Abstract
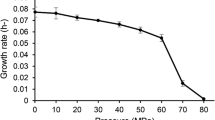
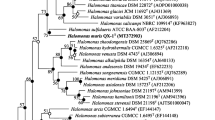
A novel Gram-stain negative, non-motile, moderately halophilic, facultatively anaerobic and spherical bacterium designated strain SS9T was isolated from the gill homogenate of a shark. Cells of SS9T were observed to be 0.8–1.2 μm in diameter. The strain was found to grow optimally at 33 °C, pH 7.0–8.0 and in the presence of 6.0 % (w/v) NaCl. On the basis of 16S rRNA gene phylogeny, strain SS9T can be affiliated with the family Halomonadaceae and is closely related to Chromohalobacter marismortui NBRC 103155T (95.6 % sequence similarity), Halomonas ilicicola SP8T (95.6 %) and Chromohalobacter salexigens DSM 3043T (95.5 %). Multilocus sequence analysis of strain SS9T using the housekeeping genes 16S rRNA, 23S rRNA, gyrB, rpoD and secA revealed the strain’s distinct phylogenetic position, separate from other known genera of the family Halomonadaceae. Strain SS9T was found to contain ubiquinone-9 (Q-9) as the predominant ubiquinone and C18:1 ω7c, C16:0 and summed feature 3 (C16:1 ω7c and/or iso-C15:0 2-OH) as the major fatty acids. The major polar lipids of strain SS9T were identified as phosphatidylglycerol and phosphatidylethanolamine. The DNA G + C content of strain SS9T was determined to be 60.4 mol%. It is evident from phylogenetic, genotypic, phenotypic and chemotaxonomic results that strain SS9T represents a novel species in a new genus, for which the name Pistricoccus aurantiacus gen. nov., sp. nov. is proposed. The type strain is SS9T (=KCTC 42586T = MCCC 1H00111T).



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anan’ina LN, Plotnikova EG, Gavrish EIu, Demakov VA, Evtushenko LI (2007) Salinicola socius gen. nov., sp. nov., a moderately halophilic bacterium from a naphthalene-utilizing microbial association. Mikrobiologiia 76:369–376 (English translation of Mikrobiologiia)
Arahal DR, Ventosa A (2006) The family Halomonadaceae. In: Dworkin M, Falkow S, Rosenberg E, Schleifer K-H, Stackebrandt E (eds) The prokaryotes, vol. 6 (Proteobacteria: Gamma subclass), 3rd edn. Springer, New York, pp 811–835
Arahal DR, Garcia MT, Vargas C, Canovas D, Nieto JJ, Ventosa A (2001a) Chromohalobacter salexigens sp. nov., a moderately halophilic species that includes Halomonas elongata DSM 3043 and ATCC 33174. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 51:1457–1462
Arahal DR, Garcia MT, Ludwig W, Schleifer KH, Ventosa A (2001b) Transfer of Halomonas canadensis and Halomonas israelensis to the genus Chromohalobacter as Chromohalobacter canadensis comb. nov. and Chromohalobacter israelensis comb. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 51:1443–1448
Arahal DR, Castillo AM, Ludwig W, Schleifer KH, Ventosa A (2002) Proposal of Cobetia marina gen. nov., comb. nov., within the family Halomonadaceae, to include the species Halomonas marina. Syst Appl Microbiol 25:207–211
Arahal DR, Vreeland RH, Litchfield CD, Mormile MR, Tindall BJ, Oren A, Bejar V, Quesada E, Ventosa A (2007) Recommended minimal standards for describing new taxa of the family Halomonadaceae. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:2436–2446
Arenas M, Banõń PI, Copa-Patinõ JL, Sánchez-Porro C, Ventosa A, Soliveri J (2009) Halomonas ilicicola sp. nov., a moderately halophilic bacterium isolated from a saltern. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 59:578–582
Ben Ali Gam Z, Abdelkafi S, Casalot L, Tholozan JL, Oueslati R, Labat M et al (2007) Modicisalibacter tunisiensis gen. nov., sp. nov., an aerobic, moderately halophilic bacterium isolated from an oilfieldwater injection sample, and emended description of the family Halomonadaceae Franzmann et al. 1989 emend Dobson and Franzmann 1996 emend. Ntougias et al. 2007. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:2307–2313
Bowman JP (2000) Description of Cellulophaga algicola sp. nov., isolated from the surfaces of Antarctic algae, and reclassification of Cytophaga uliginosa (ZoBell and Upham 1944) Reichenbach 1989 as Cellulophaga uliginosa comb. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 50:1861–1868
CLSI (2012) Performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing; 22nd informational supplement M100-S22. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute, Wayne
Cowan ST, Steel KJ (1965) Manual for the identification of medical bacteria. Cambridge University Press, London
