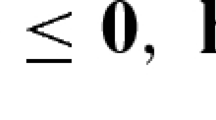Abstract
We present a branch-and-bound algorithm for discretely-constrained mathematical programs with equilibrium constraints (DC-MPEC). This is a class of bilevel programs with an integer program in the upper-level and a complementarity problem in the lower-level. The algorithm builds on the work by Gabriel et al. (Journal of the Operational Research Society 61(9):1404–1419, 2010) and uses Benders decomposition to form a master problem and a subproblem. The new dynamic partition scheme that we present ensures that the algorithm converges to the global optimum. Partitioning is done to overcome the non-convexity of the Benders subproblem. In addition Lagrangean relaxation provides bounds that enable fathoming in the branching tree and warm-starting the Benders algorithm. Numerical tests show significantly reduced solution times compared to the original algorithm. When the lower level problem is stochastic our algorithm can easily be further decomposed using scenario decomposition. This is demonstrated on a realistic case.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Audet, C., Savard, G., & Zghal, W. (2007). New branch-and-cut algorithm for bilevel linear programming. Journal of Optimization Theory and Applications, 134, 353–370.
Bard, J. F., & Moore, J. T. (1990). A branch and bound algorithm for the bilevel programming problem. SIAM Journal on Scientific and Statistical Computing, 11(2), 281–292.
Benders, J. F. (1962). Partitioning procedures for solving mixed-variables programming problems. Numerische Mathematik, 4, 238–252.
Carøe, C. C., & Schultz, R. (1999). Dual decomposition in stochastic integer programming. Operations Research Letters, 24, 37–45.
Colson, B., Marcotte, P., & Savard, G. (2007). An overview of bilevel optimization. Annals of Operations Research, 153, 235–256.
Conejo, A. J., Castillo, E., Minguez, R., & García-Bertrand, R. (2006). Decomposition techniques in mathematical programming: engineering and science application. Berlin: Springer. ISBN: 978-3-540-27685-2.
Dempe, S. (2002). Foundations of bilevel programming. New York: Kluwer Academic.
DeNegre, S. T., & Ralphs, T. K. (2009). A branch-and-cut algorithm for integer bilevel linear programs. Operations Research/Computer Science Interfaces, 47, 65–78.
Falk, J. E. (1969). Lagrange multipliers and nonconvex programs. SIAM Journal on Control, 7(4), 534–545.
Fortuny-Amat, J., & McCarl, B. (1981). A representation and economic interpretation of a two-level programming problem. The Journal of the Operational Research Society, 32(9), 783–792.
Fukushima, M., & Lin, G.-H. (2004). Smoothing methods for mathematical programs with equilibrium constraints. In Proceedings of the ICKS’04 (pp. 206–213). Los Alamitos: IEEE Comput. Soc.
Gabriel, S. A., & Leuthold, F. U. (2010). Solving discretely-constrained MPEC problems with applications in electric power markets. Energy Economics, 32(1), 3–14.
Gabriel, S. A., Shim, Y., Conejo, A. J., de la Torre, S., & Garcia-Bertrand, R. (2010). A Benders decomposition method for discretely-constrained mathematical programs with equilibrium constraints with applications in energy. The Journal of the Operational Research Society, 61(9), 1404–1419.
Geoffrion, A. M. (1974). Lagrange relaxation for integer programming. Mathematical Programming Study, 2, 82–114.
Hansen, P., Jaumard, B., & Savard, G. (1992). New branch-and-bound rules for linear bilevel programming. SIAM Journal on Scientific and Statistical Computing, 13, 1194–1217.
Hu, J., Mitchell, J. E., Pang, J., Bennett, K. P., & Kunapuli, G. (2008). On the global solution of linear programs with linear complementarity constraints. SIAM Journal of Optimization, 19(1), 445–471.
Labbé, M., Marcotte, P., & Savard, G. (1998). A bilevel model of taxation and its application to optimal highway pricing. Management Science, 44(12), 1608–1622.
