Abstract
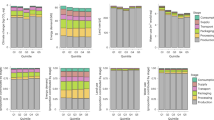
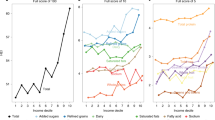
In this paper, we redefine the term luxus consumption to mean food waste and overconsumption leading to storage of body fat, health problems, and excess resource utilization. We develop estimates of the prevalence of luxus consumption and its environmental consequences using US food supply, agricultural, and environmental data and using procedures modeled after energetics analysis and ecological footprint analysis. Between 1983 and 2000, US food availability (food consumption including waste) increased by 18% or 600 kcal (2.51 MJ) per person. This luxus consumption required 0.36 hectares (ha) of land and fishing area per capita, 100.6 million ha for the US population, and 3.1% of total US energy consumption. Luxus consumption increased more for particular foods, such as high fructose corn syrup (HFCS), 22% of which was used in carbonated beverages. As an example, the luxus consumption of sweetened soda, 31.8 l per capita, used 0.8% of the US corn crop (230,555 ha of land); 33.6 million kg of nitrogen fertilizer; 175,000 kg of Atrazine herbicide; 34 million kg of nitrogen fertilizer; 2.44 trillion kcal (10.2 PJ) for production inputs and post-harvest handling; and led to 4.9 million metric tons of soil erosion. Diet soft drink luxus consumption was 43.9 l/capita. Assuming half of US soft drink luxus consumption was bottled in plastic, the energy cost for plastics would have been 2.49 trillion kcal (10.4 PJ) in 2000. Total HFCS availability above baseline in 2000 required 4.6 times the resources used for soft drinks alone. This analysis suggests the utility and applicability of the concept of luxus consumption to environmental analysis and for estimating the effects of excess food utilization.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BMI:
-
Body Mass Index
- BRFSS:
-
Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System
- Bt:
-
Bacillus Thuringiensis
- CSFII:
-
USDA Continuing Survey of Food Intakes of Individuals
- EJ:
-
etajoule (1018)
- GJ:
-
gigajoule (109)
- ha:
-
hectare
- HFCS:
-
High Fructose Corn Syrup
- kcal:
-
kilocalorie
- kg:
-
kilograms
- l:
-
liter
- MJ:
-
megajoule (106)
- NHANES:
-
National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys
- PJ:
-
petajoule (1015)
- TJ:
-
terajoule (1012)
- USFSD:
-
United States Food Supply Data
References
American Plastics Council (2002). “PlasticsResource.Com: Plastics 101: Uses of plastics.” Arlington, Virginia: American Plastics Council, Inc. Accessed July 23, 2003 at http://www.plasticsresource.com/s_plasticsresource/sec.asp?TRACKID=& CID=125&DID=227.
D. Blair (1996) “Eating in the Bioregion” J. Chesworth (Eds) The Ecology of Health: Identifying Issues and Alternatives Sage Publications Thousand Oaks, California 297–307
G. A. Bray S. J. Nielsen B. M. Popkin (2004) ArticleTitle“Consumption of high fructose corn syrup in beverages may play a role in the epidemic of obesity” American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 79 537–543
F. H. Buttel (1992) ArticleTitle“Environmentalization: Origins, processes, and implications for rural social change” Rural Sociology 57 IssueID1 1–27
M. Carley P. Spapens (1998) Sharing the World: Sustainable Living and Global Equity in the 21st Century St. Martins Press New York, New York
CDC (US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention) (2003). “US obesity trends: 1985–2001.” Atlanta, Georgia: Nutrition and Physical Activity. Accessed June 16, 2003 at http://www.cdc.gov/nccdphp/dnpa/obesity/trend/maps/index.htm.
N. Chambers C. Simmons M. Wachernagel (2000) Sharing Nature’s Interest: Ecological Footprints as an Indicator of Sustainability Earthscan Publications, Ltd London, United Kingdom
G. A. Colditz (1992) ArticleTitle“Economic costs of obesity” American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 155 503S–507S
Corn Refiners Association (2002). “The corn refining process.” Washington DC: Corn Refiners Association, Inc. Accessed June 18, 2003 at http://www.corn.org/web/process.htm.
EIA (US Energy Information Administration) (2003). “Renewables: US energy consumption by energy source, 1997–2001.” Washington DC: Energy Information Administration, Department of Energy. Accessed June 17, 2003 at http://www.eia.doe.gov/cneaf/solar.renewables/page/rea_data/ table1.html.
