Abstract
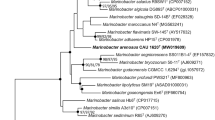
A novel Gram-stain-negative, rod-to-spiral-shaped, oxidase- and catalase- positive and facultatively aerobic bacterium, designated HS6T, was isolated from marine sediment of Yellow Sea, China. It can reduce nitrate to nitrite and grow well in marine broth 2216 (MB, Hope Biol-Technology Co., Ltd) with an optimal temperature for growth of 30–33 °C (range 12–45 °C) and in the presence of 2–3 % (w/v) NaCl (range 0.5–7 %, w/v). The pH range for growth was pH 6.2–9.0, with an optimum at 6.5–7.0. Phylogenetic analysis based on 16S rRNA gene sequences demonstrated that the novel isolate was 93.3 % similar to the type strain of Neptunomonas antarctica, 93.2 % to Neptunomonas japonicum and 93.1 % to Marinobacterium rhizophilum, the closest cultivated relatives. The polar lipid profile of the novel strain consisted of phosphatidylethanolamine, phosphatidylglycerol and some other unknown lipids. Major cellular fatty acids were summed feature 3 (C16:1 ω7c/iso-C15:0 2-OH), C18:1 ω7c and C16:0 and the main respiratory quinone was Q-8. The DNA G+C content of strain HS6T was 61.2 mol %. Based on the phylogenetic, physiological and biochemical characteristics, strain HS6T represents a novel genus and species and the name Motiliproteus sediminis gen. nov., sp. nov., is proposed. The type strain is HS6T (=ATCC BAA-2613T=CICC 10858T).


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arahal DR, Lekunberri I, González JM, Pascual J, Pujalte MJ, Pedrós-Alió C, Pinhassi J (2007) Neptuniibacter caesariensis gen. nov., sp. nov., a novel marine genome-sequenced gammaproteobacterium. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:1000–1006
Baumann P, Bowditch RD, Baumann L, Beaman B (1983) Taxonomy of marine pseudomonas species: P. stanieri sp. nov,; P. perfectomarina sp. nov., nom. rev.; P. nautica; and P. doudoroffii. Int J Syst Bacteriol 33:857–865
Chang HW, Nam YD, Kwon HY, Park JR, Lee JS, Yoon JH, An KG, Bae JW (2007) Marinobacterium halophilum sp. nov., a marine bacterium isolated from the Yellow Sea. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:77–80
Chen MH, Sheu SY, Chiu TF, Chen WM (2012) Neptuniibacter halophilus sp. nov., isolated from a salt pan, and emended description of the genus Neptuniibacter. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 62:1104–1109
Chimetto LA, Cleenwerck I, Brocchi M, Willems A, VOS DP, Thompson FL (2011) Marinobacterium coralli sp. nov., isolated from mucus of coral (Mussismilia hispida). Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 61:60–64
Cowan ST, Steel KJ (1965) Manual for the identification of medical bacteria. Cambridge University Press, London
Dimitriu PA, Shukla SK, Conradt J, Márquez MC, Ventosa A, Maglia A, Peyton BM, Pinkart HC, Mormile MR (2005) Nitrincola lacisaponensis gen. nov., sp. nov., a novel alkaliphilic bacterium isolated from an alkaline, saline lake. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 55:2273–2278
Garrity GM, Bell JA, Lilburn T (2005) Family I. Oceanospirillaceae fam nov. In: Garrity GM (ed) Bergey’s Manual of Systematic Bacteriology, 2nd edn. Springer, New York, pp 271–281
González JM, Mayer F, Moran MA, Hodson RE, Whitman WB (1997) Microbulbifer hydrolyticus gen. nov., sp. nov., and Marinobacterium georgiense gen. nov., sp. nov., two marine bacteria from a lignin-rich pulp mill waste enrichment community. Int J Syst Bacteriol 47:369–376
Hall TA (1999) BioEdit: a user-friendly sequence alignment editor and analysis program for windows 95/98/NT. Nucl Acids Symp Ser 41:95–98
Hedlund BP, Geiselbrecht AD, Bair TJ, Staley JT (1999) Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbon Degradation by a New Marine Bacterium, Neptunomonas naphthovorans gen. nov., sp. nov. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:251–259
Huo YY, Xu XW, Cao Y, Wang CS, Zhu XF, Oren A, WU M (2009) Marinobacterium nitratireducens sp. nov. and marinobacterium sediminicola sp. nov., isolated from marine sediment. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 59:1173–1178
Hylemon PB, Wells JS Jr, Krieg NR, Jannasch HW (1973) The genus Spirillum: A taxonomic study. Int J Syst Bacteriol 23:340–380
Kim H, Choo YJ, Song J, Lee JS, Lee KC, Cho JC (2007) Marinobacterium litorale sp. nov. in the order Oceanospirillales. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:1659–1662
