Abstract
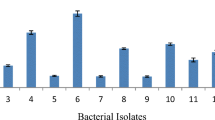
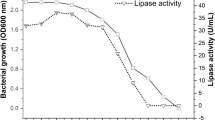
Cold-active extracellular lipases produced by different psychrotrophs are important for various industrial applications. We have isolated a Gram-negative, rod-shaped, aerobe, non-pigment producing psychrotrophic bacterial strain RSAP17 (MTCC 12991, MCC 4275) from the unexplored Arctic soil sample of NyAlesund, Svalbard, Norway (78° 55″ N, 11° 54″ E). The detailed morphological, biochemical, and molecular characteristics were investigated to characterize the isolate RSAP17. Analyses of the 16S rDNA sequence of strain RSAP17 (Accession no. MK391379) shows the closest match with Oceanisphaera marina YM319T (99.45%) and Oceanisphaera sediminis TW92 JCM 17329T (97.40%). The isolate is capable of producing extracellular lipase but not amylase, cellulase or urease. The optimal parameters for lipase production have been found in tributyrin based (10 mL/L) agar media supplemented with 3% (w/v) NaCl after 2–3 days of incubation at 20–22 °C temperature and pH 9 at shaking condition. We have purified the extracellular lipase from the RSAP17 grown culture supernatant through 75% ammonium sulfate precipitation followed by dialysis and DEAE cellulose column chromatography. The invitro lipolytic activity of the purified lipase enzymes has been done through zymogram analysis. The molecular weight found for the lipase is 103.8 kD. The optimal activity of the purified lipase has been found at 25 °C and pH 9. MALDI-TOF-MS study of the purified lipase showed the highest match with the sequence of prolipoprotein diacylglyceryl transferase with 44% sequence coverage. Further study on large-scale production, substrate utilization and enzymatic kinetics of this lipase could unravel its possibility in future biotechnological applications.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al Khudary R, Venkatachalam R, Katzer M, Elleuche S, Antranikian G (2010) A cold-adapted esterase of a novel marine isolate, Pseudoalteromonas arctica: gene cloning, enzyme purification and characterization. Extremophiles 14:273–285
Alquati C, De Gioia L, Santarossa G, Alberghina L, Fantucci P et al (2002) The cold-active lipase of Pseudomonas fragi. heterologous expression, biochemical characterization and molecular modeling. Eur J Biochem 269:3321–3328
Anand AA, Vennison SJ, Sankar SG et al (2010) Isolation and characterization of bacteria from the gut of Bombyx mori that degrade cellulose, xylan, pectin and starch and their impact on digestion. J Insect Sci 10:107. https://doi.org/10.1673/031.010.10701
Bozzola JJ, Russell LD (1999) Electron microscopy: principles and techniques for biologists. Jones and Bartlett, Boston, p 670
Cavicchioli R, Charlton T, Ertan H, Mohd Omar S, Siddiqui KS et al (2011) Biotechnological uses of enzymes from psychrophiles. Microb Biotechnol 4:449–460
Chen RP, Guo LZ, Dang HY (2011) Gene cloning, expression and characterization of a cold-adapted lipase from a psychrophilic deep-sea bacterium Psychrobacter sp. C18. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 27:431–441
Choi WC, Kang SJ, Jung YT, Oh TK, Yoon JH (2011) Oceanisphaera ostreae sp. nov., isolated from seawater of an oyster farm, and amended description of the genus Oceanisphaera, Romanenko et al. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 61(Pt 12):2880–2884. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.029496-0
Choo DW, Kurihara T, Suzuki T, Soda K, Esaki N (1998) A cold-adapted lipase of an Alaskan psychrotroph, Pseudomonas sp. strain B11–1: gene cloning and enzyme purification and characterization. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:486–491
Cieśliński H, Białkowska AM, Długołecka A, Daroch M, Tkaczuk KL et al (2007) A cold-adapted esterase from psychrotrophic Pseudoalteromas sp. strain 643A. Arch Microbiol 188:27–36
Coligan JE, Dunn BM, Speicher DW, Wingfield PT, Ploegh HL (1998) Current protocols in protein science. Wiley, Chichester
