Abstract
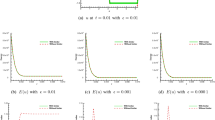
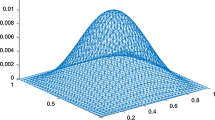
In this paper, the discontinuous finite volume element method (DFVEM) is considered to solve the Allen-Cahn equation which contains strong nonlinearity. The method is based on the DFVEM in space and the backward Euler method in time. The energy stability and unique solvability of the proposed fully discrete scheme are derived. The error estimates for the semi-discrete and fully discrete scheme are also established. A series of numerical experiments verify the efficiency of the proposed numerical method. The results show that our method can not only accurately capture the dynamic information of the phase transition, but also ensure the stability of the system during long-term numerical simulations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Li, Y., Lee, H.G., Kim, J.: A fast, robust, and accurate operator splitting method for phase-field simulations of crystal growth. J. Cryst. Growth. 321(1), 176–182 (2011)
Zhao, Y., Zhao, C., Xu, Z.: Numerical study of solid-liquid phase change by phase field method. Comput. Fluids. 164, 94–101 (2018)
Feng, X., Li, Y.: Analysis of symmetric interior penalty discontinuous Galerkin methods for the Allen-Cahn equation and the mean curvature flow. IMA. J. Numer. Anal. 35(4), 1622–1651 (2015)
Lei, Y., Cheng, T.L., Abernathy, H., Epting, W., Kalapos, T., Hackett, G., Wen, Y.: Phase field simulation of anode microstructure evolution of solid oxide fuel cell through \( Ni(OH)_2 \) diffusion. J. Power. Sources. 482, 367–383 (2010)
Levitas, V.I., Lee, D.W., Preston. D.L.: Interface propagation and microstructure evolution in phase field models of stress-induced martensitic phase transformations. Int. J. Plasticity. 26(3), 395–422 (2010)
Takaki, T., Yamanaka, A., Tomita, Y.: Phase-field modeling and simulation of nucleation and growth of recrystallized grains. Mater. Sci. Forum. 558–559(2), 1195–1200 (2007)
Elder, K.R., Thornton, K.S., Hoyt, J.J.: The kirkendall effect in the phase field crystal model. Philos. Mag. 91(1), 151–164 (2011)
Tu, X., Ray, A., Ghosh, S.: A coupled crystal plasticity FEM and phase-field model for crack evolution in microstructures of 7000 series aluminum alloys. Eng. Fract. Mech. 230, 106970 (2020)
Meher, R., Gohil, V.P.: Modelling of counter current imbibition phenomenon in two-phase fluid flows through fractured heterogeneous porous media under the effect of magnetic field. Int. J. Comput. Mat. Sci. 9(2), 2050006 (2020)
Zelepukina, E.V., Zubov, V.A., Merkin, A.A., Mironova. T.V.: Analysis of the amplitude and phase structure of transmitting media with probing field registration in the image plane. Opt. Spectrosc+. 93(5),752–756 (2002)
Esedog, S., Tsai, Y.H.R.: Threshold dynamics for the piecewise constant Mumford-Shah functional. J. Comput. Phys. 211(1), 367–384 (2006)
Lee, H.G., Shin, J., Lee. J.Y.: First and second order operator splitting methods for the phase field crystal equation. J. Comput. Phys. 299, 82–91 (2015)
Feng, X., Song, H., Tao, T., Jiang, Y.: Nonlinear stability of the implicit-explicit methods for the Allen-Cahn equation. Inverse Probl. Imaging. 7(3), 679 (2013)
Rafalko, G., Mosdorf, R., Górski, G.: Two-phase flow pattern identification in minichannels using image correlation analysis. Int. Commum. Heat. Mass. 113, 104508 (2020)
Steinbach, I., Nestler, B., Seesselberg, M., Prieler, R., Schmitz, G.T., Rezende, J.L.L., Pezzolla, F.: A phase field concept for multiphase systems. Physica. D. 94(3), 135–147 (1996)
Fan, D., Chen, L.: Computer simulation of grain growth using a continuum field model. Acta. Mater. 45(2), 611–622 (1997)
Kobayashi, R., Carter, W.C., Warren, J.A.: A continuum model of grain boundaries. Physica. D. 140(1–2), 141–150 (2000)
Herndon, J.M.: Solar system processes underlying planetary formation, geodynamics, and the georeactor. Earth. Moon. and Planets. 99(1–4), 53–89 (2006)
Iwashita, T., Hayase, Y., Nakanishi, H.: Phase field model for dynamics of sweeping interface. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 74(6), 1657–1660 (2005)
