Abstract
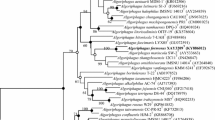
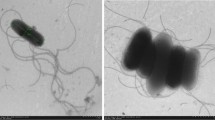
Two gram-positive, aerobic, spore-forming, rod-shaped bacteria, designated HB09003T and HB12160, were isolated from seawater and sediment in the northern South China Sea, respectively. Cells were found to be motile by means of peritrichous flagella. The strains were found to grow with 0–15 % (w/v) NaCl, at 10–45 °C and pH 5.0–10.7, with an optimum of 3 % NaCl, 28 °C and pH 8.5, respectively. The predominant isoprenoid quinone of strain HB09003T, selected as the representative strain, was identified as MK-7. This strain was found to possess anteiso-C15:0, iso-C15:0, anteiso-C17:0 and C16:0 as the major fatty acids. The G+C contents of strain HB09003T and HB12160 were determined to be 34.1 and 34.3 mol%, respectively. Analysis of the 16S rRNA gene sequences of the two strains showed an affiliation with the genus Gracilibacillus, with Gracilibacillus kekensis CGMCC 1.10681T (similarity of 97.4, 98.0 %, respectively) and Gracilibacillus ureilyticus CGMCC 1.7727T (similarity of 97.1, 97.8 %, respectively) as their closest relatives. The DNA–DNA hybridization values between strain HB09003T and the two type strains were 42.2 and 54.1 %, respectively. On the basis of phenotypic and genotypic data, strain HB09003T and HB12160 are proposed to represent a novel species of the genus Gracilibacillus, for which the name Gracilibacillus marinus sp. nov. is proposed. The type strain is HB09003T (=CGMCC 1.10343T = DSM 23372T).

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- MK:
-
Menaquinone
References
Ahmed I, Yokota A, Fujiwara T (2007) Gracilibacillus boraciitolerans sp. nov., a highly boron-tolerant and moderately halotolerant bacterium isolated from soil. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:796–802
Carrasco IJ, Márquez MC, Yanfen X, Ma Y, Cowan DA, Jones BE, Grant WD, Ventosa A (2006) Gracilibacillus orientalis sp. nov., a novel moderately halophilic bacterium isolated from a salt lake in Inner Mongolia, China. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 56:599–604
Chamroensaksri N, Tanasupawat S, Akaracharanya A, Visessanguan W, Kudo T, Itoh T (2010) Gracilibacillus thailandensis sp. nov., from fermented fish (pla-ra). Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 60:944–948
Chen Y, Cui X, Zhang Y, Li W, Wang Y, Xu L, Peng Q, Wen M, Jiang C (2008) Gracilibacillus halophilus sp. nov., a moderately halophilic bacterium isolated from saline soil. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 58:2403–2408
Christensen H, Angen O, Mutters R, Olsen JE, Bisgaard M (2000) DNA–DNA hybridization determined in micro-wells using covalent attachment of DNA. Int J Syst Evol Bacteriol 50:1095–1102
Chun J, Lee JH, Jung Y, Kim M, Kim S, Kim BK, Lim YW (2007) EzTaxon: a web-based tool for the identification of prokaryotes based on 16S ribosomal RNA gene sequences. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:2259–2261
Collins MD (1994) Isoprenoid quinones. In: Goodfellow M, O’Donnell AG (eds) Chemical methods in prokaryotic systematics. Wiley, Chichester, pp 265–309
Dong XZ, Cai MY (2001) Common bacterial system identification manual. Science (in Chinese), Beijing, pp 354–357
Ezaki T, Hashimoto Y, Yabuuchi E (1989) Fluorometric deoxyribonucleic acid-deoxyribonucleic acid hybridization in microdilution wells as an alternative to membrane filter hybridization in which radioisotopes are used to determine genetic relatedness among bacterial strains. Int J Syst Bacteriol 39:224–229
Felsenstein J (1981) Evolutionary trees from DNA sequences: a maximum likelihood approach. J Mol Evol 17:368–376
Felsenstein J (1985) Confidence limits on phylogenies: an approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 39:783–791
