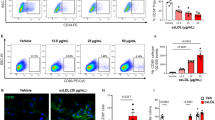
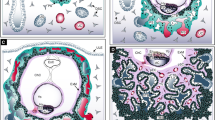
Abstract
Infantile hemangioma is a vascular tumor that occurs in 5–10% of infants of European descent. A defining feature of infantile hemangioma is the dramatic growth and development into a disorganized mass of blood vessels. Subsequently, a slow spontaneous involution begins around 1 year of age and continues for 4–6 years. The growth and involution of infantile hemangioma is very different from other vascular tumors and vascular malformations, which do not regress and can occur at any time during childhood or adult life. Much has been learned from careful study of the tissue morphology and gene expression patterns during the life-cycle of hemangioma. Tissue explants and tumor-derived cell populations have provided further insight to unravel the cellular and molecular basis of infantile hemangioma. A multipotent progenitor cell capable of de novo blood vessel formation has been isolated from infantile hemangioma, which suggests that this common tumor of infancy, long considered to be a model for pathologic angiogenesis, may also represent pathologic vasculogenesis. Whether viewed as angiogenesis or vasculogenesis, infantile hemangioma represents a vascular perturbation during a critical period of post-natal growth, and as such provides a unique opportunity to decipher mechanisms of human vascular development.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mulliken JB, Fishman SJ, Burrows PE (2000) Vascular anomalies. Curr Probl Surg 37:517–584
Drolet BA, Esterly NB, Frieden IJ (1999) Hemangiomas in children. N Engl J Med 341:173–181
Haggstrom AN, Drolet BA, Baselga E, Chamlin SL, Garzon MC, Horii KA, Lucky AW, Mancini AJ, Metry DW, Newell B et al (2007) Prospective study of infantile hemangiomas: demographic, prenatal, and perinatal characteristics. J Pediatr 150:291–294
Frieden IJ, Haggstrom AN, Drolet BA, Mancini AJ, Friedlander SF, Boon L, Chamlin SL, Baselga E, Garzon MC, Nopper AJ et al (2005) Infantile hemangiomas: current knowledge, future directions. In: Proceedings of a research workshop on infantile hemangiomas, April 7–9, 2005, Bethesda. Pediatr Dermatol 22:383–406
Metry DW, Haggstrom AN, Drolet BA, Baselga E, Chamlin S, Garzon M, Horii K, Lucky A, Mancini AJ, Newell B et al (2006) A prospective study of PHACE syndrome in infantile hemangiomas: demographic features, clinical findings, and complications. Am J Med Genet A 140:975–986
Huang SA, Tu HM, Harney JW, Venihaki M, Butte AJ, Kozakewich HP, Fishman SJ, Larsen PR (2000) Severe hypothyroidism caused by type 3 iodothyronine deiodinase in infantile hemangiomas. N Engl J Med 343:185–189
Boon LM, MacDonald DM, Mulliken JB (1999) Complications of systemic corticosteroid therapy for problematic hemangioma. Plast Reconstr Surg 104:1616–1623
Enjolras O, Breviere GM, Roger G, Tovi M, Pellegrino B, Varotti E, Soupre V, Picard A, Leverger G (2004) Vincristine treatment for function- and life-threatening infantile hemangioma. Arch Pediatr 11:99–107
Fawcett SL, Grant I, Hall PN, Kelsall AW, Nicholson JC (2004) Vincristine as a treatment for a large haemangioma threatening vital functions. Br J Plast Surg 57:168–171
Ezekowitz RA, Mulliken JB, Folkman J (1992) Interferon alfa-2a therapy for life-threatening hemangiomas of infancy. N Engl J Med 326:1456–1463
Chang E, Boyd A, Nelson CC, Crowley D, Law T, Keough KM, Folkman J, Ezekowitz RA, Castle VP (1997) Successful treatment of infantile hemangiomas with interferon-alpha-2b. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol 19:237–244
