Abstract
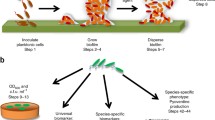
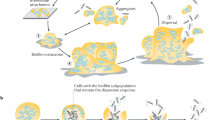
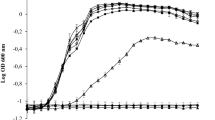
We examined the cell-surface physicochemical properties, the biofilm formation capability and the antibiotic susceptibility in dispersed cells (from an artificial biofilm of alginate beads) and compared with their planktonic (free-swimming) counterparts. The strains used were from different origins, such as clinical (Acinetobacter baumannii AB4), cosmetic industry (Klebsiella oxytoca EU213, Pseudomonas aeruginosa EU190), and environmental (Halomonas venusta MAT28). In general, dispersed cells adhered better to surfaces (measured as the “biofilm index”) and had a greater hydrophobicity [measured as the microbial affinity to solvents (MATS)] than planktonic cells. The susceptibility to two antibiotics (ciprofloxacin and tetracycline) of dispersed cells was higher compared with that of their planktonic counterparts (tested by the “bactericidal index”). Dispersed and planktonic cells exhibited differences in cell permeability, especially in efflux pump activity, which could be related to the differences observed in susceptibility to antibiotics. At 1 h of biofilm formation in microtiter plates, dispersed cells treated with therapeutic concentration of ciprofloxacin yielded a lower biofilm index than the control dispersed cells without ciprofloxacin. With respect to the planktonic cells, the biofilm index was similar with and without the ciprofloxacin treatment. In both cases there were a reduction of the number of bacteria measured as viable count of the supernatant. The lower biofilm formation in dispersed cells with ciprofloxacin treatment may be due to a significant increase of biofilm disruption with respect to the biofilm from planktonic cells. From a clinical point of view, biofilms formed on medical devices such as catheters, cells that can be related to an infection were the dispersed cells. Our results showed that early treatment with ciprofloxacin of dispersed cells could diminishe bacterial dispersion and facilitate the partial elimination of the new biofilm formed.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agwuh KN, MacGowan A (2006) Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of the tetracyclines including glycylcyclines. J Antimicrob Chemother 58:256–265
Ahamad PYA, Kunhi AAM (2011) Enhanced degradation of phenol by Pseudomonas sp. CP4 entrapped in agar and calcium alginate beads in batch and continuous processes. Biodegradation 22:253–265
Barros J, Grenho L, Manuel CM, Ferreira C, Melo LF, Nunes OC, Monteiro FJ, Ferraz MP (2013) A modular reactor to simulate biofilm development in orthopedic materials. Int Microbiol 16:191–198
Bazyleu A, Kumar A (2014) Incubation temperature, osmolarity, and salicylate affect the expression of resistance-nodulation-division efflux pumps and outer membrane porins in Acinetobacter baumannii ATCC19606T. FEMS Microbiol Lett 357:136–143
Bellon-Fontaine MN, Rault J, van Oss CJ (1996) Microbial adhesion to solvents: a novel method to determine the electron-donor/electron-acceptor or Lewis acid-base properties of microbial cells. Colloid Surf B 7:47–53
Berlanga M, Guerrero R (2016) Living together in biofilms: the microbial cell factory and its biotechnological implications. Microb Cell Fact 15:165. doi:10.1186/s12934-016-0569-5
Berlanga M, Viñas M (2000) Salicylate induction of phenotypic resistance to quinolones in Serratia marcescens. J Antimicrob Chemother 46:279–282
Berlanga M, Ruiz N, Hernández-Borrell J, Montero T, Viñas M (2000) Role of the outer membrane in the accumulation of quinolones by Serratia marcescens. Can J Microbiol 46:716–722
Berlanga M, Montero MT, Hernández-Borrell J, Viñas M (2004) Influence of the cell wall on ciprofloxacin susceptibility in selected wild-type Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria. Int J Antimicrob Agents 23:627–630
Berlanga M, Miñana-Galbis D, Domènech Ò, Guerrero R (2012) Enhanced polyhydroxyalkanoates accumulation by Halomonas spp. in artificial biofilms of alginate beads. Int Microbiol 15:191–199
Berlanga M, Domènech Ò, Guerrero R (2014) Biofilm formation on polystyrene in detached vs. planktonic cells of polyhydroxyalkanoate-accumulation Halomonas venusta. Int Microbiol 17:205–212