Fitch WM (1972) Toward defining the course of evolution: minimum change for a specific tree topology. Syst Zool 20:406–416
Gao M, Liu ZZ, Zhou YG, Liu HC, Ma YC, Wang L, Chen SF, Ji XC (2012) Gracilibacillus kekensis sp. nov., a moderate halophile isolated from Keke Salt Lake. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 62:1032–1036
Hasgawa T, Takizawa M, Tanida S (1983) A rapid analysis for chemical grouping of aerobic actinomycetes. J Gen Appl Microbiol 29:319–322
Heyndrickx M, Lebbe L, Kersters K, De Vos P, Forsyth G, Logan NA (1998) Virgibacillus: a new genus to accommodate Bacillus pantothenticus (Proom and Knight 1950). Emended description of Virgibacillus pantothenticus. Int J Syst Bacteriol 48:99–106
Holt JG, Krieg NR (1994) Enrichment and isolation. In: Gerhart P, Murray RGE, Wood WA, Krieg NR (eds) Methods for general and molecular bacteriology. American Society for Microbiology, Washington, DC, pp 179–215
Huo YY, Xu XW, Lin H, Wu M (2010) Gracilibacillus ureilyticus sp. nov., a halotolerant bacterium from saline-alkali soli in China. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 60:1383–1386
Javor B (1989) Hypersaline environments: microbiology and biogeochemistry. Springer, Berlin
Jeon CO, Lim JM, Jang HH, Park DJ, Xu LH, Jiang CL, Kim CJ (2008) Gracilibacillus lacisalsi sp. nov., a halophilic gram-positive bacterium from a salt lake in China. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 58:2282–2286
Kim P, Lee JC, Park DJ, Shin KS, Kim JY, Kim CJ (2012) Gracilibacillus bigeumensis sp. nov., a moderately halophilic bacterium from solar saltern soil. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 62:1857–1863
Komagata K, Suzuki KI (1987) Lipids and cell-wall analysis in bacterial systematics. Methods Microbiol 19:161–207
Kuykendall LD, Roy MA, O’Neill JJ, Devine TE (1988) Fatty acids, antibiotic resistance, and deoxyribonucleic acid homology groups of Bradyrhizobium japonicum. Int J Syst Bacteriol 38:358–361
Leifson E (1963) Determination of carbohydrate metabolism of marine bacteria. J Bacteriol 85:1183–1184
Minnikin DE, O’Donnell AG, Goodfellow M, Alderson G, Athalye M, Schaal A, Parlett JK (1984) An integrated procedure for the extraction of isoprenoid quinones and polar lipids. J Microbiol Methods 2:233–241
Pitcher DG, Saunders NA, Owen RJ (1989) Rapid extraction of bacterial genomic DNA with guanidinium thiocyanate. Lett Appl Microbiol 8:109–114
Reasoner DJ, Geldreich EE (1985) A new medium for the enumeration and subculture of bacteria from potable water. Appl Environ Microbiol 49:1–7
Ren PG, Zhou PJ (2005) Salinibacillus aidingensis gen. nov., sp nov and Salinibacillus kushneri sp nov., moderately halophilic bacteria isolated from a neutral saline lake in Xin-Jiang, China. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 55:949–953
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining methods: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425
Smibert RM, Krieg NR (1981) General characterization. In: Gerhardt P, Murray RGE, Costilow RN, Nester EW, Wood WA, Krieg NR, Phillips GB (eds) Manual of methods for general bacteriology. American Society for Microbiology, Washington, DC, pp 409–443
Stackebrandt E, Frederiksen W, Garrity GM et al (2002) Report of the ad hoc committee for the re-evaluation of the species definition in bacteriology. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 52:1043–1047
Tamaoka J, Komagata K (1984) Determination of DNA base composition by reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography. FEMS Microbiol Lett 25:125–128
Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S (2011) MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol 28:2731–2739
Tang SK, Wang Y, Lou K, Mao PH, Jin X, Jiang CL, Xu LH, Li WJ (2009) Gracilibacillus saliphilus sp. nov., a moderately halophilic bacterium isolated from a salt lake. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 59:1620–1624
