Abstract
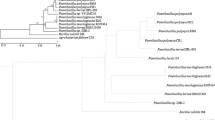
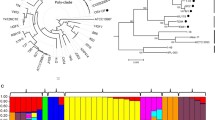
Rapid development of gene sequencing technologies has led to an exponential increase in microbial sequencing data. Genome research of a single organism does not capture the changes in the characteristics of genetic information within a species. Pan-genome analysis gives us a broader perspective to study the complete genetic information of a species. Paenibacillus polymyxa is a Gram-positive bacterium and an important plant growth-promoting rhizobacterium with the ability to produce multiple antibiotics, such as fusaricidin, lantibiotic, paenilan, and polymyxin. Our study explores the pan-genome of 14 representative P. polymyxa strains isolated from around the world. Heap’s law model and curve fitting confirmed an open pan-genome of P. polymyxa. The phylogenetic and collinearity analyses reflected that the evolutionary classification of P. polymyxa strains are not associated with geographical area and ecological niches. Few genes related to phytohormone synthesis and phosphate solubilization were conserved; however, the nif cluster gene associated with nitrogen fixation exists only in some strains. This finding is indicative of nitrogen fixing ability is not stable in P. polymyxa. Analysis of antibiotic gene clusters in P. polymyxa revealed the presence of these genes in both core and accessory genomes. This observation indicates that the difference in living environment led to loss of ability to synthesize antibiotics in some strains. The current pan-genomic analysis of P. polymyxa will help us understand the mechanisms of biological control and plant growth promotion. It will also promote the use of P. polymyxa in agriculture.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alcock BP, Raphenya AR, Lau TTY, Tsang KK, Bouchard M, Edalatmand A, Huynh W, Nguyen A-LV, Cheng AA, Liu S, Min SY, Miroshnichenko A, Tran H-K, Werfalli RE, Nasir JA, Oloni M, Speicher DJ, Florescu A, Singh B, Faltyn M, Hernandez-Koutoucheva A, Sharma AN, Bordeleau E, Pawlowski AC, Zubyk HL, Dooley D, Griffiths E, Maguire F, Winsor GL, Beiko RG, Brinkman FSL, Hsiao WWL, Domselaar GV, McArthur AG (2020) CARD 2020: antibiotic resistome surveillance with the comprehensive antibiotic resistance database. Nucleic Acids Res 48:D517–D525. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkz935
Altschul SF, Madden TL, Schäffer AA, Zhang J, Zhang Z, Miller W, Lipman DJ (1997) Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res 25:3389–3402. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/25.17.3389
Araujo R, Dunlap C, Franco CMM (2020) Analogous wheat root rhizosphere microbial successions in field and greenhouse trials in the presence of biocontrol agents Paenibacillus peoriae SP9 and Streptomyces fulvissimus FU14. Mol Plant Pathol 21:622–635. https://doi.org/10.1111/mpp.12918
Arnison PG, Bibb MJ, Bierbaum G, Bowers AA, Bugni TS, Bulaj G, Camarero JA, Campopiano DJ, Challis GL, Clardy J, Cotter PD, Craik DJ, Dawson M, Dittmann E, Donadio S, Dorrestein PC, Entian K-D, Fischbach MA, Garavelli JS, Göransson U, Gruber CW, Haft DH, Hemscheidt TK, Hertweck C, Hill C, Horswill AR, Jaspars M, Kelly WL, Klinman JP, Kuipers OP, Link AJ, Liu W, Marahiel MA, Mitchell DA, Moll GN, Moore BS, Müller R, Nair SK, Nes IF, Norris GE, Olivera BM, Onaka H, Patchett ML, Piel J, Reaney MJT, Rebuffat S, Ross RP, Sahl H-G, Schmidt EW, Selsted ME, Severinov K, Shen B, Sivonen K, Smith L, Stein T, Süssmuth RD, Tagg JR, Tang G-L, Truman AW, Vederas JC, Walsh CT, Walton JD, Wenzel SC, Willey JM, van der Donk WA (2013) Ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptide natural products: overview and recommendations for a universal nomenclature. Nat Prod Rep 30:108–160. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2np20085f
Ash C, Priest FG, Collins MD (1993) Molecular identification of rRNA group 3 bacilli (Ash, Farrow, Wallbanks and Collins) using a PCR probe test. Proposal for the creation of a new genus Paenibacillus. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 64:253–260. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00873085
Baron S, Hadjadj L, Rolain J-M, Olaitan AO (2016) Molecular mechanisms of polymyxin resistance: knowns and unknowns. Int J Antimicrob Agents 48:583–591. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2016.06.023
