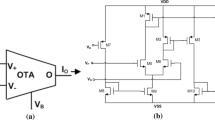
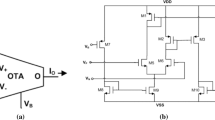
Abstract
In this paper, memristor emulator circuit which is built with off the shelf electronic devices is presented. It consists of three operational transconductance amplifiers (OTA) and four second generation current conveyors (CCII). Using OTA offers an extra control parameter, operational transconductance parameter (gm), in addition to frequency (f) and amplitude value of voltage across emulator (v m ). Since gm is proportional to current flowing through the bias terminal of OTA, it is possible to change the memristance variation via a simple change of amplitude value. Since gm parameter is adjustable via an external dc voltage/current source, the memristance of presented emulator circuit is electronically tuneable. Mathematical model is derived to characterize the behaviour of the emulator circuit. Frequency analysis is performed to determine how to maintain the pinched hysteresis loop at high frequencies. The presented emulator circuit is simulated with SPICE simulation program. The breadboard experiment of emulator circuit is built using CA3080 and AD844 ICs for OTA and CCII devices respectively. Frequency dependent pinched hysteresis loop in the current versus voltage plane holds up to 10 kHz. Mathematical model and theoretical analyses show a good agreement with SPICE simulation and experimental test results.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chua, L. O. (1971). Memristor-the missing circuit element. IEEE Transactions on Circuit Theory, 18(5), 507–519.
Chua, L. O., & Kang, S. M. (1976). Memristive devices and systems. Proceedings of the IEEE, 64(2), 209–223.
Strukov, D. B., Snider, G. S., Stewart, D. R., & Williams, R. S. (2008). The missing memristor found. Nature, 453, 80–83.
Di Ventra, M., Pershin, Y. V., & Chua, L. O. (2009). Circuit elements with memory: Memristors, memcapacitors, and meminductors. Proceedings of the IEEE, 97(10), 1717–1724.
Kim, H., Sah, M. P., Yang, C., Roska, T., & Chua, L. O. (2012). Memristor bridge synapses. Proceedings of the IEEE, 100(6), 2061–2070.
Pershin, Y. V., & Di Ventra, M. (2012). Neuromorphic, digital, quantum computation with memory circuit elements. Proceedings of the IEEE, 100(6), 2071–2080.
Merrikh-Bayat, F., Bagheri-Shouraki, S., & Rohani, A. (2011). Memristor crossbar-based hardware implementation of IDSmethod. EEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 19(6), 1083–1096.
Shin, S., Kim, K., & Kang, S. M. (2013). Resistive computing: Memristors enabled signal multiplication. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers, 60(5), 1241–1249.
Talukdar, A., Radwan, A., & Salama, K. (2011). A memristor-based third-order oscillator: Beyond oscillation. Applied Nanoscience, 1(3), 1–3.
Yilmaz, Y., & Mazumder, P. (2013). Image processing by a programmable grid comprising quantum dots and memristors. IEEE Transactions on Nanotechnology, 12(6), 879–887.
Sedra, A., & Smith, K. (1970). A second-generation current conveyor and its applications. IEEE Transactions on Circuit Theory, 17(1), 132–134.
Zhang, Y., Zhang, X., & Yu, J. (2009). Approximated SPICE model for memristor. In International conference on communications, circuits and systems (ICCCAS), Milpitas, CA (pp. 928–931).
Benderli, S., & Wey, T. A. (2009). On SPICE macromodelling of TiO2 memristors. Electronics Letters, 45(7), 377–379.
Biolek, D., Biolek, Z., & Biolkova, V. (2009). SPICE modeling of memristive, memcapacitative and meminductive systems. In Proceedings of the European conference on circuits theory and design (ECCTD’09), Antalya, Turkey (pp. 249–252).
Mahvash, M., & Parker, A. (2010). A memristor SPICE model for designing memristor circuits. In Proceedings of the 53rd IEEE international midwest symposium on circuits and systems (MWSCAS), Seattle,USA (pp. 989–992).
Batas, D., & Fiedler, H. (2011). A memristor SPICE implementation and a new approach for magnetic flux-controlled memristor modeling. IEEE Transactions on Nanotechnology, 10(2), 250–255.
Rak, A., & Cserey, G. (2010). Macromodelling of the memristor in SPICE. IEEE Transactions on Computer-Aided Design of Integrated Circuits and Systems, 29(4), 632–636.
Sharifi, M. J., & Banadaki, Y. M. (2010). General SPICE models for memristor and application to circuit simulation of memristor-based synapses and memory cells. Journal of Circuits, Systems and Computers, 19(2), 407–424.
