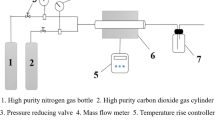
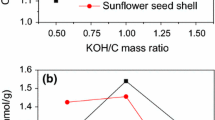
Abstract
This study investigates the effects of different combinations of potassium hydroxide (KOH)–nitrogen (N2)/carbon monoxide (CO)/air activation on the low-temperature ammonia (NH3) removal NO performance of coconut shell-activated carbon. KOH–N2-combined activation resulted in expanded pores of activated carbon, while high temperatures caused structural collapse. While increasing the activation temperature induced larger average pore sizes, introducing nitrogen-containing functional groups on the surface positively affected the NO conversion rate. Furthermore, while KOH–CO2-combined activation yielded activated carbon with denser and more ordered pore structures upon increasing activation temperature, a relatively large specific surface area and total pore volume were also observed. Introducing functional groups such as C = C on the surface yielded a higher overall NO conversion rate. Although KOH–air activation resulted in developed porous structures, some pore sizes were blocked, thereby yielding a smaller specific surface area. Nevertheless, introducing nitrogen-containing functional groups contributed to an overall increase in the NO conversion rate. Orthogonal experimental analysis revealed that activation time significantly impacted the physical activation process of KOH-activated carbon, followed by activation temperature, with activation gas minimally affecting the activated carbon structure and NO conversion rate. Notably, the optimal activation conditions included 1-h activated carbon activation in 3 mol/L of KOH, followed by 1-h CO2 activation at 150℃.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
References
Gao, F.Y., Chu, C., Zhu, W.J., Tang, X.L., Yi, H.H., Zhang, R.C.: High-efficiency catalytic oxidation of nitric oxide over spherical Mn-Co spinel catalyst at low temperature. Appl. Surf. Sci. 479, 548–556 (2019)
Hao, J.M., Tian, H.Z., Lu, Y.Q.: Emission inventories of NOx from commercial energy consumption in China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 36(4), 552–560 (2002)
Rubio, B., Izquierdo, M.T.: Low cost adsorbents for low temperature cleaning of flue gases. Fuel. 77(6), 631–637 (1998)
Li, K., Tang, X.L., Yi, H.H., Ning, P., Kang, D.J., Wang, C.: Low-temperature catalytic oxidation of NO over Mn-Co-Ce-Ox catalyst. Chem. Eng. J. 192, 99–104 (2012)
Abdulrasheed, A.A., Jalil, A.A., Triwahyono, S., Zaini, M.A.A., Gambo, Y., Ibrahim, M.: Surface modification of activated carbon for adsorption of SO2 and NOx: A review of existing and emerging technologies. Renew. Sust Energ. Rev. 94, 1067–1085 (2018)
Cui, L., Lu, J.W., Song, X.D., Tang, L.S., Li, Y.Z., Dong, Y.: Energy conservation and efficiency improvement by coupling wet flue gas desulfurization with condensation desulfurization. Fuel. 285, 119209 (2021)
Yi, H., Nakabayashi, K., Yoon, S.H., Miyawaki, J.: Pressurized physical activation: A simple production method for activated carbon with a highly developed pore structure. Carbon. 183, 735–742 (2021)
Lillo-Ródenas, M.A., Cazorla-Amorós, D., Linares-Solano, A.: Understanding chemical reactions between carbons and NaOH and KOH: An insight into the chemical activation mechanism. Carbon. 41, 267–275 (2003)
Wu, M.B., Zha, Q.F., Qiu, J.S., Guo, Y.S., Shang, H.Y., Yuan, A.J.: Preparation and characterization of porous carbons from PAN-based preoxidized cloth by KOH activation. Carbon. 42, 205–210 (2004)
Tsai, W.T., Jiang, T.J.: Optimization of physical activation process for activated carbon preparation from water caltrop husk. Biomass Convers. Bior 1–10. (2021)
Alabadi, A.A., Abbood, H.A., Dawood, A.S., Tan, B.: Ultrahigh-CO2 adsorption capacity and CO2/N2 selectivity by nitrogen-doped porous activated carbon monolith. B Chem. Soc. Jpn. 93(3), 421–426 (2020)