S. S. Elliott N. L. Keim J. S. Stern K. Teff P. Havel (2002) ArticleTitle“Fructose, weight gain, and the insulin resistance syndrome” American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 76 911–922
C. Enns J. Wilkenson D. Goldman A. Cook (1997) ArticleTitle“Trends in food and nutrient intakes by adults: NFCS 1977–78, CSFII 1989–91, and CSFII 1994–95” Family Economics and Nutrition Review 10 IssueID4 2–15
EPA (US Environmental Protection Agency) (2002). “Product stewardship: Packaging: Industry initiatives.” Washington DC: US Environmental Protection Agency. Accessed on June 23, 2003 at http://www.epa.gov/epaoswer/non-hw/reduce/epr/products/pindust.html.
EPA (US Environmental Protection Agency) (2003). “Charge to the FIFRA Scientific Advisory Panel: Atrazine carcinogenicity, June 27–29, 2000.” Washington DC: Scientific Advisory Panel, US Environmental Protection Agency. Accessed on June 23, 2003, at http://www.epa.gov/scipoly/sap/2000/june27/charge.htm.
ERS (US Economic Research Service) (2002). “Data: Food consumption (per capita) data system.” Washington DC: Economic Research Service, US Department of Agriculture. Accessed on June 27, 2003 at http://www.ers.usda.gov/data/foodconsumtion/.
ERS (US Economic Research Service) (2003). “US food supply: Food supply data base.” Washington DC: Economic Research Service, US Department of Agriculture. Accessed on June 24, 2003 at http://www.ers.usda.gov/data/foodcon sumption/FoodAvailIndex.htm.
H. C. Farnsworth (1961) ArticleTitle“Defects, uses, and abuses of national food supply and consumption data” Food Research Institute Studies 2 179–201
A. R. B. Ferguson (2002) ArticleTitle“The assumptions underlying eco-footprinting” Population and Environment 23 IssueID3 3003–3013 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1013051713184
K. M. Flegal M. D. Carrol R. J. Kuczmarski C. L. Johnson (1998) ArticleTitle“Overweight and obesity in the United States: Prevalence and trends, 1960–1994” International Journal of Obesity 22 39–47 Occurrence Handle10.1038/sj.ijo.0800541
Gallo, A. E. (1980). “Consumer food waste in the United States.” National Food Review (Fall): 13–16.
R. S. Gibson (1990) Principles of Nutritional Assessment Oxford University Press New York, New York
R. A. Gordon (1990) Anorexia and Bulimia: Anatomy of a Social Epidemic Basil Blackwell Cambridge, Massachusetts
J. D. Gussow (1999) ArticleTitle“Dietary guidelines for sustainability: Twelve years later” Journal of Nutrition Education 31 194–200
A. A. Hedley C. L. Ogden C. L. Johnson M. D. Carroll L. R. Curtin K. M. Flegal (2004) ArticleTitle“Prevalence of overweight and obesity among US children, adolescents, and adults” Journal of the American Medical Association 291 IssueID23 2847–2850 Occurrence Handle10.1001/jama.291.23.2847
Information Ventures (2003). “Atrazine: Pesticide fact sheet prepared for the US Department of Agriculture Forest Services.” Information Ventures, Inc. Accessed on June 23, 2003 at http://infoventures.com/e-hlth/pestcide/atrazine.html.
L. S. Kantor K. Lipton A. Manchester V. Oliveria (1997) ArticleTitle“Estimating and addressing America’s food losses” Food Review 20 IssueID1 2–12
A. Kimbrell (Eds) (2002) Fatal Harvest: The Tragedy of Industrial Agriculture Island Press Washington DC
R. Lal F. P. Miller T. J. Logan (1988) ArticleTitle“Are intensive agricultural practices environmentally and ethically sound?” Journal of Agricultural Ethics 1 143–210 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF01833409
A. H. Mokdad B. A. Bowman E. S. Ford F. Vinicor J. S. Marks J. P. Koplan (2001) ArticleTitle“The continuing epidemics of obesity and diabetes in the United States” Journal of the American Medical Association 286 1195–1200 Occurrence Handle10.1001/jama.286.10.1195
A. H. Mokdad E. S. Ford B. A. Bowman W. H. Dietz F. Vinicor V. S. Bales J. S. Marks (2003) ArticleTitle“Prevalence of obesity, diabetes, and obesity-related health risk factors, 2001” Journal of the American Medical Association 289 76–79 Occurrence Handle10.1001/jama.289.1.76
A. H. Mokdad M. K. Serdula W. H. Dietz B. A. Bowman J. S. Marks J. P. Koplan (1999) ArticleTitle“The spread of the obesity epidemic in the United States, 1991–1998” Journal of the American Medical Association 282 IssueID16 1519–1522 Occurrence Handle10.1001/jama.282.16.1519
A. Must J. Spadano E. H. Coakley A. E. Field G. Colditz W. H. Dietz (1999) ArticleTitle“The disease burden associated with overweight and obesity” Journal of the American Medical Association 282 IssueID16 1523–1529 Occurrence Handle10.1001/jama.282.16.1523
NASS (US National Agricultural Statistics Service) (2001). “Agricultural chemical usage: 2000 Field crops summary.” Washington DC: National Agricultural Statistics Service, US Department of Agriculture. Accessed on June 23, 2003 at http://usda.mannlib.cornell.edu/reports/nassr/other/pcu-bb/agcs0501.txt.
