Abstract
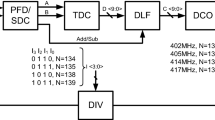
A fast-settling all-digital phase-locked loop (ADPLL) is presented in this paper. We propose two techniques for reducing the settling time of an ADPLL, i.e. the oscillator tuning word (OTW) presetting technique and counter-based mode switching controller (CB-MSC). In the first technique, the OTW is preset in process, voltage, and temperature (PVT) calibration mode (P-mode), which leads to the digitally controlled oscillator being initialized with a frequency closer to the target. In the second technique, the CB-MSC is used to shorten the mode switching time. A prototype 1.9 GHz ADPLL with a 13 MHz reference is implemented in 0.18 μm CMOS process. Measurements show that the proposed techniques reduce the settling time by about 33 %. The proposed ADPLL settles within 130 reference cycles and presents a phase noise of −116 dBc/Hz@1 MHz.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Staszewski, R., Muhammad, K., Leipold, D., Hung, C. M., Ho, Y. C., Wallberg, J., Fernando, C., Maggio, K., Staszewski, R., Jung, T., Koh, J., John, S., Deng, I. Y., Sarda, V., Moreira-Tamayo, O., Mayega, V., Katz, R., Friedman, O., Eliezer, O., de Obaldia, E., & Balsara, P. (2004). All-digital TX frequency synthesizer and discrete-time receiver for Bluetooth radio in 130-nm CMOS. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits 39(12), 2278–2291. doi:10.1109/JSSC.2004.836345.
Kim, D. S., Song, H., Kim, T., Kim, S., & Jeong, D. K. (2010). A 0.3–1.4 GHz all-digital fractional-N PLL with adaptive loop gain controller. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits 45(11), 2300–2311. doi:10.1109/JSSC.2010.2064050.
Staszewski, R., Wallberg, J., Rezeq, S., Hung, C. M., Eliezer, O., Vemulapalli, S., Fernando, C., Maggio, K., Staszewski, R., Barton, N., Lee, M. C., Cruise, P., Entezari, M., Muhammad, K., & Leipold, D. (2005). All-digital PLL and transmitter for mobile phones. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits 40(12), 2469–2482. doi:10.1109/JSSC.2005.857417.
Staszewski, R. B., & Balsara, P. T. (2007). All-digital PLL with ultra fast settling. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs 54(2), 181–185. doi:10.1109/TCSII.2006.886896.
Xu, L., Stadius, K., & Ryynanen, J. (2012). An all-digital PLL frequency synthesizer with an improved phase digitization approach and an optimized frequency calibration technique. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers PP(99), 1. doi:10.1109/TCSI.2012.2189055.
Yang, S. Y., Chen, W. Z., & Lu, T. Y. (2010). A 7.1 mW, 10 GHz all digital frequency synthesizer with dynamically reconfigured digital loop filter in 90 nm CMOS technology. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits 45(3), 578–586. doi:10.1109/JSSC.2009.2039530.
Lee, J. Y., Park, M. J., Min, B. H., Kim, S., Park, M. Y., & Yu, H. K. (2012). A 4-GHz all digital PLL with low-power TDC and phase-error compensation. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers 59(8), 1706–1719. doi:10.1109/TCSI.2012.2206500.
Yu, G., Wang, Y., Yang, H., & Wang, H.(2009). A fast-locking all-digital phase-locked loop with a novel counter-based mode switching controller. In IEEE Region 10 Conference TENCON (pp. 1–5). doi:10.1109/TENCON.2009.5396168.
Yu, G., Wang, Y., Yang, H., & Wang, H. (2010). Fast-locking all-digital phase-locked loop with digitally controlled oscillator tuning word estimating and presetting. IET Circuits, Devices Systems 4(3), 207–217. doi:10.1049/iet-cds.2009.0173.
Staszewski, R., Wallberg, J., Koh, J., & Balsara, P. (2004). High-speed digital circuits for a 2.4 GHz all-digital RF frequency synthesizer in 130 nm CMOS. In Proceedings of the 2004 IEEE Dallas/CAS Workshop. Implementation of High Performance Circuits (DCAS-04) (pp. 167–170). doi:10.1109/DCAS.2004.1360452.
Staszewski, R.B., & Balsara, P.T. (2006). All-digital frequency synthesizer in deep-submicron CMOS. New York: Wiley-Interscience.
Yu, G., Wang, Y., & Yang, H. (2011). A low power time-to-digital converter for all-digital phase-locked loop. Journal of Electronics (China) 28(3), 402–408.
Zhao, B., Lian, Y., & Yang, H. (2013). A low-power fast-settling bond-wire frequency synthesizer with a dynamic-bandwidth scheme. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers PP(99), 1–12. doi:10.1109/TCSI.2013.2249177.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation funded project under Grant 2012T50091 and Grant 2011M500308, the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) under Grant 61204032 and Grant 61261160501, 973 program under Grant 2013CB329000, and Tsinghua University Initiative Scientific Research Program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, B., Yu, G., Lian, Y. et al. A 1.9 GHz ADPLL with 130 reference cycles settling time in 0.18 μm CMOS technology. Analog Integr Circ Sig Process 76, 81–89 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-013-0070-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-013-0070-6