Beatty PH, Jensen SE (2002) Paenibacillus polymyxa produces fusaricidin-type antifungal antibiotics active against Leptosphaeria maculans, the causative agent of blackleg disease of canola. Can J Microbiol 48:159–169. https://doi.org/10.1139/w02-002
Bertelli C, Laird MR, Williams KP, Lau BY, Hoad G, Winsor GL, Brinkman FS (2017) IslandViewer 4: expanded prediction of genomic islands for larger-scale datasets. Nucleic Acids Res 45:W30–W35. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkx343
Bhardwaj T, Somvanshi P (2017) Pan-genome analysis of Clostridium botulinum reveals unique targets for drug development. Gene 623:48–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2017.04.019
Bierbaum G, Sahl H-G (2009) Lantibiotics: mode of action, biosynthesis and bioengineering. Curr Pharm Biotechnol 10:2–18. https://doi.org/10.2174/138920109787048616
Blin K, Shaw S, Steinke K, Villebro R, Ziemert N, Lee SY, Medema MH, Weber T (2019) AntiSMASH 5.0: updates to the secondary metabolite genome mining pipeline. Nucleic Acids Res 47:W81–W87. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkz310
Bohlool BB, Ladha JK, Garrity DP, George T (1992) Biological nitrogen fixation for sustainable agriculture: a perspective. Plant Soil 141:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00011307
Buchfink B, Xie C, Huson DH (2015) Fast and sensitive protein alignment using DIAMOND. Nat Methods 12:59–60. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.3176
Burkett-Cadena M, Sastoque L, Cadena J, Dunlap CA (2019) Lysinibacillus capsici sp. nov, isolated from the rhizosphere of a pepper plant. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 112:1161–1167. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-019-01248-w
Chatterjee C, Paul M, Xie L, van der Donk WA (2005) Biosynthesis and mode of action of lantibiotics. Chem Rev 105:633–684. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr030105v
Chaudhari NM, Gupta VK, Dutta C (2016) BPGA- an ultra-fast pan-genome analysis pipeline. Sci Rep 6:24373. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep24373
Choi S-K, Park S-Y, Kim R, Lee C-H, Kim JF, Park S-H (2008) Identification and functional analysis of the fusaricidin biosynthetic gene of Paenibacillus polymyxa E681. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 365:89–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2007.10.147
Choi S-K, Park S-Y, Kim R, Kim S-B, Lee C-H, Kim JF, Park S-H (2009) Identification of a polymyxin synthetase gene cluster of Paenibacillus polymyxa and heterologous expression of the gene in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol 191:3350–3358. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.01728-08
Chowdhury SP, Hartmann A, Gao X, Borriss R (2015) Biocontrol mechanism by root-associated Bacillus amyloliquefaciens FZB42—a review. Front Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2015.00780
Cochrane SA, Vederas JC (2016) Lipopeptides from Bacillus and Paenibacillus spp.: a gold mine of antibiotic candidates. Med Res Rev 36:4–31. https://doi.org/10.1002/med.21321
Cochrane SA, Findlay B, Bakhtiary A, Acedo JZ, Rodriguez-Lopez EM, Mercier P, Vederas JC (2016) Antimicrobial lipopeptide tridecaptin A1 selectively binds to gram-negative lipid II. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 113:11561–11566. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1608623113
de Werra P, Péchy-Tarr M, Keel C, Maurhofer M (2009) Role of gluconic acid production in the regulation of biocontrol traits of Pseudomonas fluorescens CHA0. Appl Environ Microbiol 75:4162–4174. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.00295-09
Dutta C, Pan A (2002) Horizontal gene transfer and bacterial diversity. J Biosci 27:27–33. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02703681
Eastman AW, Heinrichs DE, Yuan Z-C (2014a) Comparative and genetic analysis of the four sequenced Paenibacillus polymyxa genomes reveals a diverse metabolism and conservation of genes relevant to plant-growth promotion and competitiveness. BMC Genom. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-15-851
Eastman AW, Weselowski B, Nathoo N, Yuan Z-C (2014b) Complete genome sequence of Paenibacillus polymyxa CR1, a plant growth-promoting bacterium isolated from the corn rhizosphere exhibiting potential for biocontrol, biomass degradation, and biofuel production. Genome Announc. https://doi.org/10.1128/genomeA.01218-13