de la Haba RR, Arahal DR, Márquez MC, Ventosa A (2010) Phylogenetic relationships within the family Halomonadaceae based on comparative 23S and 16S rRNA gene sequence analysis. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 60:737–748
de la Haba RR, Márquez MC, Papke RT, Ventosa A (2012) Multilocus sequence analysis of the family Halomonadaceae. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 62:520–538
Dong XZ, Cai MY (eds) (2001) Chapter 14. Determination of biochemical characteristics. In manual for the systematic identification of general bacteria. Science Press, Beijing, pp 370–398
Du ZJ, Wang Y, Dunlap C, Rooney AP, Chen GJ (2014) Draconibacterium orientale gen. nov., sp. nov., isolated from two distinct marine environments, and proposal of Draconibacteriaceae fam. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 64:1690–1696
Elazari-Volcani B (1940) Studies on the microflora of the Dead Sea. Ph.D. thesis, Hebrew University, Jerusalem
Felsenstein J (1981) Evolutionary trees from DNA sequences: a maximum likelihood approach. J Mol Evol 17:368–376
Felsenstein J (2005) PHYLIP (Phylogeny Inference Package) version 3.6. Distributed by the author. Department of Genome Sciences, University of Washington, Seattle
Fendrich C (1988) Halovibrio variabilis gen. nov., sp. nov., Pseudomonas halophila sp. nov. and a new halophilic aerobic coccoid Eubacterium from Great Salt Lake, Utah, USA. Syst Appl Microbiol 11:36–43
Fitch WM (1971) Towards defining the course of evolution: minimum change for a specific tree topology. Syst Zool 20:406–416
Franzmann PD, Wehmeyer U, Stackebrandt E (1988) Halomonadaceae fam. nov., a new family of the class Proteobacteria to accommodate the genera Halomonas and Deleya. Syst Appl Microbiol 11:16–19
Garriga M, Ehrmann MA, Arnau J, Hugas M, Vogel RF (1998) Carnimonas nigrificans gen. nov., sp. nov., a bacterial causative agent for black spot formation on cured meat products. Int J Syst Bacteriol 48:677–686
Gordon RE, Smith MM (1955) Rapidly growing, acid fast bacteria. II. Species description of Mycobacterium fortuitum Cruz. J Bacteriol 69:502–507
Huval JH, Latta R, Wallace R, Kushner DJ, Vreeland RH (1995) Description of two new species of Halomonas: Halomonas israelensis sp. nov. and Halomonas canadensis sp. nov. Can J Microbiol 41:1124–1131
Ivanova EP, Flavier S, Christen R (2004) Phylogenetic relationships among marine Alteromonas-like proteobacteria: emended description of the family Alteromonadaceae and proposal of Pseudoalteromonadaceae fam. nov., Colwelliaceae fam. nov., Shewanellaceae fam. nov., Moritellaceae fam. nov., Ferrimonadaceae fam. nov., Idiomarinaceae fam. nov. and Psychromonadaceae fam. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 54:1773–1788
Jukes TH, Cantor CR (1969) Evolution of the protein molecules. In: Munro HN (ed) Mammalian protein metabolism. Academic Press, New York, pp 21–132
Kim OS, Cho YJ, Lee K, Yoon SH, Kim M, Na H, Park SC, Jeon YS, Lee JH, Yi H, Won S, Chun J (2012) Introducing EzTaxon-e: a prokaryotic 16S rRNA gene sequence data-basewithphylotypes thatrepresent uncultured species. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 62:716–721
Kimura M (1980) A simple method for estimating evolutionary rates of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide sequences. J Mol Evol 16:111–120
León MJ, Sánchez-Porro C, de la Haba RR, Llamas I, Ventosa A (2014) Larsenia salina gen. nov., sp. nov., a new member of the family Halomonadaceae based on multilocus sequence analysis. Syst Appl Microbiol 37:480–487
Li JH, Oliver IM, Cam N, Boudier T, Blondeau M, Leroy E, Cosmidis J, Skouri-Panet F, Guigner JM, Férard C, Poinsot M, Moreira D, Lopez-Garcia P, Cassier-Chauvat C, Chauvat F, Benzerara K (2016) Biomineralization patterns of intracellular carbonatogenesis in cyanobacteria: molecular hypotheses. Minerals. doi:10.3390/min6010010
Ludwig W, Strunk O, Westram R, Richter L, Meier H, Yadhukumar Buchner A, Lai T, Steppi S et al (2004) ARB: a software environment for sequence data. Nucleic Acids Res 32:1363–1371
Martίnez-Cánovas MJ, Quesada E, Llamas I, Béjar V (2004) Halomonas ventosae sp. nov., a moderately halophilic, denitrifying, exopolysaccharide-producing bacterium. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 54:733–737
Mata JA, Martίnez-Cánovas J, Quesada E, Béjar V (2002) A detailed phenotypic characterisation of the type strains of Halomonas species. Syst Appl Microbiol 25:360–375
Mesbah M, Premachandran U, Whitman WB (1989) Precise measurement of the G + C content of deoxyribonucleic acid by high-performance liquid chromatography. Int J Syst Bacteriol 39:159–167