Das A, Chakrabarti K (2018) A cold tolerant lipase develops enhanced activity, thermal tolerance and solvent stability in the presence of calcium nanoparticles: alternative approach to genetic modulation. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcab.05.002
De Pascale D, Cusano AM, Autore F, Parrilli E, di Prisco G et al (2008) The cold-active Lip1 lipase from the Antarctic bacterium Pseudoalteromonas haloplanktis TAC125 is a member of a new bacterial lipolytic enzyme family. Extremophiles 12:311–323
Dey A, Chattopadhyay A, Mukhopadhyay SK, Saha P, Chatterjee S et al (2014) Production, partial purification and characterization of an extracellular psychrotrophic lipase from Pseudomonas sp. ADT3. J Bioremed Biodeg 5:242. https://doi.org/10.4172/2155-6199.1000242
Feller G, Gerday C (2003) Psychrophilic enzymes: hot topics in cold adaptation. Nat Rev Microbiol 1(3):200–208. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro773
Feller G, Thiry M, Arpigny JL, Gerday C (1991) Cloning and expression in Escherichia coli of three lipase-encoding genes from the psychrotrophic antarctic strain Moraxella TA144. Gene 102:111–115
Jaeger KE, Eggert T (2002) Lipases for biotechnology. Curr Opin Biotechnol 13:390–397
Joseph B, Ramteke PW, Thomas G (2008) Cold active microbial lipases: some hot issues and recent developments. Biotechnol Adv 26:457–470
Kampfer P, Kroppenstedt RM (1996) Numerical analysis of fatty acid patterns of coryneform bacteria and related taxa. Can J Microbiol 42:989–1005. https://doi.org/10.1139/m96-128
Kasana RC, Kaur B, Yadav SK (2008) Isolation and identification of a psychrotrophic Acinetobacter sp. CR9 and characterization of its alkaline lipase. J Basic Microbiol 48:207–212
Kimura M (1980) A simple method for estimating evolutionary rates of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide sequences. J Mol Evol 16:111–120. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01731581(1980)
Kiran GS, Shanmughapriya S, Jayalakshmi J et al (2008) 2008) Optimization of extracellular psychrophilic alkaline lipase produced by marine Pseudomonas sp. (MSI057. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 31:483–492. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-007-0186-0
Kouker G, Jaeger KE (1987) Specific and sensitive plate assay for bacterial lipases. Appl Environ Microbiol 53:211–213
Kumar D, Kumar L, Nagar S, Raina C, Parshad R, Gupta VK (2012) Screening, isolation and production of lipase/esterase producing Bacillus sp. strain DVL2 and its potential evaluation in esterification and resolution reactions. Arch Appl Sci Res 4:1763–1770
Kumar S, Stecher G, Tamura K (2016) MEGA7: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger data sets. Mol Biol Evol 33:1870–1874. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msw054
Kumar A, Mukhia S, Kumar N, Acharya V, Kumar S, Kumar R (2020) A broad temperature active lipase purified from a psychrotrophic bacterium of sikkim himalaya with potential application in detergent formulation. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 8:642. https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2020.00642
Lan DM, Yang N, Wang WK, Shen YF, Yang B et al (2011) A novel cold-active lipase from Candida albicans: cloning, expression and characterization of the recombinant enzyme. Int J Mol Sci 12:3950–3965
Lee HK, Ahn MJ, Kwak SH, Song WH, Jeong BC et al (2003) Purification and characterization of cold active lipase from psychrotrophic Aeromonas sp. LPB 4. J Microbiol 41:22–27
Lin XZ, Cui SS, Xu GY, Wang S, Du N et al (2010) Cloning and heterologous expression of two cold-active lipases from the Antarctic bacterium Psychrobacter sp. G Polar Res 29:421–429
Liu J, Sun YW, Zhang DD, Li SN, Zhang DC (2017) Oceanisphaera marina sp. nov., isolated from a deep-sea seamount. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 67:1996–2000
Lo Giudice A, Michaud L, de Pascale D, De Domenico M, di Prisco G, Fani R, Bruni V (2006) Lipolytic activity of Antarctic cold-adapted marine bacteria (Terra Nova Bay, Ross Sea). J Appl Microbiol 101(5):1039–1048. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2672.2006.03006.x.