Luo, Z. Q., Pang, J. S., & Ralph, D. (1996). Mathematical programs with equilibrium constraints. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN: 0-521-57290-8.
Meng, Q., & Wang, X. (2011). Intermodal hub-and-spoke network design: incorporating multiple stakeholders and multi-type containers. Transportation Research. Part B, 45(4), 724–742.
Meng, Q., Huang, Y., & Cheu, R. L. (2009). Competitive facility location on decentralized supply chains. European Journal of Operational Research, 196, 487–499.
Mesbah, M., Sarvi, M., Ouveysi, I., & Currie, G. (2011). Optimization of transit priority in the transportation network using a decomposition methodology. Transportation Research. Part C, 19, 363–373.
Midthun, K. T. (2007). Optimization models for liberalized natural gas markets. PhD thesis 2007:205. Trondheim, Norway: Norwegian University of Science and Technology. URL: http://ntnu.diva-portal.org/smash/get/diva2:123659/FULLTEXT01.
Mitsos, A. (2010). Global solution of nonlinear mixed-integer bilevel programs. Journal of Global Optimization, 47(4), 557–582.
Moore, J. T., & Bard, J. F. (1990). The mixed integer linear bilevel programming problem. Operations Research, 38, 911–921.
Outrata, J., Kocvara, M., & Zowe, J. (1998). Nonsmooth approach to optimization problems with equilibrium constraints: theory, applications and numerical results. Boston: Kluwer Academic. ISBN: 978-0-7923-5170-2.
Rockafellar, R. T., & Wets, R. J.-B. (1976). Nonanticipativity and l1-martingales in stochastic optimization problems. Mathematical Programming Study, 6, 170–187.
Saharidis, G. K., & Ierapetritou, M. G. (2009). Resolution method for mixed bilevel linear problems based on decomposition technique. Journal of Global Optimization, 44, 29–51.
Saharidis, G. K., & Ierapetritou, M. G. (2010). Improving Benders decomposition using maximum feasible subsystem (MFS) cut generation strategy. Computers and Chemical Engineering, 34, 1237–1245.
Saharidis, G. K., Boile, M., & Theofanis, S. (2011). Initialization of the Benders master problem using valid inequalities applied to fixed-charge network problems. Expert Systems with Applications, 38, 6627–6636.
van Roy, T. J. (1983). Cross decomposition for mixed integer programming. Mathematical Programming, 25, 46–63.
van Roy, T. J. (1986). A cross decomposition algorithm for capacitated facility location. Operations Research, 34(1), 145–163.
Wang, D. Z. W., & Lo, H. K. (2008). Multi-fleet ferry service network design with passenger preferences for differential services. Transportation Research. Part B, 42, 798–822.
Wen, U. P., & Yang, Y. H. (1990). Algorithms for solving the mixed integer two-level linear programming problem. Computers and Operations Research, 17(2), 133–142.
Acknowledgements
The project is partially supported by the Research Council of Norway under grant 175967/S30.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendix
Appendix
Theorem 2
The solution of (SP) from the Benders decomposition algorithm provides an upper bound on z MILP=d T x+d T y for any given partition, and the optimal solution z MILP=d T x ∗+d T y ∗ for any partition where α(x) is convex.
Proof
By the assumption (A2) any x (v) which is a feasible in (MP) is also feasible in (MILP). For a given x (v) the feasible region of (SP) is identical to the feasible region for the variables \(y, z, \bar {b}\) and \(\tilde{b}\) of (MILP), which makes a solution of (SP) feasible in (MILP). And since the function z up(x (v)) is identical to the objective function of (MILP), it is an upper bound of (MILP). Benders (1962) proves that Benders decomposition algorithm converges to the optimal solution in the case of a convex α(x). □
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shim, Y., Fodstad, M., Gabriel, S.A. et al. A branch-and-bound method for discretely-constrained mathematical programs with equilibrium constraints. Ann Oper Res 210, 5–31 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-012-1191-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-012-1191-5