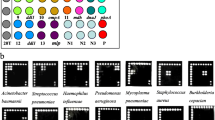
Abstract
Among the 50 species and 70 serogroups of Legionella identified, Legionella pneumophila, comprising three subsp. (subsp. pneumophila, subsp. fraseri, and subsp. pasculleii), is recognized as the major cause of epidemic legionellosis. Rapid and reliable assays to identify pathogenic Legionella spp., and the three L. pneumophila subsp. in particular, are in great demand. In this study, we analyzed the gyrB genes of eleven Legionella spp. and subsp., comprising L. anisa, L. bozemanii, L. dumoffii, L. feeleii, L. gormanii, L. longbeachae, L. micdadei, L. waltersii, L. pneumophila subsp. pneumophila, L. pneumophila subsp. fraseri, and L. pneumophila subsp. pasculleii. We developed a rapid oligonucleotide microarray detection technique to identify accurately these common pathogenic Legionella spp. and L. pneumophila subsp. To detect multiple Legionella species with high specificity, 31 reproducible probes were designed in the array. Sixty-one strains were analyzed in total, including 37 target pathogens and 24 non-target bacterial species used to validate the microarray. The sensitivity of the detection was 1.0 ng using genomic DNA of three Legionella spp., L. anisa, L. dumoffii, and L. waltersii, or 13 CFU/100 mL using the cultured L. pneumophila subsp. pneumophila. Eight isolated strains were tested using the microarray with 100% accuracy. The data indicated that the technique is an efficient method to diagnose and detect Legionella spp. and subsp. in basic microbiology, clinical diagnosis, epidemiological surveillance, and food safety applications. In addition, a phylogenetic study based on the gyrB gene revealed the genetic relationship among the different Legionella spp. and subsp.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cao B, Yao F, Liu X, Feng L, Wang L (2013) Development of a DNA microarray method for detection and identification of all 15 distinct O-antigen forms of Legionella pneumophila. Appl Environ Microbiol 79:6647–6654. doi:10.1128/AEM.01957-13
Cao B, Liu X, Yu X, Chen M, Feng L, Wang L (2014) A new oligonucleotide microarray for detection of pathogenic and non-pathogenic Legionella spp. PLoS ONE 9:e113863. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0113863
Doleans A et al (2004) Clinical and environmental distributions of Legionella strains in France are different. J Clin Microbiol 42:458–460
Fields BS, Benson RF, Besser RE (2002) Legionella and Legionnaires’ disease: 25 years of investigation. Clin Microbiol Rev 15:506–526
Guan W, Xu Y, Chen DL, Xu JN, Tian Y, Chen JP (2012) Application of multilocus sequence analysis (MLSA) for accurate identification of Legionella spp. Isolated from municipal fountains in Chengdu, China, based on 16S rRNA, mip, and rpoB genes. J Microbiol 50:127–136. doi:10.1007/s12275-012-1243-1
Izumi S, Yamamoto M, Suzuki K, Shimizu A, Aranishi F (2007) Identification and detection of Pseudomonas plecoglossicida isolates with PCR primers targeting the gyrB region. J Fish Dis 30:391–397. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2761.2007.00820.x
Kakinuma K, Fukushima M, Kawaguchi R (2003) Detection and identification of Escherichia coli, Shigella, and Salmonella by microarrays using the gyrB gene. Biotechnol Bioeng 83:721–728. doi:10.1002/bit.10709
Kang Y, Takeda K, Yazawa K, Mikami Y (2009) Phylogenetic studies of Gordonia species based on gyrB and secA1 gene analyses. Mycopathologia 167:95–105. doi:10.1007/s11046-008-9151-y
Kasuga O, Takagi K, Tani k, Kinumaki A (1999) Studies on detection methods for Legionella species from environmental water. Kansenshogaku Zasshi 73:25–34
Kirby BM, Everest GJ, Meyers PR (2010) Phylogenetic analysis of the genus Kribbella based on the gyrB gene: proposal of a gyrB-sequence threshold for species delineation in the genus Kribbella. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 97:131–142. doi:10.1007/s10482-009-9393-9
Ko KS, Hong SK, Lee KH, Lee HK, Park MY, Miyamoto H, Kook YH (2003) Detection and identification of Legionella pneumophila by PCR-restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis of the RNA polymerase gene (rpoB). J Microbiol Methods 54:325–337
Park SH, Kim HJ, Kim JH, Kim TW, Kim HY (2007) Simultaneous detection and identification of Bacillus cereus group bacteria using multiplex PCR. J Microbiol Biotechnol 17:1177–1182