Biniarz P, Baranowska G, Feder-Kubis J, Krasowska A (2015) The lipopeptides pseudofactin II and surfactin effectively decrease Candida albicans adhesion and hydrophobicity. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 108:343–353
Boonaert CJP, Dufrêne YF, Derclaye SR, Rouxhet PG (2001) Adhesion of Lactococcus lactis to model substrata: direct study of the interface. Colloid Surface B 22:171–182
Bos R, van der Mei HC, Busscher HJ (1999) Physico-chemistry of initial microbial adhesive interactions—its mechanisms and methods for study. FEMS Microbiol Rev 23:179–230
Boy D, Well M, Kinzing-Schippers M, Sörgel F, Ankel-Fuchs D, Naver KD (2004) Urinary bactericidal activity, urinary excretion and plasma concentrations of gatifloxacin (400 mg) versus ciprofloxacin (500 mg) in healthy volunteers after a single oral dose. Int J Antimicrob Agents 23:S6–S16
Bruchmann S, Dötsch A, Nouri B, Chaberny IF, Häussler S (2013) Quantitative contributions of target alteration and decreased drug accumulation to Pseudomonas aeruginosa fluoroquinolone resistance. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 57:1361–1368
Chagnot C, Zorgani MA, Astruc T, Desvaux M (2013) Proteinaceous determinants of surface colonization in bacteria: bacterial adhesion and biofilm formation from a protein secretion perspective. Front Microbiol 4:303. doi:10.3389/fmicb.2013.00303
Chen G, Walker SL (2007) Role of solution chemistry and ion valence on the adhesion kinetics of groundwater and marine bacteria. Langmuir 23:7162–7169
Chia TWR, Fegan N, McMeekin TA, Dykes GA (2008) Salmonella Sofia differs from other poultry-associated Salmonella serovars with respect to cell surface hydrophobicity. J Food Protect 71:2421–2428
Chua SL, Liu Y, Yam JKH, Chen Y, Vejborg RM, Tan BGC, Kjelleberg S, Tolker-Nielsen T, Givskov M, Yang L (2014) Dispersed cells represent a distinct stage in the transition from bacterial biofilm to planktonic lifestyles. Nat Commun 5:4462. doi:10.1038/ncomms5462
De Angelis M, Siragusa S, Campanella D, Di Cagno R, Gobbetti M (2015) Comparative proteomic analysis of biofilm and planktonic cells of Lactobacillus plantarum DB200. Proteomics 15:2244–2257
Delcour AH (2009) Outer membrane permeability and antibiotic resistance. Biochem Biophys Acta 1794:808–816
Djeribi R, Boucherit Z, Bouchloukh W, Zouaoui W, Latrache H, Hamadi F, Menaa B (2013) A study of pH effects on the bacterial surface physicochemical properties of Acinetobacter baumannii. Colloids Surface B 102:540–545
Donlan RM (2002) Biofilms: microbial life on surfaces. Emerg Infect Dis 8:881–890
Giaouris E, Chapot-Chartier M-P, Briandet R (2009) Surface physicochemical analysis of natural Lactococcus lactis strains reveals the existence of hydrophobic and low charged strains with altered adhesive properties. Int J Food Microbiol 131:2–9
Gilley RP, Orihuela CJ (2014) Pneumococci in biofilms are non-invasive: implications on nasopharyngeal colonization. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 4:163. doi:10.3389/fcimb.2014.00163
Gomes LC, Silva LN, Simões M, Melo LF, Mergulhão FJ (2014) Escherichia coli adhesion, biofilm development and antibiotic susceptibility on biomedical materials. J Biomed Mater Res 103:1414–1423
Guilhen C, Charbonnel N, Parisot N, Gueguen N, Iltis A, Forestier C, Balestrino D (2016) Transcriptional profiling of Klebsiella pneumoniae defines signatures for planktonic, sessile and biofilm-dispersed cells. BMC Genomics. doi:10.1186/s12864-016-2557-x
He X, Lu F, Yuan F, Jiang D, Zhao P, Zhu J, Cheng H, Cao J, Guozhong L (2015) Biofilm formation caused by clinical Acinetobacter baumannii isolates is associated with overexpression of the AdeFGH efflux pump. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 59:4817–4825
Horii T, Osaki M, Muramatsu H (2008) Fluoroquinolone resistance in clinical isolates of Klebsiella oxytoca. Chemotherapy 54:323–327
Huang H-Y, Tang Y-J, King VA-E, Chou J-W, Tsen J-H (2015) Properties of Lactobacillus reuteri chitosan-calcium-alginate encapsulation under simulated gastrointestinal conditions. Int Microbiol 18:61–69
Hunt SM, Werner EM, Huang B, Hamilton MA, Stewart PS (2004) Hypothesis for the role of nutrient starvation in biofilm detachment. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:7418–7425
Jensen PØ, Givskov M, Bjamsholt T, Moser C (2010) The immune System vs Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol 59:292–305