Erturk Y, Ercisli S, Haznedar A, Cakmakci R (2010) Effects of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) on rooting and root growth of kiwifruit (Actinidia deliciosa) stem cuttings. Biol Res 43:91–98. https://doi.org/10.4067/S0716-97602010000100011
Farag MA, Zhang H, Ryu C-M (2013) Dynamic chemical communication between plants and bacteria through airborne signals: induced resistance by bacterial volatiles. J Chem Ecol 39:1007–1018. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10886-013-0317-9
Finking R, Marahiel MA (2004) Biosynthesis of nonribosomal peptides1. Annu Rev Microbiol 58:453–488. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.micro.58.030603.123615
Frost LS, Leplae R, Summers AO, Toussaint A (2005) Mobile genetic elements: the agents of open source evolution. Nat Rev Microbiol 3:722–732. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro1235
Galea CA, Han M, Zhu Y, Roberts K, Wang J, Thompson PE, Velkov T (2017) Characterization of the polymyxin D synthetase biosynthetic cluster and product profile of Paenibacillus polymyxa ATCC 10401. J Nat Prod 80:1264–1274. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jnatprod.6b00807
Goris J, Konstantinidis KT, Klappenbach JA, Coenye T, Vandamme P, Tiedje JM (2007) DNA-DNA hybridization values and their relationship to whole-genome sequence similarities. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:81–91. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.64483-0
Grady EN, MacDonald J, Liu L, Richman A, Yuan Z-C (2016) Current knowledge and perspectives of Paenibacillus: a review. Microb Cell Fact 15:203. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12934-016-0603-7
Gu Z, Gu L, Eils R, Schlesner M, Brors B (2014) Circlize implements and enhances circular visualization in R. Bioinformatics 30:2811–2812. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btu393
Guo D, Kong S, Chu X, Li X, Pan H (2019) De novo biosynthesis of indole-3-acetic acid in engineered Escherichia coli. J Agric Food Chem 67:8186–8190. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.9b02048
Gupta M, Kiran S, Gulati A, Singh B, Tewari R (2012) Isolation and identification of phosphate solubilizing bacteria able to enhance the growth and aloin-A biosynthesis of Aloe barbadensis Miller. Microbiol Res 167:358–363. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micres.2012.02.004
Hahnke RL, Meier-Kolthoff JP, García-López M, Mukherjee S, Huntemann M, Ivanova NN, Woyke T, Kyrpides NC, Klenk H-P, Göker M (2016) Genome-based taxonomic classification of bacteroidetes. Front Microbiol 7:2003. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2016.02003
Hao T, Chen S (2017) Colonization of wheat, maize and cucumber by Paenibacillus polymyxa WLY78. PLoS ONE 12:e0169980. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0169980
He Z, Kisla D, Zhang L, Yuan C, Green-Church KB, Yousef AE (2007) Isolation and identification of a Paenibacillus polymyxa strain that coproduces a novel lantibiotic and polymyxin. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:168–178. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.02023-06
Heulin T, Berge O, Mavingui P, Gouzou L, Hebbar KP, Balandreau J (1994) Bacillus polymyxa and Rahnella aquatilis, the dominant N2-fixing bacteria associated with wheat rhizosphere in French soils. Eur J Soil Biol Fr
Heyndrickx M, Vandemeulebroecke K, Scheldeman P, Kersters K, de Vos P, Logan NA, Aziz AM, Ali N, Berkeley RCA et al (1996) A polyphasic reassessment of the genus Paenibacillus, reclassification of Bacillus lautus (Nakamura 1984) as Paenibacillus lautus comb. nov. and of Bacillus peoriae (Montefusco et al. 1993) as Paenibacillus peoriae comb. nov., and emended descriptions of P. lautus and of P. peoriae. Int J Syst Bacteriol 46:988–1003. https://doi.org/10.1099/00207713-46-4-988
Hsiao W, Wan I, Jones SJ, Brinkman FSL (2003) IslandPath: aiding detection of genomic islands in prokaryotes. Bioinformatics 19:418–420. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btg004
Hudson CM, Lau BY, Williams KP (2015) Islander: a database of precisely mapped genomic islands in tRNA and tmRNA genes. Nucleic Acids Res 43:D48–D53. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gku1072