Maiangwa J, Ali MS, Salleh AB, Rahman RN, Shariff FM, Leow TC (2015) Adaptational properties and applications of cold-active lipases from psychrophilic bacteria. Extremophiles 19(2):235–247. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-014-0710-5
Maiti PK, Mandal S (2019) Majority of actinobacterial strains isolated from Kashmir Himalaya soil are rich source of antimicrobials and industrially important biomolecules. Adv Microbiol 9:220–238. https://doi.org/10.4236/aim.2019.93016
Maiti PK, Das S, Sahoo P, Mandal S (2020) Streptomyces sp. SM01 isolated from Indian soil produces a novel antibiotic picolinamycin effective against multi drug resistant bacterial strains. Sci Rep 10:10092. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-66984-w
Mandal M, Paul S, Uddin MR, Mondal MA, Mandal S (2016) In vitro antibacterial potential of Hydrocotyle javanica Thunb. Asian Pac J Trop Dis 6:54–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/s2222-1808(15)60985-9
Mao G, Zhao Y, Kang X et al (2016) Crystal structure of E. coli lipoprotein diacylglyceryl transferase. Nat Commun 7:10198. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms10198
Marmur J (1961) A procedure for the isolation of deoxyribonucleic acid from micro-organisms. J Mol Biol 3:208–218. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-2836(61)80047-8
Park IH, Kim SH, Lee YS, Lee SC, Zhou Y et al (2009) Gene cloning, purification, and characterization of a cold-adapted lipase produced by Acinetobacter baumannii BD5. J Microbiol Biotechnol 19:128–135
Pratuangdejkul J, Dharmsthiti S (2000) Purification and characterization of lipase from psychrophilic Acinetobacter calcoaceticus LP009. Microbiol Res 155:95–100
Rashid N, Shimada Y, Ezaki S, Atomi H, Imanaka T (2001) Low-temperature lipase from psychrotrophic Pseudomonas sp. strain KB700A. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:4064–4069
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4(4):406–425. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040454
Salwoom L, Raja Abd Rahman RNZ, Salleh AB (2019) Isolation, characterization, and lipase production of a cold-adapted bacterial strain Pseudomonas sp. LSK25 isolated from Signy Island, Antarctica. Molecules 24(4):715. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24040715
Sasser M (1990) Identification of bacteria by gas chromatography of cellular fatty acids, MIDI Technical Note 101. MIDI Inc., Newark
Shin NR, Whon TW, Roh SW, Kim MS, Kim YO, Bae JW (2012) Oceanisphaera sediminis sp. nov., isolated from marine sediment. Int J Syst Bacteriol 62(7):1552–1557. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.034645-0
Shirling EB, Gottlieb D (1966) Methods for characterization of Streptomyces species. Int J Syst Bacteriol 16:313–340. https://doi.org/10.1099/00207713-16-3-313
Srinivas TNR, Nageswara Rao SSS, VishnuVardhan R, Pratibha MS, Sailaia B, Kavya B, Hara Kishore K, Begum Z, Singh SM, Shivaji S (2009) Bacterial diversity and bioprospecting for cold-active lipases, amylases and proteases, from culturable bacteria of Kongsfjorden and Ny-A°lesund, Svalbard, Arctic. Curr Microbiol 59:537–547
Torossian K, Bell AW (1991) Purification and characterization of an acid resistant triacylglycerol lipase from Aspergillus niger. Biotechnol Appl Biochem 13:205–211
Turner S, Pryer KM, Miao VP, Palmer JD (1999) Investigating deep phylogenetic relationships among cyanobacteria and plastids by small subunit rRNA sequence analysis. J Eukaryot Microbiol 46(4):327–338. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1550-7408.1999.tb04612.x
Williams ST, Goodfellow M, Alderson G, Wellington EM, Sneath PH, Sackin MJ (1983) Numerical classification of Streptomyces and related genera. J Gen Microbiol 129(6):1743–1813. https://doi.org/10.1099/00221287-129-6-1743
Wiseman A (1995) Handbook of enzyme biotechnology. TJ Pres Ltd, Cornwall, pp 465–466
Xu Z, Zhang XY, Su HN, Yu ZC, Liu C, Li H, Chen XL, Song XY, Xie BB, Qin QL, Zhou BC, Shi M, Huang Y, Zhang YZ (2014) Oceanisphaera profunda sp. nov., a marine bacterium isolated from deep-sea sediment, and emended description of the genus Oceanisphaera. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.058115-0
Yoon SH, Ha SM, Kwon S et al (2017) Introducing EzBioCloud: a taxonomically united database of 16S rRNA gene sequences and whole-genome assemblies. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 67(5):1613–1617. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.001755
Zhang JW, Zeng RY (2008) Molecular cloning and expression of a coldadapted lipase gene from an Antarctic deep sea psychrotrophic bacterium Pseudomonas sp. 7323. Mar Biotechnol (NY) 10:612–621
Zhang J, Lin S, Zeng R (2007) Cloning, expression, and characterization of a cold-adapted lipase gene from an antarctic deep-sea psychrotrophic bacterium, Psychrobacter sp 7195. J Microbiol Biotechnol 17:604–610
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Dr. Pulak Kumar Maiti for his suggestion on analyzing the phylogeny of the strains. We are also especially thankful to Mr. Pinaki Hazra for his technical help in column chromatography.
Funding
There is no financial support to declare.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
RU performed all the experiments, interpreted data and prepared the manuscript; PR helped in procuring sample and edited the manuscript. SM conceptualized the research, designed the experiments, wrote and edited the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author declared no competing financial and/or non-financial interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Uddin, M.R., Roy, P. & Mandal, S. Production of extracellular lipase from psychrotrophic bacterium Oceanisphaera sp. RSAP17 isolated from arctic soil. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 114, 2175–2188 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-021-01671-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-021-01671-y