Zhang, B., He, Z.: The preparation of Agi/Au/foam-Cu as a framework of composite for water-based cool storage phase-change material with low supercooling. Thermochim. Acta. 674, 52–57 (2019)
Colli, P., Gilardi, G., Hilhorst, D.: On a Cahn-Hilliard type phase field system related to tumor growth. Discrete. Contin. Dyn. Syst. Ser. A. 35(6), 2423–2442 (2015)
Xu, J., Vilanova, G., Gómez, H.: Phase-field model of vascular tumor growth: Three-dimensional geometry of the vascular network and integration with imaging data. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Engrg. 359, 112648 (2020)
Zhu, J., Lu, X., Balieu, R., Kringos, N.: Modelling and numerical simulation of phase separation in polymer modified bitumen by phase-field method. Mater. Design. 107, 322–332 (2016)
Liang, M., Xin, X., Fan, W., Wang, H., Sun, W.: Phase field simulation and microscopic observation of phase separation and thermal stability of polymer modified asphalt. Constr. Build. Mater. 204, 132–143 (2019)
Elliott. C.M and Stinner. B.: Modeling and computation of two phase geometric biomembranes using surface finite elements. J. Comput. Phys. 229(18), 6585–6612 (2010)
Boettinger, W.J., Warren, J.A., Beckermann, C., Karma, A.: Phase-field simulation of solidification. Annu. Rev. Mater. Sci. 32(1), 163–194 (2002)
Feng, X.: Fully discrete finite element approximations of the Navier-Stokes-Cahn-Hilliard diffuse interface model for two-phase fluid flows. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 44(3), 1049–1072 (2006)
Feng, X., Li, Y., Zhang, Y.: A fully discrete mixed finite element method for the stochastic Cahn-Hilliard equation with gradient-type multiplicative noise. J. Sci. Comput. 83(1), 1–24 (2020)
Feng, X., Karakashian, O.A.: Fully discrete dynamic mesh discontinuous Galerkin methods for the Cahn-Hilliard equation of phase transition. Math. Comput. 76(259), 1093–1117 (2007)
Feng, X., Prohl, A.: Numerical analysis of the Allen-Cahn equation and approximation for mean curvature flows. Numer. Math. 94(1), 33–65 (2003)
Bhowmick, S., Liu, G.: A phase-field modeling for brittle fracture and crack propagation based on the cell-based smoothed finite element method. Eng. Fract. Mech. 204, 369–387 (2018)
Bai, F., He, X., Yang, X., Zhou, R., Wang, C.: Three dimensional phase-field investigation of droplet formation in microfluidic flow focusing devices with experimental validation. Int. J. Multiphase. Flow. 93, 130–141 (2017)
Gao, Y., He, X., Mei, L., Yang, X.: Decoupled, linear, and energy stable finite element method for the Cahn-Hilliard-Navier-Stokes-Darcy phase field model. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 40(1), B110–B137 (2018)
Han, D., Wang, X.: A second order in time, uniquely solvable, unconditionally stable numerical scheme for Cahn-Hilliard-Navier-Stokes equation. J. Comput. Phys. 290, 139–156 (2015)
Hua, J., Lin, P., Liu, C., Wang, Q.: Energy law preserving \( {C}^0 \) finite element schemes for phase field models in two-phase flow computations. J. Comput. Phys. 230(19), 7115–7131 (2011)
Yang, J., Mao, S., He, X., Yang, X., He, Y.: A diffuse interface model and semi-implicit energy stable finite element method for two-phase magnetohydrodynamic flows. Comput. Methods. Appl. Mech. Engrg. 356, 435–464 (2019)
Du, Q., Nicolaides, R.A.: Numerical analysis of a continuum model of phase transition. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 28(5), 1310–1322 (1991)
Chen, Y., Huang, Y., Yi, N.: A SCR-based error estimation and adaptive finite element method for the Allen-Cahn equation. Comput. Math. Appl. 78(1), 204–223 (2019)
Chen, Y., Huang, Y., Yi, N.: Recovery type a posteriori error estimation of adaptive finite element method for Allen-Cahn equation. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 369, 112574 (2020)
Shi, Y.: A phase field method for the numerical simulation of rigid particulate in two-phase flows. Fluid. Dyn. Res. 52(1), 015512 (2020)
Xu, J., Li, Y., Wu, S., Bousquet, A.: On the stability and accuracy of partially and fully implicit schemes for phase field modeling. 345. (2019)
Li, X., Shen, J., Rui, H.: Energy stability and convergence of SAV block-centered finite difference method for gradient flows. Math. Comput. 88(319), 2047–2068 (2019)