Saad, M.J., Sajab, M.S., Busu, W.N.W., Misran, S., Zakaria, S., Chin, S.X., Chia, C.H.: Comparative adsorption mechanism of rice straw activated carbon activated with NaOH and KOH. Sains Malays. 49(11), 2721–2734 (2020)
Kalderis, D., Bethanis, S., Paraskeva, P., Diamadopoulos, E.: Production of activated carbon from bagasse and rice husk by a single-stage chemical activation method at low retention times. Bioresource Technol. 99, 6809–6816 (2008)
Teng, H., Wang, S.C.: Preparation of porous carbons from phenol-formaldehyde resins with chemical and physical activation. Carbon. 38, 817–824 (2000)
Nowicki, P., Kazmierczak, J., Pietrzak, R.: Comparison of physicochemical and sorption properties of activated carbons prepared by physical and chemical activation of cherry stones. Powder Technol. 269, 312–319 (2015)
Illingworth, J.M., Rand, B., Williams, P.T.: Non-woven fabric activated carbon produced from fibrous waste biomass for sulphur dioxide control. Process. Saf. Environ. 122, 209–220 (2019)
Dogan, M., Sabaz, P., Bicil, Z., Kizilduman, B.K., Turhan, Y.: Activated carbon synthesis from tangerine peel and its use in hydrogen storage. J. Energy Inst. 93, 2176–2185 (2020)
Ahmed, M.J., Theydan, S.K.: Optimization of microwave preparation conditions for activated carbon from albizia lebbeck seed pods for methylene blue dye adsorption. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrol. 105, 199–208 (2014)
Mazlan, M.A.F., Uemura, Y., Yusup, S., Elhassan, F., Uddin, A., Hiwada, A., Demiya, M.: Activated carbon from rubber wood sawdust by carbon dioxide activation. Procedia Eng. 148, 530–537 (2016)
Long, H.M., Huang, B.F., Shi, Z., Liu, L.P., Wang, D.F., Li, L.: Physicochemical properties of coconut husk activated carbon modified by Fe(NO3)3 and mn(NO3)2. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 28(5), 530–537 (2021)
Nowicki, P., Pietrzak, R., Wachowska, H.: Sorption properties of active carbons obtained from walnut shells by chemical and physical activation. Catal. Today. 150, 107–114 (2010)
Singh, J., Bhunia, H., Basu, S.: Adsorption of CO2 on KOH activated carbon adsorbents: Effect of different mass ratios. J. Environ. Manage. 250, 109457 (2019)
Zhu, X., Zhang, L.Q., Zhang, M.Z., Ma, C.Y.: Effect of N-doping on NO2 adsorption and reduction over activated carbon: An experimental and computational study. Fuel. 258, 116109 (2019)
De-souza, L.K.C., Wickramaratne, N.P., Ello, A.S., Costa, M.J.F., Da-costa, C.E.F., Jaroniec, M.: Enhancement of CO2 adsorption on phenolic resin-based mesoporous carbons by KOH activation. Carbon. 65, 334–340 (2013)
Shahkarami, S., Azargohar, R., Dalai, A.K., Soltan, J.: Breakthrough CO2 adsorption in bio-based activated carbons. J. Environ. Sci. 34, 68–76 (2015)
Song, M., Jin, B.S., Xiao, R., Yang, L., Wu, Y.M., Zhong, Z.P., Huang, Y.J.: The comparison of two activation techniques to prepare activated carbon from corn cob. Biomass Bioenerg. 48, 250–256 (2013)
Szymanski, G.S., Karpinski, Z., Biniak, S., Swiatkowski, A.: The effect of the gradual thermal decomposition of surface oxygen species on the chemical and catalytic properties of oxidized activated carbon. Carbon. 40, 2627–2639 (2002)
Wang, W.X., Quan, H.Y., Gao, W.M., Zou, R., Chen, D.Z., Dong, Y.H., Guo, L.: N-doped hierarchical porous carbon from waste boat-fruited sterculia seed for high performance supercapacitors. RSC Adv. 7, 16678–16687 (2017)
Zhang, C.M., Song, W., Ma, Q.L., Xie, L.J., Zhang, X.C., Guo, H.: Enhancement of CO2 capture on biomass-based carbon from black Locust by KOH activation and ammonia modification. Energy Fuels. 30(5), 4181–4190 (2016)
Choma, J., Osuchowski, L., Marszewski, M., Dziura, A., Jaroniec, M.: Developing microporosity in kevlar(R)-derived carbon fibers by CO2 activation for CO2 adsorption. J. CO2 Util. 16, 17–22 (2016)