Minnikin DE, ODonnell AG, Goodfellow M, Alderson G, Athalye M, Schaal A, Parlett JH (1984) An integrated procedure for the extraction of bacterial isoprenoid quinones and polar lipids. J Microbiol Methods 2:233–241
Ntougias S, Zervakis GI, Fasseas C et al (2007) Halotalea alkalilenta gen. nov., sp. nov., a novel osmotolerant and alkalitolerant bacterium from alkaline olive mill wastes, and emended description of the family Halomonadaceae Franzmann et al. 1989, emend. Dobson and Franzmann 1996. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:1975–1983
Okamoto T, Taguchi H, Nakamura K, Ikenaga H, Kuraishi H, Yamasato K (1993) Zymobacter palmae gen. nov., sp. nov., a new ethanol-fermenting peritrichous bacterium isolated from palm sap. Arch Microbiol 160:333–337
Peçonek J, Gruber C, Gallego V, Ventosa A, Busse H-J, Kämpfer P, Radax C, Stan-Lotter H (2006) Reclassification of Pseudomonas beijerinckii Hof 1935 as Chromohalobacter beijerinckii comb. nov., and emended description of the species. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 56:1953–1957
Pruesse E, Peplies J, Glöckner FO (2012) SINA: accurate highthroughput multiple sequence alignment of ribosomal RNA genes. Bioinformatics 28:1823–1829
Quesada E, Valderrama MJ, Béjar V, Ventosa A, Gutierrez MC, Ruiz-Berraquero F, Ramos-Cormenzana A (1990) Volcaniella eurihalina gen. nov., sp. nov., a moderately halophilic nonmotile gram-negative rod. Int J Syst Bacteriol 40:261–267
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425
Sánchez-Porro C, de la Haba RR, Soto-Ramírez N, Márquez MC, MontalvoRodríguez R, Ventosa A (2009) Description of Kushneria aurantia gen. nov., sp. nov., a novel member of the family Halomonadaceae, and a proposal for reclassification of Halomonas marisflavi as Kushneria marisflavi comb. nov., of Halomonas indalinina as Kushneria indalinina comb. nov. and of Halomonas avicenniae as Kushneria avicenniae comb. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 59:397–405
Smibert RM, Krieg NR (1994) Phenotypic characterization. In: Gerhardt P, Murray RGE, Wood WA, Krieg NR (eds) Methods for general, molecular bacteriology. American Society for Microbiology, Washington, DC, pp 607–654
Stamatakis A (2006) RAxML-VI-HPC: maximum likelihood-based phylogenetic analyses with thousands of taxa and mixed models. Bioinformatics 22:2688–2690
Stanier RY, Pallonier NJ, Doudoroff M (1966) The aerobic pseudomonadads: a taxonomic study. J Gen Microbiol 43:159–271
Tamura K, Stecher G, Peterson D, Filipsk A, Kumar S (2013) MEGA6: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Mol Biol Evol 30:2725–2729
Tindall BJ (1990a) A comparative study of the lipid composition of Halobacterium saccharovorum from various sources. Syst Appl Microbiol 13:128–130
Tindall BJ (1990b) Lipid composition of Halobacterium lacusprofundi. FEMS Microbiol Lett 66:199–202
Ventosa A, Gutierrez MC, Garcia MT, Ruiz-Berraquero F (1989) Classification of ‘‘Chromobacterium marismortui’’ in a new genus, Chromohalobacter gen. nov., as Chromohalobacter marismortui comb. nov., nom. rev. Int J Syst Bacteriol 39:382–386
Vreeland RH, Litchfield CD, Martin EL, Elliot E (1980) Halomonas elongata, a new genus and species of extremely salttolerant bacteria. Int J Syst Bacteriol 30:485–495
Wang Y, Tang SK, Lou K, Lee JC, Jeon CO, Xu LH, Kim CJ, Li WJ (2009) Aidingimonas halophila gen. nov., sp. nov., a moderately halophilic bacterium isolated from a salt lake. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 59:3088–3094
Yarza P, Richter M, Peplies J, Euzéby J, Amann R, Schleifer KH, Ludwig W, Glöckner FO, Rosselló-Móra R (2008) The all-species living tree project: a 16S rRNA-based phylogenetic tree of all sequenced type strains. Syst Appl Microbiol 31:241–250
Zhong FX, Ren HH, Li Y (2007) Comparison of methods in determination of polysaccaride content. Li Shi Zhen Medicion Mater Res 18:1916–1917
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31370057, 31290231) and 2013 Shandong Provincial Second Group Projects on Resource Platforms for Marine Economic and Innovative Development Regions: Marine Microorganisms Preservation Platform (2150299).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, ZX., Liang, QY., Lu, DC. et al. Pistricoccus aurantiacus gen. nov., sp. nov., a moderately halophilic bacterium isolated from a shark. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 109, 1593–1603 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-016-0760-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-016-0760-z