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, Jeanmougin F, Higgins DG (1997) The GLUSTAL X windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res 25:4876–4882
Ventosa A, García MT, Kamekura M, Onishi H, Ruiz-Berraquero F (1989) Bacillus halophilus sp. nov., a moderately halophilic Bacillus species. Syst Appl Microbiol 12:162–165
Vreeland RH, Hochstein LI (1993) The biology of halophilic bacteria. CRC, Boca Raton
Wainø M, Tindall B, Schumann P, Ingvorsen K (1999) Gracilibacillus gen. nov., with description of Gracilibacillus halotolerans gen. nov., sp. nov.; transfer of Bacillus dipsosauri to Gracilibacillus dipsosauri comb. nov., and Bacillus salexigens to the genus Salibacillus gen. nov., as Salibacillus salexigens comb. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 49:821–831
Wayne LG, Brenner DJ, Colwell RR, International Committee on Systematic Bacteriology et al (1987) Report of the ad hoc committee on reconciliation of approaches to bacterial systematics. Int J Syst Bacteriol 37:463–464
Weisburg WG, Barns SM, Pelletier DJ, Lane DJ (1991) 16S ribosomal DNA amplification for phylogenetic study. J Bacteriol 173:697–703
Williams ST, Goodfellow M, Alderson G, Wellington EMH, Sneath PHA, Sackin MJ (1983) Numerical classification of Streptomyces and related genera. J Gen Microbiol 129:1743–1813
Xu LH, Li WJ, Liu ZH, Jiang CL (2007) Actinomycete taxonomy: principles, methods and practices. Science, Beijing
Yoon JH, Weiss N, Lee KC, Kang KH, Park YH (2001) Jeotgalibacillus alimentarius gen. nov., sp. nov., a novel bacterium isolated from jeotgal with l-lysine in the cell wall, and reclassification of Bacillus marinus Rüger 1983 as Marinibacillus marinus gen. nov., comb. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 51:2087–2093
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge the help of M Wu and S F Chen for offering the related two strains. This research was supported by grants from Haninan Major Technology Project (ZDZX2013023-1), the Foundation of Chinese National Program for High Technology Research and Development (2007AA09Z447) and National Non-profit Institute Research Grant of CATAS-ITBB from Chinese Government (1630052013004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Fig. S1
Scanning electron micrograph of cells from a 7-day-old culture of strain HB09003T grown on modified R2A agar at 28 °C. Bar 5 μm. (JPEG 25 kb)
Supplementary Fig. S2
Micrograph of strain HB09003T showing spore-forming rods. (JPEG 20 kb)
Supplementary Fig. S3
The polar lipids of strain HB09003T assayed by TLC plate method. The polar liquids consist of DPG diphosphatidylglycerol, PG phosphatidylglycerol, NPG unidentified phospholipids, AL amino-polar lipid and GL glycolipids. (JPEG 10 kb)
Supplementary Fig. S4
Maximum parsimony tree showing the relationship between strain HB09003T, HB12160 and the type strains of genus Gracilibacillus. Bootstrap values (1,000 replicates) are shown as percentages at each node for values; values > 50 % were shown. The scale bar represents 0.005 nucleotide substitutions per position. (DOC 42 kb)
Supplementary Fig. S5
Maximum likelihood tree showing the relationship between strain HB09003T, HB12160 and the type strains of genus Gracilibacillus. Bootstrap values (1,000 replicates) are shown as percentages at each node for values; values > 50 % were shown. The scale bar represents 0.005 nucleotide substitutions per position. (DOC 42 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, Hq., Wang, Y., Yuan, Wd. et al. Gracilibacillus marinus sp. nov., isolated from the northern South China Sea. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 104, 695–701 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-013-9977-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-013-9977-2