Abdalla, H., & Pickett, M. D. (2011). SPICE modelling of memristors. In IEEE international symposium on circuits and systems (ISCAS), Rio de Janeiro (pp. 1832–1835).
Abraham, I., Kaya, S., & Pennington, G. (2012). A closed form memristor SPICE model and oscillator. In IEEE 55th international midwest symposium on circuits and systems (MWSCAS), Boise, ID (pp. 1192–1195).
Jameel, S., Koraslı, C., & Nacaroglu, A. (2013). Realization of biquadratic filter by using memristor. In International conference on technological advances in electrical, electronics and computer engineering, (TAEECE), Konya, Turkey (pp. 52–56).
Ascoli, A., Tetzlaf, R., Corinto, F., & Gilli, M. (2013). PSpice switch-based versatile memristor model. In IEEE international symposium on circuits and systems, (ISCAS), Beijing (pp. 205–208).
Berdan, R., Lim, C., Khiat, A., Papavassiliou, C., & Prodromakis, T. (2014). A memristor SPICE model accounting volatile characteristics of practical ReRAM. IEEE Electron Device Letters, 35(1), 135–137.
Biolek, D., Biolek, Z., & Biolkova, V. (2010). Pspice modeling of memcapacitor. Electronics Letters, 46(7), 520–522.
Biolek, D., Biolek, Z., & Biolkova, V. (2011). Pspice modeling of meminductor. Analog Integrated Circuits and Signal Processing, 66(1), 129–137.
Bo-Cheng, B., Jian-Ping, X., Gua-Hua, Z., Zheng-Hua, M., & Ling, Z. (2011). Chaotic memristive circuit: Equivalent circuit realization and dynamical analysis. Chinese Physics B, 20(12), 120502-1–120502-6.
Pershin, Y. V., & Di Ventra, M. (2010). Practical approach to programmable analog circuits with memristors. IEEE Transactions Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers, 57(8), 1857–1864.
Biolek, D., Bajer, J., Biolkova, V., & Kolka, Z. (2011). Mutators for transforming nonlinear resistor into memristor. In 20th European conference on circuit theory and design (ECCTD) (pp. 488–491).
Valsa, J., Biolek, D., & Biolek, Z. (2011). An analogue model of the memristor. International Journal of Numerical Modelling, 24(4), 400–408.
Kim, H., Sah, M. P., Yang, C., Cho, S., & Chua, L. O. (2012). Memristor emulator for memristor circuit applications. IEEE Transactions Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers, 59(10), 2422–2431.
Mutlu, R., & Karakulak, E. (2010). Emulator circuit of TiO2 memristor with linear dopant drift made using analog multiplier. In National conference on electrical, electronics and computer engineering (ELECO), Bursa, Turkey (pp. 380–384).
Abuelma’atti, M. T., & Khalifa, Z. J. (2014). A new memristor emulator and its application in digital modulation. Analog Integrated Circuits Signal Processing, 80, 577–584.
Abuelma’atti, M. T., & Khalifa, Z. J. (2015). A continuous-level memristor emulator and its application in a multivibrator circuit. International Journal of Electronics and Communications, 69, 771–775.
Yu, D. S., Chen, H., & Iu, H. C. (2013). Design of a practical memcapacitor emulator without grounded restriction. IEEE Transaction On Circuits and Systems- II, 60(4), 207–211.
López, S. C., López, J. M., Carrasco-Aguilar, M. A., & Montero, M. C. (2014). A floating analog memristor emulator circuit. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs, 61(5), 309–313.
Yu, D., Iu, H., Fitch, A. L., & Liang, Y. (2014). A floating memristor emulator based relaxation oscillator. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers, 61(10), 2888–2896.
Yu, D. S., Chen, H., & Iu, H. H. C. (2013). A meminductive circuit based on floating memristive emulator. In IEEE international symposium on circuits and systems (ISCAS), Beijing (pp. 1692–1695).
Elwakil, A. S., Fouda, M. E., & Radwan, A. G. (2013). A simple model of double-loop hysteresis behavior in memristive elements. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs, 60(8), 487–491.
Yesil, A., Babacan, Y., & Kacar, F. (2014). A new DDCC based memristor emulator circuit and its applications. Microelectronics Journal, 45(3), 282–287.
Sozen, H., & Cam, U. (2015). New memristor emulator circuit using OTAs and CCIIs. In International conference on electrical and electronics engineering, Bursa, Turkey.
Martinez, J. S., & Sinencio, E. S. (1986). Analogue OTA multiplier without input voltage swing restrictions, and temperature-compensated. Electronics Letters, 22(11), 599–600.
Data Sheet CA3080. www.intersil.com.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sözen, H., Çam, U. Electronically tunable memristor emulator circuit. Analog Integr Circ Sig Process 89, 655–663 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-016-0785-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-016-0785-2