Barlow CF, Priebe CJ, Mulliken JB, Barnes PD, Mac Donald D, Folkman J, Ezekowitz RA (1998) Spastic diplegia as a complication of interferon Alfa-2a treatment of hemangiomas of infancy. J Pediatr 132:527–530
Greinwald JH Jr, Burke DK, Bonthius DJ, Bauman NM, Smith RJ (1999) An update on the treatment of hemangiomas in children with interferon alfa-2a. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 125:21–27
Leaute-Labreze C, Dumas de la Roque E, Hubiche T, Boralevi F, Thambo JB, Taieb A (2008) Propranolol for severe hemangiomas of infancy. N Engl J Med 358:2649–2651
Chang LC, Haggstrom AN, Drolet BA, Baselga E, Chamlin SL, Garzon MC, Horii KA, Lucky AW, Mancini AJ, Metry DW et al (2008) Growth characteristics of infantile hemangiomas: implications for management. Pediatrics 122:360–367
Mancini AJ, Smoller BR (1996) Proliferation and apoptosis within juvenile capillary hemangiomas. Am J Dermatopathol 18:505–514
Smoller BR, Apfelberg DB (1993) Infantile (juvenile) capillary hemangioma: a tumor of heterogeneous cellular elements. J Cutan Pathol 20:330–336
Takahashi K, Mulliken JB, Kozakewich HP, Rogers RA, Folkman J, Ezekowitz RA (1994) Cellular markers that distinguish the phases of hemangioma during infancy and childhood. J Clin Invest 93:2357–2364
Chang J, Most D, Bresnick S, Mehrara B, Steinbrech DS, Reinisch J, Longaker MT, Turk AE (1999) Proliferative hemangiomas: analysis of cytokine gene expression and angiogenesis. Plast Reconstr Surg 103:1–9 (discussion 10)
Picard A, Boscolo E, Khan ZA, Bartch TC, Mulliken JB, Vazquez MP, Bischoff J (2008) IGF-2 and FLT-1/VEGF-R1 mRNA levels reveal distinctions and similarities between congenital and common infantile hemangioma. Pediatr Res 63:263–267
Yu Y, Varughese J, Brown LF, Mulliken JB, Bischoff J (2001) Increased Tie2 expression, enhanced response to angiopoietin-1, and dysregulated angiopoietin-2 expression in hemangioma-derived endothelial cells. Am J Pathol 159:2271–2280
Yu Y, Flint AF, Mulliken JB, Wu JK, Bischoff J (2004) Endothelial progenitor cells in infantile hemangioma. Blood 103:1373–1375
North PE, Waner M, Mizeracki A, Mrak RE, Nicholas R, Kincannon J, Suen JY, Mihm MC Jr (2001) A unique microvascular phenotype shared by juvenile hemangiomas and human placenta. Arch Dermatol 137:559–570
Barnes CM, Huang S, Kaipainen A, Sanoudou D, Chen EJ, Eichler GS, Guo Y, Yu Y, Ingber DE, Mulliken JB et al (2005) Evidence by molecular profiling for a placental origin of infantile hemangioma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:19097–19102
Barnes CM, Christison-Lagay EA, Folkman J (2007) The placenta theory and the origin of infantile hemangioma. Lymphat Res Biol 5:245–255
Chang EI, Chang EI, Thangarajah H, Hamou C, Gurtner GC (2007) Hypoxia, hormones, and endothelial progenitor cells in hemangioma. Lymphat Res Biol 5:237–243
Pittman KM, Losken HW, Kleinman ME, Marcus JR, Blei F, Gurtner GC, Marchuk DA (2006) No evidence for maternal-fetal microchimerism in infantile hemangioma: a molecular genetic investigation. J Invest Dermatol 126:2533–2538
Regnier S, Dupin N, Le Danff C, Wassef M, Enjolras O, Aractingi S (2007) Endothelial cells in infantile haemangiomas originate from the child and not from the mother (a fluorescence in situ hybridization-based study). Br J Dermatol 157:158–160
Bauland CG, van Steensel MA, Steijlen PM, Rieu PN, Spauwen PH (2006) The pathogenesis of hemangiomas: a review. Plast Reconstr Surg 117:29e–35e
Pack GT, Miller TR (1950) Hemangiomas; classification, diagnosis and treatment. Angiology 1:405–426
Virchow R (1863) Die Krankhaften Geschwulste. August Hirschwald, Berlin
Pack G (1950) Hemangiomas, classification, diagnosis, and treatment. Angiology 1:40
