
Lee I, Ouk Kim Y, Park SC, Chun J (2016) OrthoANI: an improved algorithm and software for calculating average nucleotide identity. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 66:1100–1103
Lopez MM, Lopez-Soriano P, Garita-Cambronero J, Beltran C, Taghouti G, Portier P, Cubero J, Fischer-LeSaux M, Marco-Noales E (2018) Xanthomonas prunicola sp. nov., a novel pathogen that affects nectarine (Prunus persica var. nectarina) trees. Int J Syst Evolut Microbiol 68:1857–1866
Meier-Kolthoff JP, Auch AF, Klenk HP, GöKER M (2013) Genome sequence-based species delimitation with confidence intervals and improved distance functions. BMC Bioinform 14:60
Meier-Kolthoff JP, Carbasse JS, Peinado-Olarte RL, GöKER M (2021) TYGS and LPSN: a database tandem for fast and reliable genome-based classification and nomenclature of prokaryotes. Nucleic Acids Res 50:D801–D807
Merda D, Bonneau S, Guimbaud J-F, Durand K, Brin C, Boureau T, Lemaire C, Jacques MA, Fischer-Le Saux M (2016) Recombination-prone bacterial strains form a reservoir from which epidemic clones emerge in agroecosystems. Environ Microbiol Rep 8(5):572–581
Powers EM (1995) Efficacy of the Ryu nonstaining KOH technique for rapidly determining gram reactions of food-borne and waterborne bacteria and yeasts. Appl Environ Microbiol 61:3756–3758
Rana R, Madhavan VN, Saroha T, Bansal K, Kaur A, Sonti RV, Patel HK, Patil PB (2022) Xanthomonas indica sp. nov., a novel member of non-pathogenic Xanthomonas community from healthy rice seeds. Curr Microbiol 79:304
Richter M, Rossello-Mora R (2009) Shifting the genomic gold standard for the prokaryotic species definition. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106:19126–19131
Rossello-Mora R, Amann R (2015) Past and future species definitions for Bacteria and Archaea. Syst Appl Microbiol 38:209–216
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method—a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425
Sasser M (1990) Identification of bacteria by gas chromatography of cellular fatty acids. Usfcc Newsl
Stackebrandt E, Ebers J (2006) Taxonomic parameters revisited: tarnished gold standards. Microbiol Today 8:6–9
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, Jeanmougin F, Higgins DG (1997) The CLUSTAL_X windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res 25:4876–4882
Vauterin L, Hoste B, Kersters K, Swings J (1995) Reclassification of Xanthomonas. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 45:472–489
Vauterin L, Rademaker J, Swings J (2000) Synopsis on the taxonomy of the genus Xanthomonas. Phytopathology 90:677–682
Wilson KH, Blitchington RB, Greene RC (1990) Amplification of bacterial 16S ribosomal DNA with polymerase chain reaction. J Clin Microbiol 28:1942–1946
Xia X (2020) Maximum parsimony method in phylogenetics. In: A Mathematical primer of molecular phylogenetics
Yoon SH, Ha SM, Kwon S, Lim J, Kim Y, Seo H, Chun J (2017a) Introducing EzBioCloud: a taxonomically united database of 16S rRNA gene sequences and whole-genome assemblies. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 67:1613–1617
Yoon SH, Ha SM, Lim J, Kwon S, Chun J (2017b) A large-scale evaluation of algorithms to calculate average nucleotide identity. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek Int J Gen Mol Microbiol 110:1281–1286
Acknowledgements
This work was supported financially by Special scientific Research Project of Education Department of Shaanxi Province (No. 21JK0992), Special fund for science and technology of Yan’an City (No.2019-27; No.203010105), Doctor Support Project of Yan’an University (No. YDBK2019-43, YDBK2019-44).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ZD performed Material preparation. XL, XH and XL performed Data collection and analysis. XL and YJ wrote the main manuscript text. YJ designed and supervised the study. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, X., Liu, X., Deng, Z. et al. Xanthomonas chitinilytica sp. nov., a novel chitinolytic bacterium isolated from a microbial fermentation bed material. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 117, 17 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-023-01904-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-023-01904-2