Junter G-A, Coquet L, Vilain S, Jouenne T (2002) Immobilized-cell physiology: current data and potentialities of proteomics. Enzyme Microb Technol 31:201–212
Katsikogianni M, Missirlis YF (2004) Concise review of mechanisms of bacterial adhesion to biomaterials and of techniques used in estimating bacteria-material interactions. Eur Cells Mater 8:37–57
Knudsen GM, Nielsen M-B, Grassby T, Danino-Appleton V, Thomsen LE, Colquhoun IJ, Brocklehurst TF, Olsen JE, Hinton JCD (2012) A third mode of surface-associates growth: immobilization of Salmonella enterica serovar Thyphimurium modulates the RpoS-directed transcriptional programme. Environ Microbiol 14:1855–1875
Koerdt A, Gödeke J, Berger J, Thormann KM, Albers S-J (2010) Crenarchaeal biofilm formation under extreme conditions. PLoS ONE 5:e14104. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0014104
Kolter R (2010) Biofilms in lab and nature: a molecular geneticist’s voyage to microbial ecology. Int Microbiol 13:1–7
Krasowska A, Sigler K (2014) How microorganisms use hydrophobicity and what does this mean for human needs? Front Cell Infect Microbiol 4:112. doi:10.3389/fcimb.2014.00112
Lallemand EA, Lacroix MZ, Toutain P-L, Boullier S, Ferran AA, Bousquet-Melou A (2016) In vitro degradation of antimicrobials during use of broth microdilution method can increase the measured minimal inhibitory and micromal bactericidal concentrations. Front Microbiol. doi:10.3389/fmicb.2016.02051
Liu J, Ling J-Q, Wu CD (2013) Physiological properties of Streptococcus mutants UA159 biofilm-detached cells. FEMS Microbiol Lett 340:11–18
Lüdecke C, Jandt KD, Siegismund D, Kujau MJ, Zang E, Rettenmayr M, Bossert J, Roth M (2014) Reproducible biofilm cultivation of chemostat-grown Escherichia coli and investigation of bacterial adhesion on biomaterials using a non-constant-depth film fermenter. PLoS ONE 9:e84837. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0084837
Ly MH, Vo NH, Le TM, Belin J-M, Waché Y (2006) Diversity of the surface properties of Lactococci and consequences on adhesion to food components. Colloids Surface B 52:149–153
McDougald D, Rice SA, Barraud N, Steinberg PD, Kjelleberg S (2012) Should we stay or should we go: mechanisms and ecological consequences for biofilm dispersal. Nat Rev Microbiol 10:39–50
Monds RD, O’Toole GA (2009) The development model of microbial biofilms: ten years of a paradigm up for review. Trends Microbiol 17:73–87
Morrissey I (1997) Bactericidal index: a new way to assess quinolone bactericidal activity in vitro. J Antimicrob Chemother 39:713–717
Nielsen IE, Cars O, Friberg LE (2011) Pharmacokinetic/Pharmacodynamic (PK/PD) indices of antibiotics predicted by a semimechanistic PKPD model: a step toward model-based dose optimization. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 55:4619–4630
O’Toole GA, Kolter R (1998) Initiation of biofilm formation in Pseudomonas fluorescens WCS365 proceeds via multiple, convergent signaling pathways: a genetic analysis. Mol Microbiol 28:449–461
Orús P, Gomez-Perez L, Leranoz S, Berlanga M (2015) Increasing antibiotic resistance in preservative-tolerant bacterial strains isolated from cosmetic products. Int Microbiol 18:51–59
Pagès J-M, James CE, Winterhalter M (2008) The porin and the permeating antibiotic: a selective diffusion barrier in Gram-negative bacteria. Nat Rev Microbiol 6:893–903
Palmer J, Flint S, Brooks J (2007) Bacterial cell attachment, the beginning of a biofilm. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 34:577–588
Park AJ, Murphy K, Krieger JR, Brewer D, Taylor P, Habash M, Khursigara CM (2014) A temporal examination of the planktonic and biofilm proteome of whole cell Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 using quantitative mass spectrometry. Mol Cell Proteomics 13:1095–1105
Perez F, Endimiani A, Ray AJ et al (2010) Carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii and Klebsiella pneumoniae across a hospital system: impact of post-acute care facilities on dissemination. J Antimicrob Chemother. doi:10.1093/jac/dkq191
Peter H, Ylla I, Gudasz C, Romani AM, Sabater S, Tranvik LJ (2011) Multifunctionality and diversity in bacterial biofilms. PLoS ONE 6:e23225. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0023225
Petrova OE, Sauer K (2016) Escaping the biofilm in more than one way: desorption, detachment or dispersion. Curr Opin Microbiol 30:67–78