Malan E (1974) Vascular Malformations (Angiodysplasias). Carlo Erba Foundation, Milan, p 4
Mulliken JB, Zetter BR, Folkman J (1982) In vitro characteristics of endothelium from hemangiomas and vascular malformations. Surgery 92:348–353
Dosanjh A, Chang J, Bresnick S, Zhou L, Reinisch J, Longaker M, Karasek M (2000) In vitro characteristics of neonatal hemangioma endothelial cells: similarities and differences between normal neonatal and fetal endothelial cells. J Cutan Pathol 27:441–450
Boye E, Yu Y, Paranya G, Mulliken JB, Olsen BR, Bischoff J (2001) Clonality and altered behavior of endothelial cells from hemangiomas. J Clin Invest 107:745–752
Dadras SS, North PE, Bertoncini J, Mihm MC, Detmar M (2004) Infantile hemangiomas are arrested in an early developmental vascular differentiation state. Mod Pathol 17:1068–1079
Walter JW, North PE, Waner M, Mizeracki A, Blei F, Walker JW, Reinisch JF, Marchuk DA (2002) Somatic mutation of vascular endothelial growth factor receptors in juvenile hemangioma. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 33:295–303
Khan ZA, Melero-Martin JM, Wu X, Paruchuri S, Boscolo E, Mulliken JB, Bischoff J (2006) Endothelial progenitor cells from infantile hemangioma and umbilical cord blood display unique cellular responses to endostatin. Blood 108:915–921
O’Reilly MS, Boehm T, Shing Y, Fukai N, Vasios G, Lane WS, Flynn E, Birkhead JR, Olsen BR, Folkman J (1997) Endostatin: an endogenous inhibitor of angiogenesis and tumor growth. Cell 88:277–285
Kleinman ME, Tepper OM, Capla JM, Bhatt KA, Ceradini DJ, Galiano RD, Blei F, Levine JP, Gurtner GC (2003) Increased circulating AC133+ CD34+ endothelial progenitor cells in children with hemangioma. Lymphat Res Biol 1:301–307
Ozerdem U, Grako KA, Dahlin-Huppe K, Monosov E, Stallcup WB (2001) NG2 proteoglycan is expressed exclusively by mural cells during vascular morphogenesis. Dev Dyn 222:218–227
Tigges U, Hyer EG, Scharf J, Stallcup WB (2008) FGF2-dependent neovascularization of subcutaneous Matrigel plugs is initiated by bone marrow-derived pericytes and macrophages. Development 135:523–532
Li Q, Yu Y, Bischoff J, Mulliken JB, Olsen BR (2003) Differential expression of CD146 in tissues and endothelial cells derived from infantile haemangioma and normal human skin. J Pathol 201:296–302
Crisan M, Yap S, Casteilla L, Chen CW, Corselli M, Park TS, Andriolo G, Sun B, Zheng B, Zhang L et al (2008) A perivascular origin for mesenchymal stem cells in multiple human organs. Cell Stem Cell 3:301–313
Tang W, Zeve D, Suh JM, Bosnakovski D, Kyba M, Hammer RE, Tallquist MD, Graff JM (2008) White fat progenitor cells reside in the adipose vasculature. Science 322:583–586
Khan ZA, Boscolo E, Picard A, Psutka S, Melero-Martin JM, Bartch TC, Mulliken JB, Bischoff J (2008) Multipotential stem cells recapitulate human infantile hemangioma in immunodeficient mice. J Clin Invest 118:2592–2599
Ritter MR, Dorrell MI, Edmonds J, Friedlander SF, Friedlander M (2002) Insulin-like growth factor 2 and potential regulators of hemangioma growth and involution identified by large-scale expression analysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:7455–7460
North PE, Waner M, Mizeracki A, Mihm MC Jr (2000) GLUT1: a newly discovered immunohistochemical marker for juvenile hemangiomas. Hum Pathol 31:11–22
Melero-Martin JM, De Obaldia ME, Kang SY, Khan ZA, Yuan L, Oettgen P, Bischoff J (2008) Engineering robust and functional vascular networks in vivo with human adult and cord blood-derived progenitor cells. Circ Res 103:194–202
Loffredo F, Lee RT (2008) Therapeutic vasculogenesis: it takes two. Circ Res 103:128–130