NASS (US National Agricultural Statistics Service) (2002). “2000–2001 Statistical highlights of US agriculture: Field crops: Acreage, yield, production, price, value and stocks.” Washington DC: National Agricultural Statistics Service, US Department of Agriculture. Accessed on June 18, 2003 at http://www.usda.gov/nass/pubs/stathigh/2001/tables/crops_1.htm.
H. Nawaz W. Chan M. Abdulrahman D. Larson D. L. Katz (2001) ArticleTitle“Self-reported weight and height: Implications for obesity research” American Journal of Preventive Medicine 20 294–298 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0749-3797(01)00293-8
NCHS (US National Center for Health Statistics) (2002). “Health E-Stats – Prevalence of overweight and obesity among adults: United States, 1999–2000.” Hyattsville, Maryland: National Center for Health Statistics, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Accessed on January 8, 2003 at http://www.cdc.gov/nchs/products/pubs/pubd/hestats/obese/obse99.htm.
InstitutionalAuthorNameNIH (National Institutes of Health) (1985) ArticleTitle“Health implications of obesity: National Institutes of Health Consensus Development Conference Statement” Annals of Internal Medicine 103 1073–1077
J. A. Pennington (1998) Bowes and Church Food Values of Portions Commonly Used 7. Lippencott-Raven Publishers Philadelphia, Pennsylvania
D. Pimentel M. Pimentel (Eds) (1996) Food, Energy and Society, Revised Edition University Press of Colorado Niwot, Colorado
F. X. Pi-Sunyer (1993) ArticleTitle“Medical hazards of obesity” Annals of Internal Medicine 119 655–660
E. Pollitt P. Amante (Eds) (1984) Energy Intake and Activity Alan R. Liss, Inc. New York, New York
B. M. Popkin C. M. Doak (1998) ArticleTitle“The obesity epidemic is a worldwide phenomenon” Nutrition Reviews 56 IssueID4 106–114
B. M. Popkin J. J. Nielsen (2003) ArticleTitle“The sweetening of the world’s diet” Obesity Research 11 1325–1332
J. Poppendieck (1986) Breadlines Knee-Deep in Wheat: Food Assistance in the Great Depression Rutgers University Press New Brunswick, New Jersey
J. N. Pretty (2002) Agri-culture: Reconnecting People, Land, and Nature Earthscan London, United Kingdom
J. J. Putnam (1999) ArticleTitle“US food supply providing more food and calories.” Food Review 22 IssueID3 2–12
Putnam, J. J. and J. E. Allshouse (1999). Food Consumption, Prices and Expenditures: 1970–1997. Food and Rural Economics Division, Economic Research Service, US Department of Agriculture Statistical Bulletin #965. Accessed on July 14, 2003 at http://www.ers.usda.gov/publications/sb965/.