Post DMB, Held JM, Ketterer MR, Philips NJ, Sahu A, Apicella MA, Gibson BW (2014) Comparative analyses of proteins from Haemophilus influenzae biofilm and planktonic populations using metabolic labeling and mass spectrometry. BMC Microbiol. doi:10.1186/s12866-014-0329-9
Prada-López I, Quintas V, Casares-De-Cal MA, Suárez-Quintanilla JA, Suárez-Quintanilla D, Tomás I (2015) Ex vivo vs. in vivo antibacterial activity of two antiseptics on oral biofilm. Front Microbiol 6:655. doi:10.3389/fmicb.2015.00655
Preedy E, Perni S, Nipiĉ D, Bohinc K, Prokopovich P (2014) Surface roughness mediated adhesion forces between borosilicate glass and Gram-positive bacteria. Langmuir 30:9466–9476
Rollet C, Gal L, Guzzo J (2009) Biofilm-detached cells, a transition from a sessile to planktonic phenotype: a comparative study of adhesion and physiological characteristics in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. FEMS Microbiol Lett 290:135–142
Rumbo-Feal S, Gómez MJ, Gayoso C et al (2013) Whole transcriptome analysis of Acinetobacter baumannii assessed by RNA-sequencing reveals different mRNA expression profiles in Biofilm compared to planktonic cells. PLoS ONE. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0072968
Sachs JL, Hollowed AC (2012) The origins of cooperative bacterial communities. mBio 3:e00099–12. doi:10.1128/mBio.00099-12
Selimoglu SM, Elibol M (2010) Alginate as an immobilization material for Mab production via encapsulated hybridoma cells. Crit Rev Biotechnol 30:145–159
Seper A, Pressler K, Kariisa A, Haid AG, Roier S, Leitner DR, Reidl J, Tamayo R, Schild S (2014) Identification of genes induced in Vibrio cholera in a dynamic biofilm system. Int J Med Microbiol 304:749–763
Silva-Dias A, Miranda IM, Branco J, Monteiro-Soares M, Pina-Vaz C, Rodrigues AG (2015) Adhesion, biofilm formation, cell surface hydrophobicity, and antifungal planktonic susceptibility: relationship among Candida spp. Front Microbiol 6:205. doi:10.3389/fmicb.2015.00205
Simões LC, Simões M, Vieira MJ (2010) Adhesion and biofilm formation on polystyrene by drinking water-isolated bacteria. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 98:317–329
Thormann KM, Saville RM, Shukla S, Spormann AM (2005) Induction of rapid detachment in Shewanella oneidensis MR-1 biofilms. J Bacteriol 187:1014–1021
Tokunaga H, Mitsuo K, Kamekura M, Tokunaga M (2004) Major outer membrane proteins in moderately halophilic eubacteria of genera Chromohalobacter and Halomonas. J Basic Microbiol 44:232–240
Trémoulet F, Duché O, Namane A, Martinie B (2002) European Listeria Genome Consortium, Labadie JC. Comparison of protein patterns of Listeria monocytogenes grown in biofilm or in planktonic mode by proteomic analysis. FEMS Microbiol Lett 210:25–31
Uppuluri P, Chaturvedi AK, Srinivasan A et al (2010) Dispersion as an important step in the Candida albicans biofilm developmental cycle. PLoS Pathog 6:e1000828
Van der Werf MJ, Pieterse B, van Luijk N, Schuren F, van der Werff-van der Vat B, Overkamp K, Jellema RH (2006) Multivariate analysis of microarray data by principal component discriminant analysis: prioritizing relevant transcripts linked to the degradation of different carbohydrates in Pseudomonas putida S12. Microbiology 152:257–272
Van Gestel J, Vlamakis H, Kolter R (2015) Division of labor in biofilms: the ecology of cell differentiation. Microbiol Spectrum. doi:10.1128/microbiolspec.MB-0002-2014
Van Merode AEJ, van der Mei HC, Busscher HJ, Krom BP (2006) Influence of culture heterogeneity in cell surface charge on adhesion and biofilm formation by Enterococcus faecalis. J Bacteriol 188:2421–2426
Zhang Y-W, Prabhu P (2010) Alginate immobilization of recombinant Escherichia coli whole cells harboring l-arabinose isomerase for l-ribulose production. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 33:741–748
Funding
This study was funded by Department of Biology, Health and Environment, Section of Microbiology to MB.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Berlanga, M., Gomez-Perez, L. & Guerrero, R. Biofilm formation and antibiotic susceptibility in dispersed cells versus planktonic cells from clinical, industry and environmental origins. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 110, 1691–1704 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-017-0919-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-017-0919-2