Au P, Tam J, Fukumura D, Jain RK (2008) Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells facilitate engineering of long-lasting functional vasculature. Blood 111:4551–4558
Tan ST, Wallis RA, He Y, Davis PF (2004) Mast cells and hemangioma. Plast Reconstr Surg 113:999–1011
Pasyk KA, Cherry GW, Grabb WC, Sasaki GH (1984) Quantitative evaluation of mast cells in cellularly dynamic and adynamic vascular malformations. Plast Reconstr Surg 73:69–77
Ritter MR, Reinisch J, Friedlander SF, Friedlander M (2006) Myeloid cells in infantile hemangioma. Am J Pathol 168:621–628
Nguyen VA, Furhapter C, Romani N, Weber F, Sepp N (2004) Infantile hemangioma is a proliferation of beta 4-negative endothelial cells adjacent to HLA-DR-positive cells with dendritic cell morphology. Hum Pathol 35:739–744
Jang YC, Isik FF, Gibran NS (2000) Nerve distribution in hemangiomas depends on the proliferative state of the microvasculature. J Surg Res 93:144–148
Berard M, Sordello S, Ortega N, Carrier JL, Peyri N, Wassef M, Bertrand N, Enjolras O, Drouet L, Plouet J (1997) Vascular endothelial growth factor confers a growth advantage in vitro and in vivo to stromal cells cultured from neonatal hemangiomas. Am J Pathol 150:1315–1326
Jinnin M, Medici D, Park L, Limaye N, Liu Y, Boscolo E, Bischoff J, Vikkula M, Boye E, Olsen BR (2008) Suppressed NFAT-dependent VEGFR1 expression and constitutive VEGFR2 signaling in infantile hemangioma. Nat Med 14:1236–1246
Zhang L, Lin X, Wang W, Zhuang X, Dong J, Qi Z, Hu Q (2005) Circulating level of vascular endothelial growth factor in differentiating hemangioma from vascular malformation patients. Plast Reconstr Surg 116:200–204
Fong GH, Rossant J, Gertsenstein M, Breitman ML (1995) Role of the Flt-1 receptor tyrosine kinase in regulating the assembly of vascular endothelium. Nature 376:66–70
Blei F, Walter J, Orlow SJ, Marchuk DA (1998) Familial segregation of hemangiomas and vascular malformations as an autosomal dominant trait. Arch Dermatol 134:718–722
Walter JW, Blei F, Anderson JL, Orlow SJ, Speer MC, Marchuk DA (1999) Genetic mapping of a novel familial form of infantile hemangioma. Am J Med Genet 82:77–83
Pramanik K, Chun CZ, Garnaas MK, Samant GV, Li K, Horswill MA, North PE, Ramchandran R (2009) Dusp-5 and Snrk-1 coordinately function during vascular development and disease. Blood 113:1184–1191
Qian F, Zhen F, Ong C, Jin SW, Meng Soo H, Stainier DY, Lin S, Peng J, Wen Z (2005) Microarray analysis of zebrafish cloche mutant using amplified cDNA and identification of potential downstream target genes. Dev Dyn 233:1163–1172
Sumanas S, Jorniak T, Lin S (2005) Identification of novel vascular endothelial-specific genes by the microarray analysis of the zebrafish cloche mutants. Blood 106:534–541
St Croix B, Rago C, Velculescu V, Traverso G, Romans KE, Montgomery E, Lal A, Riggins GJ, Lengauer C, Vogelstein B et al (2000) Genes expressed in human tumor endothelium. Science 289:1197–1202
Arbiser JL, Weiss SW, Arbiser ZK, Bravo F, Govindajaran B, Caceres-Rios H, Cotsonis G, Recavarren S, Swerlick RA, Cohen C (2001) Differential expression of active mitogen-activated protein kinase in cutaneous endothelial neoplasms: implications for biologic behavior and response to therapy. J Am Acad Dermatol 44:193–197
Suri C, Jones PF, Patan S, Bartunkova S, Maisonpierre PC, Davis S, Sato TN, Yancopoulos GD (1996) Requisite role of angiopoietin-1, a ligand for the TIE2 receptor, during embryonic angiogenesis. Cell 87:1171–1180