Kim YG, Jin YA, Hwang CY, Cho BC (2008) Marinobacterium rhizophilum sp. nov., isolated from the rhizosphere of the coastal tidal-flat plant Suaeda japonica. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 58:164–167
Kim H, Oh HM, Yang SJ, Lee JS, Hong JS, Cho JC (2009a) Marinobacterium marisflavi sp. nov., isolated from a costal seawater. Curr Microbiol 58:511–515
Kim SJ, Park SJ, Yoon DN, Park BJ, Choi BR, Lee DH, Roh Y, Rhee SK (2009b) Marinobacterium maritimum sp. nov., a marine bacterium isolated from Arctic sediment. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 59:3030–3034
Kim JM, Lee SH, Jung JY, Jeon CO (2010) Marinobacterium lutimaris sp. nov., isolated from a tidal flat. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 60:1828–1831
Kim OS, Cho YJ, Lee K, Yoon SH, Kim M, Na H, Park SC, Jeon YS, Lee JH, Yi H, Won S, Chun J (2012) Introducing EzTaxon-e: a prokaryotic 16S rRNA gene sequence database with phylotypes that represent uncultured species. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 62:716–721
Lane DJ (1991) 16S/23S rRNA sequencing. In: Stackebrandt E, Goodfellow M (eds) Nucleic acid techniques in bacterial systematics. Wiley, Chichester, pp 115–175
Larkin MA, Blackshields G, Brown NP, Chenna R, McGettigan PA, McWilliam H, Valentin F, Wallace IM, Wilm A, Lopez R, Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Higgins DG (2007) Clustal W and Clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics 23:2947–2948
Lee HW, Shin NR, Lee J, Roh SW, Whon TW, Bae JW (2012) Neptunomonas concharum sp. nov., isolated from a dead ark clam, and emended description of the genus Neptunomonas. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 62:2657–2661
Liu A, Zhang XY, Chen CX, Xie BB, Qin QL, Liu C, Li GW, Li H, Xu Z, Chen XL, Zhou BC, Zhang YZ (2013) Neptunomonas qingdaonensis sp. nov., isolated from intertidal sand. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 63:1673–1677
Mesbah M, Premachandran U, Whitman WB (1989) Precise measurement of the G+C content of deoxyribonucleic acid by high-performance liquid chromatography. Int J Syst Bacteriol 38:159–167
Miyazaki M, Nogi Y, Fujiwara Y, Kawato M, Kubokawa K, Horikoshi K (2008) Neptunomonas japonica sp. nov., an Osedax japonicus symbiont-like bacterium isolated from sediment adjacent to sperm whale carcasses off Kagoshima, Japan. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 58:866–871
Murray RGE, Doetsch RN, Robinow F (1994) Determinative and cytological light microscopy. In: Gerhardt P, Murray RGE, Wood WA, Krieg NR (eds) Methods for general and molecular bacteriology. American Society for Microbiology, Washington, DC, pp 21–41
Sasser M (1990) Identification of bacteria by gas chromatography of cellular fatty acids. MIDI Technical Note 101. MIDI, Inc, Newark
Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S (2011) MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol 28:2731–2739
Tindall BJ (1990a) A comparative study of the lipid composition of Halobacterium saccharovorum from various sources. Syst Appl Microbiol 13:128–130
Tindall BJ (1990b) Lipid composition of Halobacterium lacusprofundi. FEMS Microbiol Letts 66:199–202
Tindall BJ, Sikorski J, Smibert RM, Kreig NR (2007) Phenotypic characterization and the principles of comparative systematics. In: Reddy CA, Beveridge TJ, Breznak JA, Marzluf G, Schmidt TM, Snyder LR (eds) Methods for general and molecular microbiology, 3rd edn. ASM press, Washington DC, pp 330–393
Zhang XY, Zhang YJ, Yu Y, Li HJ, Gao ZM, Chen XL, Chen B, Zhang YZ (2010) Neptunomonas antarctica sp. nov., isolated from marine sediment. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 60:1958–1961
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31370057, 31290231, 31370108) and the China Ocean Mineral Resources R & D Association (COMRA) Special Foundation (DY125-15-T-05). Z. J. Wang acknowledges grant of Graduate Innovation Foundation of Shandong University at WeiHai, GIFSDUWH yjs12037.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The GenBank accession number for the 16S rRNA gene sequence of Motiliproteus sediminis HS6T is KF953945.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, ZJ., Xie, ZH., Wang, C. et al. Motiliproteus sediminis gen. nov., sp. nov., isolated from coastal sediment. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 106, 615–621 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-014-0232-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-014-0232-2