Jeong H, Choi S-K, Ryu C-M, Park S-H (2019) Chronicle of a soil bacterium: Paenibacillus polymyxa E681 as a tiny guardian of plant and human health. Front Microbiol 10:467. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2019.00467
Kim JF, Jeong H, Park S-Y, Kim S-B, Park YK, Choi S-K, Ryu C-M, Hur C-G, Ghim S-Y, Oh TK, Kim JJ, Park CS, Park S-H (2010) Genome sequence of the polymyxin-producing plant–probiotic rhizobacterium Paenibacillus polymyxa E681. J Bacteriol 192:6103–6104. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.00983-10
Koga J, Adachi T, Hidaka H (1991) IAA biosynthetic pathway from tryptophan via indole-3-pyruvic acid in Enterobacter cloacae. Agric Biol Chem 55:701–706. https://doi.org/10.1080/00021369.1991.10870678
Kumar S, Stecher G, Li M, Knyaz C, Tamura K (2018) MEGA X: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms. Mol Biol Evol 35:1547–1549. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msy096
Kurtz S, Phillippy A, Delcher AL, Smoot M, Shumway M, Antonescu C, Salzberg SL (2004) Versatile and open software for comparing large genomes. Genome Biol 5:R12. https://doi.org/10.1186/gb-2004-5-2-r12
Lagesen K, Hallin P, Rødland EA, Stærfeldt H-H, Rognes T, Ussery DW (2007) RNAmmer: consistent and rapid annotation of ribosomal RNA genes. Nucleic Acids Res 35:3100–3108. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkm160
Lal S, Tabacchioni S (2009) Ecology and biotechnological potential of Paenibacillus polymyxa: a minireview. Indian J Microbiol 49:2–10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12088-009-0008-y
Langille MG, Hsiao WW, Brinkman FS (2008) Evaluation of genomic island predictors using a comparative genomics approach. BMC Bioinform 9:329. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-9-329
Lee B, Farag MA, Park HB, Kloepper JW, Lee SH, Ryu C-M (2012) Induced resistance by a long-chain bacterial volatile: elicitation of plant systemic defense by a C13 volatile produced by Paenibacillus polymyxa. PLoS ONE. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0048744
Lei M, Lu P, Jin L, Wang Y, Qin J, Xu X, Zhang L, Wang Y (2015) Complete genome sequence of Paenibacillus polymyxa CF05, a strain of plant growth-promoting rhizobacterium with elicitation of induced systemic resistance. Genome Announc 3:e00198-15. https://doi.org/10.1128/genomeA.00198-15
Li Y, Chen S (2019) Fusaricidin produced by Paenibacillus polymyxa WLY78 induces systemic resistance against fusarium wilt of cucumber. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20205240
Li L, Stoeckert CJ, Roos DS (2003) OrthoMCL: identification of ortholog groups for eukaryotic genomes. Genome Res 13:2178–2189. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.1224503
Li S, Yang D, Qiu M, Shao J, Guo R, Shen B, Yin X, Zhang R, Zhang N, Shen Q (2014) Complete genome sequence of Paenibacillus polymyxa SQR-21, a plant growth-promoting rhizobacterium with antifungal activity and rhizosphere colonization ability. Genome Announc 2:e00281-14. https://doi.org/10.1128/genomeA.00281-14
Lindberg T, Granhall U, Tomenius K (1985) Infectivity and acetylene reduction of diazotrophic rhizosphere bacteria in wheat (Triticum aestivum) seedlings under gnotobiotic conditions. Biol Fertil Soils 1:123–129. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00301779
Liu H, Liu K, Li Y, Wang C, Hou Q, Xu W, Fan L, Zhao J, Gou J, Du B, Ding Y (2017a) Complete genome sequence of Paenibacillus polymyxa YC0136, a plant growth-promoting rhizobacterium isolated from tobacco rhizosphere. Genome Announc. https://doi.org/10.1128/genomeA.01635-16
Liu H, Wang C, Li Y, Liu K, Hou Q, Xu W, Fan L, Zhao J, Gou J, Du B, Ding Y (2017b) Complete genome sequence of Paenibacillus polymyxa YC0573, a plant growth-promoting rhizobacterium with antimicrobial activity. Genome Announc 5:e01636-16. https://doi.org/10.1128/genomeA.01636-16
Luo Y, Cheng Y, Yi J, Zhang Z, Luo Q, Zhang D, Li Y (2018) Complete genome sequence of industrial biocontrol strain Paenibacillus polymyxa HY96-2 and further analysis of its biocontrol mechanism. Front Microbiol 9:1520. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2018.01520
Ma M, Wang C, Ding Y, Li L, Shen D, Jiang X, Guan D, Cao F, Chen H, Feng R, Wang X, Ge Y, Yao L, Bing X, Yang X, Li J, Du B (2011) Complete genome sequence of Paenibacillus polymyxa SC2, a strain of plant growth-promoting rhizobacterium with broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity. J Bacteriol 193:311–312. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.01234-10