Chen, M.H., Bollada, P.C., Jimack, P.K.: Dynamic load balancing for the parallel, adaptive, multigrid solution of implicit phase-field simulations. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Mod. 16(2), 297–318 (2019)
Chen, Y., Shen, J.: Efficient, adaptive energy stable schemes for the incompressible Cahn-Hilliard-Navier-Stokes phase-field model. J. Comput. Phys. 308, 40–56 (2016)
Yang, J., Du, Q., Zhang, W.: Uniform \( L^p \)-bound of the Allen-Cahn equation and its numercal discretization. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Mod. 15, 213–227 (2018)
Liu, C., Shen, J.: A phase field model for the mixture of two incompressible fluids and its approximation by a Fourier-spectral method. Physica. D. 179(3–4), 211–228 (2003)
Shen, J., Yang, X.: Decoupled, energy stable schemes for phase-field models of two-phase incompressible flows. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 53(1), 279–296 (2015)
Yang, X., Zhao, J., He, X.: Linear, second order and unconditionally energy stable schemes for the viscous Cahn-Hilliard equation with hyperbolic relaxation using the invariant energy quadratization method. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 343(1), 80–97 (2018)
Chessa. J and Belytschko. T.: An extended finite element method for two-phase fluids. J. Appl. Mech. 70(1), 10–17 (2003)
Mohammadnejad, T., Khoei, A.R.: An extended finite element method for fluid flow in partially saturated porous media with weak discontinuities; the convergence analysis local enrichment strategies. Comput. Mech. 51(3), 327–345 (2013)
Frank, F., Liu, C., Alpak, F.O., Rivière. B.: A finite volume\(/\)discontinuous Galerkin method for the advective Cahn-Hilliard equation with degenerate mobility on porous domains stemming from micro-CT imaging. Computat. Geosci. 22(2), 543–563 (2018)
Karasözen, B., Filibeliouǧlu, A.S., Uzunca, M.: Energy stable discontinuous Galerkin finite element method for the Allen-Cahn equation. Int. J. Comp. Meth-Sing. 15(03), 1850013 (2018)
Jobelin, M., Lapuerta, C., Latché, J.C., Angot, P., Piar, B.: A finite element penalty-projection method for incompressible flows. J. Comput. Phys. 217(2), 502–518 (2006)
Engwer, C., Schumacher, L.: A phase field approach to pressurized fractures using discontinuous Galerkin methods. Math. Comput. Simulat. 137, 266–285 (2017)
Li, R., Gao, Y., Chen, J., Zhang, L., He, X., Chen, Z.: Discontinuous finite volume element method for a coupled Navier-Stokes-Cahn-Hilliard phase field model. Adv. Comput. Math. 46(2), 1–35 (2020)
Hirshikesh, Pramod, A.L.N., Annabattula. R.K., Ooi, E.T., Song, C., Natarajan, S.: Adaptive phase-field modeling of brittle fracture using the scaled boundary finite element method. Comput. Meth. Appl. Mech. Eng. 355, 284–307 (2019)
Pramod, A.L.N., Hirshikesh, Natarajan, S., Ooi, E.T.: Application of adaptive phase-field scaled boundary finite element method for functionally graded materials. Int. J. Comp. Meth-Sing 18(03), 2041007 (2021)
Zhang, Z., Tang, H.: An adaptive phase field method for the mixture of two incompressible fluids. Comput. Fluids. 36(8), 1307–1318 (2007)
Lattanzio, C., Mascia, C., Plaza. R.G., Simeoni, C.: Kinetic schemes for assessing stability of traveling fronts for the Allen-Cahn equation with relaxation. Appl. Numer. Math. 141, 234–247 (2019)
Li, J., Lin, X., Chen, Z.: Finite volume method for the incompressible flows. Springer, Berlin
Li, J., Chen, Z.: A new stabilized finite volume method for the stationary Stokes equations. Adv. Comput. Math. 30(2), 141–152 (2009)
Li, J., Chen, Z.: On the semi-discrete stabilized finite volume method for the transient Navier-Stokes equations. Adv. Comput. Math. 38(2), 281–320 (2013)
Li, R., Li, J., He, X., Chen, Z.: A stabilized finite volume element method for a coupled Stokes-Darcy problem. Appl. Numer. Math. 133, 2–24 (2017)
Li, J., Chen, Z.: Optimal \(l^2, h^1\) and \(l^\infty \) analysis of finite volume methods for the stationary Navier-Stokes equations with large data. Numer. Math. 126, 75–101 (2014)