Lee, S.Y., Park, S.J.: Determination of the optimal pore size for improved CO2 adsorption in activated carbon fibers. J. Colloid Interf Sci. 389, 230–235 (2013)
Wu, F.C., Tseng, R.L.: Preparation of highly porous carbon from fir wood by KOH etching and CO2 gasification for adsorption of dyes and phenols from water. J. Colloid Interf Sci. 294, 21–30 (2006)
Mai, N.T., Nguyen, M.N., Tsubota, T., Nguyen, P.L.T., Nguyen, N.H.: Evolution of physico-chemical properties of dicranopteris linearis-derived activated carbon under various physical activation atmospheres. Sci. Rep-uk. 11,14430. (2021)
Cychosz, K.A., Thommes, M.: Progress in the physisorption characterization of nanoporous gas storage materials. Engineering-Prc. 4, 559–566 (2018)
Jiang, L.J., Liu, Q.C., Zhao, Q., Ren, S., Kong, M., Yao, L., Meng, F.: Promotional effect of ce on the SCR of NO with NH3 at low temperature over MnOx supported by nitric acid-modified activated carbon. Res. Chem. Intermediat. 44, 1729–1744 (2018)
Bashkova, S., Bandosz, T.J.: The effects of urea modification and heat treatment on the process of NO2 removal by wood-based activated carbon. J. Colloid Interf Sci. 333, 97–103 (2009)
Salker, A.V., Desai, M.S.: F. CO-NO/O2 redox reactions over Cu substituted cobalt oxide spinels. Catal. Commun. 87, 116–119 (2016)
Wang, Z.M., Kanoh, H., Kaneko, K., Lu, G.Q., Do, D.: Structural and surface property changes of macadamia nut-shell char upon activation and high temperature treatment. Carbon. 40, 1231–1239 (2002)
Ren, S., Guo, F.Q., Yang, J., Yao, L., Zhao, Q., Kong, M.: Selection of carbon materials and modification methods in low-temperature sintering flue gas denitrification. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 126, 278–285 (2017)
Ren, S., Guo, F.Q., Zhao, Q., Yang, J., Yao, L., Kong, M.: Sintering flue gas desulfurization with different carbon materials modified by microwave irradiation. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 24, 979–984 (2017)
Dogan, M., Sabaz, P., Bicil, Z., Kizilduman, B.K., Turhan, Y.: Activated carbon synthesis from tangerine peel and its use in hydrogen storage. J. Energy Inst. 93(6), 2176–2185 (2020)
Yi, H., Nakabayashi, K., Yoon, S.H., Miyawaki, J.: Study on the applicability of pressurized physically activated carbon as an adsorbent in adsorption heat pumps. RSC Adv. 12, 2558–2563 (2022)
Sultan, M., Miyazaki, T., Koyama, S.: Optimization of adsorption isotherm types for desiccant air-conditioning applications. Renew. Energ. 121, 441–450 (2018)
Li, S.X., Chen, C.Z., Li, M.F., Xiao, X.: Torrefaction of corncob to produce charcoal under nitrogen and carbon dioxide atmospheres. Bioresource Technol. 249, 348–353 (2018)
Qu, Z.B., Sun, F., Liu, X., Gao, J.H., Qie, Z.P., Zhao, G.B.: The effect of nitrogen-containing functional groups on SO2 adsorption on carbon surface: Enhanced physical adsorption interactions. Surf. Sci. 677, 78–82 (2018)
Khuong, D.A., Nguyen, H.N., Tsubota, T.: Activated carbon produced from bamboo and solid residue by CO2 activation utilized as CO2 adsorbents. Biomass Bioenerg. 148, 106039 (2021)
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 52264043) and the Open Foundation of Key Laboratory of Iron and Steel Metallurgy and Resource Utilization of the Ministry of Education (No. FMRULAB-20-4).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
B.F.: Methodology, Investigation, Validation, Writing-review & editing. W.L.: Investigation, Writing-original draft. Z.S.: Methodology. L.Y.: Methodology. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, B., Li, W., Shi, Z. et al. Effect of KOH-N2/CO/air activation on the performance of coconut shell activated carbon for low temperature NH3 removal NO. Adsorption (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10450-024-00483-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10450-024-00483-6