Medini D, Donati C, Tettelin H, Masignani V, Rappuoli R (2005) The microbial pan-genome. Curr Opin Genet Dev 15:589–594. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gde.2005.09.006
Meier-Kolthoff JP, Auch AF, Klenk H-P, Göker M (2013) Genome sequence-based species delimitation with confidence intervals and improved distance functions. BMC Bioinform 14:60. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-14-60
Metcalf WW, Wanner BL (1991) Involvement of the Escherichia coli phn (psiD) gene cluster in assimilation of phosphorus in the form of phosphonates, phosphite, Pi esters, and Pi. J Bacteriol 173:587–600. https://doi.org/10.1128/jb.173.2.587-600.1991
Modak JM, Vasan SS, Natarajan KA (1999) Calcium removal from bauxite using Paenibacillus polymyxa. Min Metall Explor 16:6–12. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03403228
Montefusco A, Nakamura LK, Labeda DP (1993) Bacillus peoriae sp. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 43:388–390. https://doi.org/10.1099/00207713-43-2-388
Moriya Y, Itoh M, Okuda S, Yoshizawa AC, Kanehisa M (2007) KAAS: an automatic genome annotation and pathway reconstruction server. Nucleic Acids Res 35:W182–W185. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkm321
Muzzi A, Masignani V, Rappuoli R (2007) The pan-genome: towards a knowledge-based discovery of novel targets for vaccines and antibacterials. Drug Discov Today 12:429–439. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.drudis.2007.04.008
Newton BA (1956) The properties and mode of action of the polymyxins. Bacteriol Rev 20:14–27
Niu B, Rueckert C, Blom J, Wang Q, Borriss R (2011) The genome of the plant growth-promoting rhizobacterium Paenibacillus polymyxa M-1 contains nine sites dedicated to nonribosomal synthesis of lipopeptides and polyketides. J Bacteriol 193:5862–5863. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.05806-11
O’Callaghan A, Bottacini F, O’Connell Motherway M, van Sinderen D (2015) Pangenome analysis of Bifidobacterium longum and site-directed mutagenesis through by-pass of restriction-modification systems. BMC Genom 16:832. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-015-1968-4
Ochman H, Lawrence JG, Groisman EA (2000) Lateral gene transfer and the nature of bacterial innovation. Nature 405:299–304. https://doi.org/10.1038/35012500
Park J-E, Kim H-R, Park S-Y, Choi S-K, Park S-H (2017) Identification of the biosynthesis gene cluster for the novel lantibiotic paenilan from Paenibacillus polymyxa E681 and characterization of its product. J Appl Microbiol 123:1133–1147. https://doi.org/10.1111/jam.13580
Phi Q-T, Park Y-M, Ryu C-M, Park S-H, Ghim S-Y (2008) Functional identification and expression of indole-3-pyruvate decarboxylase from Paenibacillus polymyxa E681. J Microbiol Biotechnol 18:1235–1244
Pieterse CMJ, Zamioudis C, Berendsen RL, Weller DM, Van Wees SCM, Bakker PAHM (2014) Induced systemic resistance by beneficial microbes. Annu Rev Phytopathol 52:347–375. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-phyto-082712-102340
Raza W, Shen Q (2010) Growth, Fe3+ reductase activity, and siderophore production by Paenibacillus polymyxa SQR-21 under differential iron conditions. Curr Microbiol 61:390–395. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-010-9624-3
Richter M, Rosselló-Móra R (2009) Shifting the genomic gold standard for the prokaryotic species definition. Proc Natl Acad Sci 106:19126–19131. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0906412106
Rodríguez H, Fraga R, Gonzalez T, Bashan Y (2006) Genetics of phosphate solubilization and its potential applications for improving plant growth-promoting bacteria. Plant Soil 287:15–21. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-006-9056-9
Rybakova D, Wetzlinger U, Müller H, Berg G (2015) Complete genome sequence of Paenibacillus polymyxa Strain Sb3-1, a soilborne bacterium with antagonistic activity toward plant pathogens. Genome Announc 3:e00052-15. https://doi.org/10.1128/genomeA.00052-15
Seppey M, Manni M, Zdobnov EM (2019) BUSCO: assessing genome assembly and annotation completeness. Gene Predict Methods Protoc. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-9173-0_14
Sieber SA, Marahiel MA (2005) Molecular mechanisms underlying nonribosomal peptide synthesis: approaches to new antibiotics. Chem Rev 105:715–738. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr0301191