Maisonpierre PC, Suri C, Jones PF, Bartunkova S, Wiegand SJ, Radziejewski C, Compton D, McClain J, Aldrich TH, Papadopoulos N et al (1997) Angiopoietin-2, a natural antagonist for Tie2 that disrupts in vivo angiogenesis. Science 277:55–60
Hawighorst T, Skobe M, Streit M, Hong YK, Velasco P, Brown LF, Riccardi L, Lange-Asschenfeldt B, Detmar M (2002) Activation of the tie2 receptor by angiopoietin-1 enhances tumor vessel maturation and impairs squamous cell carcinoma growth. Am J Pathol 160:1381–1392
Stoeltzing O, Ahmad SA, Liu W, McCarty MF, Parikh AA, Fan F, Reinmuth N, Bucana CD, Ellis LM (2002) Angiopoietin-1 inhibits tumour growth and ascites formation in a murine model of peritoneal carcinomatosis. Br J Cancer 87:1182–1187
Feng Y, vom Hagen F, Pfister F, Djokic S, Hoffmann S, Back W, Wagner P, Lin J, Deutsch U, Hammes HP (2007) Impaired pericyte recruitment and abnormal retinal angiogenesis as a result of angiopoietin-2 overexpression. Thromb Haemost 97:99–108
Perry BN, Govindarajan B, Bhandarkar SS, Knaus UG, Valo M, Sturk C, Carrillo CO, Sohn A, Cerimele F, Dumont D et al (2006) Pharmacologic blockade of angiopoietin-2 is efficacious against model hemangiomas in mice. J Invest Dermatol 126:2316–2322
Sun JF, Phung T, Shiojima I, Felske T, Upalakalin JN, Feng D, Kornaga T, Dor T, Dvorak AM, Walsh K et al (2005) Microvascular patterning is controlled by fine-tuning the Akt signal. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:128–133
Phung TL, Ziv K, Dabydeen D, Eyiah-Mensah G, Riveros M, Perruzzi C, Sun J, Monahan-Earley RA, Shiojima I, Nagy JA et al (2006) Pathological angiogenesis is induced by sustained Akt signaling and inhibited by rapamycin. Cancer Cell 10:159–170
Kleinman ME, Greives MR, Churgin SS, Blechman KM, Chang EI, Ceradini DJ, Tepper OM, Gurtner GC (2007) Hypoxia-induced mediators of stem/progenitor cell trafficking are increased in children with hemangioma. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 27:2664–2670
Isik FF, Rand RP, Gruss JS, Benjamin D, Alpers CE (1996) Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 mRNA expression in hemangiomas and vascular malformations. J Surg Res 61:71–76
Kraling BM, Razon MJ, Boon LM, Zurakowski D, Seachord C, Darveau RP, Mulliken JB, Corless CL, Bischoff J (1996) E-selectin is present in proliferating endothelial cells in human hemangiomas. Am J Pathol 148:1181–1191
Oh IY, Yoon CH, Hur J, Kim JH, Kim TY, Lee CS, Park KW, Chae IH, Oh BH, Park YB et al (2007) Involvement of E-selectin in recruitment of endothelial progenitor cells and angiogenesis in ischemic muscle. Blood 110:3891–3899
Gainers ME, Descheny L, Barthel SR, Liu L, Wurbel MA, Dimitroff CJ (2007) Skin-homing receptors on effector leukocytes are differentially sensitive to glyco-metabolic antagonism in allergic contact dermatitis. J Immunol 179:8509–8518
Hidalgo A, Weiss LA, Frenette PS (2002) Functional selectin ligands mediating human CD34(+) cell interactions with bone marrow endothelium are enhanced postnatally. J Clin Invest 110:559–569
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Arnaud Picard, Hôpital d’enfants Armand-Trousseau, Service de Chirurgie Maxillo-faciale et Plastique, Paris, France, for providing the images of the CD133 and NG2 immunostaining in Fig. 2. We also thank Ms. Kristin Johnson for her help with preparing the figures. Writing of this article was supported by a grant from the National Institutes of Health (P01 AR48564).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Boscolo, E., Bischoff, J. Vasculogenesis in infantile hemangioma. Angiogenesis 12, 197–207 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10456-009-9148-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10456-009-9148-2