L. Reibel (2001) ArticleTitle“Consuming the earth: Eating disorders and ecopsychology” Journal of Humanistic Psychology 41 IssueID2 38–58
C. Schmidt (1993) ArticleTitle“On economization and ecologization as civilizing processes” Environmental Values 2 IssueID1 33–46
J. Sobal (1999) “Sociological analysis of the stigmatisation of obesity” J. Germov L. Williams (Eds) A Sociology of Food and Nutrition: Introducing the Social Appetite Oxford University Press Melbourne, Australia 187–204
J. Sobal (2001a) ArticleTitle“Globalization and the epidemiology of obesity” International Journal of Epidemiology 30 1136–1137 Occurrence Handle10.1093/ije/30.5.1136
J. Sobal (2001b) “Social and cultural influences on obesity” P. Bjorntorp (Eds) International Textbook of Obesity John Wiley and Sons London, United Kingdom 305–322
J. Sobal M. Nelson (2003) “Food waste” S. H. Katz (Eds) Encyclopedia of Food and Culture NumberInSeriesVolume I Charles Schribner’s Sons New York, New York 28–29
M. J. Stock N. J. Rothwell (1987) “Criteria and experimental evidence for luxus consumption” E. M. Berry S. H. Blondheim H. E. Elihau E. Schafrir (Eds) Recent Advances in Obesity Research NumberInSeriesVolume 5 Food and Nutrition Press Westport, Connecticut 124–130
A. F. Subar V. Kipnis R. P. Troiano D. Midthune D. A. Schoeller S. Bingham S. O. Sharbaugh J. Trablsi S. Runswick R. Ballard-Barbash J. Sunshine A. Schatzkin (2003) ArticleTitle“Using intake biomarkers to evaluate the extent of dietary misreporting in a large sample of adults: The OPEN study” American Journal of Epidemiology 158 1–13 Occurrence Handle10.1093/aje/kwg092
K. S. Tippett L. E. Cleveland (1999) “How current diets stack up: Comparison with the Dietary Guidelines” E. Frazao (Eds) America’s Eating Patterns: Changes and Consequences US Department of Agriculture, Economic Research Service, Agriculture Information Bulletin No. 750 Washington DC 51–71
R. P. Troiano E. A. Frongillo J. Sobal D. Levitsky (1996) ArticleTitle“The relationship between body weight and mortality: A quantitative analysis of combined information from existing studies” International Journal of Obesity 20 63–75
USDA (US Department of Agriculture) (1998). “Agriculture Fact Book 1996: Linking consumers and producers: What do Americans eat?” Washington DC: US Department of Agriculture. Accessed on June 23, 2003 at http://www.usda.gov/news/pubs/factbook/001a.pdf.
USDA (US Department of Agriculture) (2003). “Agriculture Fact Book 2001–2002: Profiling food consumption in America.” Washington DC: US Department of Agriculture. Accessed on June 23, 2003 at http://www.usda.gov/factbook/2002factbook.pdf.
Vinyl Council of Canada (2002). “Environmental profile: facts about the safety of incinerating vinyl wastes.” Mississauga, Ontario: Canadian Plastics Industry Association. Accessed on July 15, 2003 at http://www.plastics.ca/StaticContent/Static Pages/vcc/environment/vccd031.shtml.
M. Wackernagel J. D. Yount (2000) ArticleTitle“Footprints for sustainability: The next steps” Environment, Development, and Sustainability 2 21–42 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1010050700699
M. Wackernagel W. Rees (1996) Our Ecological Footprint: Reducing Human Impact on the Earth New Society Publishers Gabriola Island, British Columbia
P. Warshall (2002) “Tilth and technology: The industrial redesign of our nation’s soils” A. Kimbrell (Eds) The Fatal Harvest Reader: The Tragedy of Industrial Agiculture Island Press Washington DC 167–180
J. L. Wilkins (1995) ArticleTitle“Seasonal and local diets: Consumer’s role in achieving a sustainable food system” Research in Rural Sociology and Development 6 149–166
A. M. Wolf G. A. Colditz (1998) ArticleTitle“Current estimates of the economic costs of obesity” Obesity Research 6 IssueID2 97–106
L. R. Young M. Nestle (2002) ArticleTitle“Contribution of expanding portion sizes to the US obesity epidemic” American Journal of Public Health 92 246–249
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Dorothy Blair, PhD, received her master’s and doctoral degrees in Human Nutrition from Cornell University and is currently a faculty member in the Department of Nutritional Sciences and the Science, Technology, and Society Program at Pennsylvania State University. Her research and teaching focus on food ecology, food and culture, and the food system both nationally and internationally. She has published articles on obesity, energy expenditure, agriculture and food system issues, and community food security.
Jeffery Sobal, PhD, earned a doctorate in Sociology from the University of Pennsylvania and a master’s in Public Health from Johns Hopkins University. He is currently a faculty member in the Division of Nutritional Sciences at Cornell University. His research and teaching focus on the application of social science theories and methods to food, eating, and nutrition. He has published material on social patterns and consequences of body weight, the conceptualization of the food and nutrition system, and the process of making food choices.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Blair, D., Sobal, J. Luxus Consumption: Wasting Food Resources Through Overeating. Agric Hum Values 23, 63–74 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10460-004-5869-4
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10460-004-5869-4