Price CT, Abu Kwaik Y (2014) The transcriptome of Legionella pneumophila-infected human monocyte-derived macrophages. PLoS ONE 9:e114914. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0114914
Qin T et al (2013) High prevalence, genetic diversity and intracellular growth ability of Legionella in hot spring environments. PLoS ONE 8:e59018. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0059018
Steele TW, Moore CV, Sangster N (1990) Distribution of Legionella longbeachae serogroup 1 and other legionellae in potting soils in Australia. Appl Environ Microbiol 56:2984–2988
Stolhaug A, Bergh K (2006) Identification and differentiation of Legionella pneumophila and Legionella spp. with real-time PCR targeting the 16S rRNA gene and species identification by mip sequencing. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:6394–6398. doi:10.1128/AEM.02839-05
Su HP, Tung SK, Tseng LR, Tsai WC, Chung TC, Chang TC (2009) Identification of legionella species by use of an oligonucleotide array. J Clin Microbiol 47:1386–1392. doi:10.1128/JCM.02225-08
Tabacchioni S et al (2008) Use of the gyrB gene to discriminate among species of the Burkholderia cepacia complex. FEMS Microbiol Lett 281:175–182. doi:10.1111/j.1574-6968.2008.01105.x
Takamatsu R et al (2010) Molecular characterization of Legionella pneumophila-induced interleukin-8 expression in T cells. BMC Microbiol 10:1. doi:10.1186/1471-2180-10-1
Teh CS, Chua KH, Thong KL (2010) Simultaneous differential detection of human pathogenic and nonpathogenic Vibrio species using a multiplex PCR based on gyrB and pntA genes. J Appl Microbiol 108:1940–1945. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2672.2009.04599.x
Wilson DA, Yen-Lieberman B, Reischl U, Gordon SM, Procop GW (2003) Detection of Legionella pneumophila by real-time PCR for the mip gene. J Clin Microbiol 41:3327–3330
Winiecka-Krusnell J, Linder E (1999) Free-living amoebae protecting Legionella in water: the tip of an iceberg? Scand J Infect Dis 31:383–385
Wu JG, Wang JF, Zhang XH, Zhang SS, Hu XF, Chen JS (2010) A gyrB-targeted PCR for rapid identification of Paenibacillus mucilaginosus. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 87:739–747. doi:10.1007/s00253-010-2501-y
Yang G, Benson R, Pelish T, Brown E, Winchell JM, Fields B (2010) Dual detection of Legionella pneumophila and Legionella species by real-time PCR targeting the 23S-5S rRNA gene spacer region. Clin Microbiol Infect 16:255–261. doi:10.1111/j.1469-0691.2009.02766.x
Yin H et al (2008) Molecular diversity of 16S rRNA and gyrB genes in copper mines. Arch Microbiol 189:101–110. doi:10.1007/s00203-007-0298-6
Zhou G, Cao B, Dou Y, Liu Y, Feng L, Wang L (2011a) PCR methods for the rapid detection and identification of four pathogenic Legionella spp. and two Legionella pneumophila subspecies based on the gene amplification of gyrB. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 91:777–787. doi:10.1007/s00253-011-3283-6
Zhou G et al (2011b) Development of a DNA microarray for detection and identification of Legionella pneumophila and ten other pathogens in drinking water. Int J Food Microbiol 145:293–300. doi:10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2011.01.014
Acknowledgements
This work was funded by the National Special Project on Research and Development of Key Biosafety Technologies [Grant Number 2016YFC1200100], the National 973 Program of China [Grant Number 2013CB733904], and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) [Grant Numbers 31530083, 31270003, 81471904, 31371259, 31270133, 31470194].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
10482_2017_903_MOESM1_ESM.doc
Supplementary material 1 (DOC 139 kb). The sensitivity of the microarray analysis to detect the genomic DNA of L. 457 anisa, L. dumoffii, and L. waltersii. a – d genomic DNA of L. anisa at concentrations 458 of 100 ng, 10 ng, 1 ng, and 0.1 ng; e – h genomic DNA of L. dumoffii, at 459 concentrations of 100 ng, 10 ng, 1 ng, and 0.1 ng; i – l genomic DNA of L. waltersii, 460 at concentrations of 100 ng, 10 ng, 1 ng, and 0.1 ng
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xi, D., Dou, Y., Ren, W. et al. A gyrB oligonucleotide microarray for the specific detection of pathogenic Legionella and three Legionella pneumophila subsp.. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 110, 1515–1525 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-017-0903-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-017-0903-x