Soucy SM, Huang J, Gogarten JP (2015) Horizontal gene transfer: building the web of life. Nat Rev Genet 16:472–482. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg3962
Storm DR, Rosenthal KS, Swanson PE (1977) Polymyxin and related peptide antibiotics. Annu Rev Biochem 46:723–763. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.bi.46.070177.003451
Tettelin H, Masignani V, Cieslewicz MJ, Donati C, Medini D, Ward NL, Angiuoli SV, Crabtree J, Jones AL, Durkin AS, Deboy RT, Davidsen TM, Mora M, Scarselli M, Margarit Ros I, Peterson JD, Hauser CR, Sundaram JP, Nelson WC, Madupu R, Brinkac LM, Dodson RJ, Rosovitz MJ, Sullivan SA, Daugherty SC, Haft DH, Selengut J, Gwinn ML, Zhou L, Zafar N, Khouri H, Radune D, Dimitrov G, Watkins K, O’Connor KJB, Smith S, Utterback TR, White O, Rubens CE, Grandi G, Madoff LC, Kasper DL, Telford JL, Wessels MR, Rappuoli R, Fraser CM (2005) Genome analysis of multiple pathogenic isolates of Streptococcus agalactiae: implications for the microbial “pan-genome”. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:13950–13955. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0506758102
Tettelin H, Riley D, Cattuto C, Medini D (2008) Comparative genomics: the bacterial pan-genome. Curr Opin Microbiol 11:472–477. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mib.2008.09.006
Thomas CM, Nielsen KM (2005) Mechanisms of, and barriers to, horizontal gene transfer between bacteria. Nat Rev Microbiol 3:711–721. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro1234
Thompson JD, Higgins DG, Gibson TJ (1994) CLUSTAL W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res 22:4673–4680. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/22.22.4673
Vernikos G, Medini D, Riley DR, Tettelin H (2015) Ten years of pan-genome analyses. Curr Opin Microbiol 23:148–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mib.2014.11.016
Waack S, Keller O, Asper R, Brodag T, Damm C, Fricke WF, Surovcik K, Meinicke P, Merkl R (2006) Score-based prediction of genomic islands in prokaryotic genomes using hidden Markov models. BMC Bioinform 7:142. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-7-142
Wang L, Zhang L, Liu Z, Zhao D, Liu X, Zhang B, Xie J, Hong Y, Li P, Chen S, Dixon R, Li J (2013) A minimal nitrogen fixation gene cluster from Paenibacillus sp. WLY78 enables expression of active nitrogenase in Escherichia coli. PLoS Genet. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1003865
Weissman KJ, Leadlay PF (2005) Combinatorial biosynthesis of reduced polyketides. Nat Rev Microbiol 3:925–936. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro1287
Wen Y, Wu X, Teng Y, Qian C, Zhan Z, Zhao Y, Li O (2011) Identification and analysis of the gene cluster involved in biosynthesis of paenibactin, a catecholate siderophore produced by Paenibacillus elgii B69. Environ Microbiol 13:2726–2737. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1462-2920.2011.02542.x
Xie J, Shi H, Du Z, Wang T, Liu X, Chen S (2016) Comparative genomic and functional analysis reveal conservation of plant growth promoting traits in Paenibacillus polymyxa and its closely related species. Sci Rep 6:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep21329
Zhou C, Guo J, Zhu L, Xiao X, Xie Y, Zhu J, Ma Z, Wang J (2016) Paenibacillus polymyxa BFKC01 enhances plant iron absorption via improved root systems and activated iron acquisition mechanisms. Plant Physiol Biochem 105:162–173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2016.04.025
Funding
This work was jointly supported by the Key R & D projects (No. 20181BBF6003) of Jiangxi Provincial Science and Technology Department, and the Grant (No. 31760547) from the National Natural Science Foundation of China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
LLZ: designed the experiments, analyzed the data, and wrote the manuscript. TZ, ST, XQF, SJY: manuscript revision. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, L., Zhang, T., Tang, S. et al. Pan-genome analysis of Paenibacillus polymyxa strains reveals the mechanism of plant growth promotion and biocontrol. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 113, 1539–1558 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-020-01461-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-020-01461-y