Li, J.: Numerical methods for the incompressible Navier-Stokes equations. Science Press, Beijing (2019)
Rebholz, L.G., Wise, S.M., Xiao, M.: Penalty-projection schemes for the Cahn-Hilliard Navier-Stokes diffuse interface model of two phase flow, and their connection to divergence-free coupled schemes. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Model. 15, 649–676 (2018)
Liang, H., Li, Y., Chen, J., Xu, J.: Axisymmetric lattice Boltzmann model for multiphase flows with large density ratio. Int. J. Heat. Mass. Tran. 130, 1189–1205 (2019)
Hu, Y., Li, D., Niu, X., Shu, S.: A diffuse interface lattice Boltzmann model for thermocapillary flows with large density ratio and thermophysical parameters contrasts. Int. J. Heat. Mass. Tran. 138, 809–824 (2019)
Aldakheel, F., Hudobivnik, B., Wriggers, P.: Virtual element formulation for phase-field modeling of ductile fracture. Int. J. Multtscale. Com. 17(2), 181–200 (2019)
Aldakheel, F., Hudobivnik, B., Hussein, A., Wriggers, P.: Phase-field modeling of brittle fracture using an efficient virtual element scheme. Comput. Meth. Appl. Mech. Eng. 341(1), 443–466 (2018)
Li, J., Chen, Z., He, Y.: A stabilized multi-level method for non-singular finite volume solutions of the stationary 3D Navier-Stokes equations. Numer. Math. 122(2), 279–304 (2012)
Lin, F., He, X., Wen, X.: Fast, unconditionally energy stable large time stepping method for a new Allen-Cahn type square phase-field crystal model. Appl. Math. Lett. 98, 248–255 (2019)
Shen, J., Yang, X.: Numerical approximations of Allen-Cahn and Cahn-Hilliard equations. Discrete. Contin. Dyn. Syst. Ser. A. 28(4), 1669–1691 (2010)
Xu, C., Chen, C., Yang, X., He, X.: Numerical approximations for the hydrodynamics coupled binary surfactant phase field model: Second-order, linear, unconditionally energy stable schemes. Commun. Math. Sci. 17(3), 835–858 (2019)
Yang, X.: Error analysis of stabilized semi-implicit method of Allen-Cahn equation. Discrete. Cont. Dyn-B. 11(4), 1057–1070 (2009)
Zhang, J., Chen, C., Yang, X., Chu, Y., Xia, Z.: Efficient, non-iterative, and second-order accurate numerical algorithms for the anisotropic Allen-Cahn equation with precise nonlocal mass conservation. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 363, 444–463 (2020)
Li, J., Chen, Z., Shen, L.: Convergence and stability of a stabilized finite volume method for the stationary Navier-Stokes equations. BIT. 50(4), 823–842 (2010)
Shen, L., Li, J., Chen, Z.: Analysis of a stabilized finite volume method for the transient Stokes equations. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Mod. 6(3), 505–519 (2009)
Li, J., Bai, Y., Zhao, X.: Modern numerical methods for mathematical physics equations. Science Press, Beijing (2023)
Allen, S.M., Cahn, J.W.: A microscopic theory for antiphase boundary motion and its application to antiphase domain coarsening. Acta. Metall. 27(6), 1085–1095 (1979)
Ye, X.: A new discontinuous finite volume method for elliptic problems. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 42(3), 1062–1072 (2004)
Liu, J., Mu, L., Ye, X., Jari, R.: Convergence of the discontinuous finite volume method for elliptic problems with minimal regularity. J. Compt. Appl. Math. 236(17), 4537–4546 (2012)
Liu, J., Mu, L., Ye, X.: An adaptive discontinuous finite volume method for elliptic problems. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 235(18), 5422–5431 (2011)
Bi, C., Liu, M.: A discontinuous finite volume element method for second order elliptic problems. Numer. Methods Partial Differ. Equ. 28(2), 425–440 (2012)
Bi, C., Geng, J.: Discontinuous finite volume element method for parabolic problems. Numer. Methods Partial Differ. Equ. 26(2), 367–383 (2010)
Zhang, K. Gan, X.: The discontinuous finite volume element method for parabolic and hyperbolic equations. Journal of Northwest Normal University(Natural Science). 26(2), 367–383 (2010)
Li, R., Zhang, Y., Wu, J., Chen, Z.: Discontinuous finite volume element method for Darcy flows in fractured porous media. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 381, 113025 (2021)
Ye, X.: A discontinuous finite volume method for the Stokes problems. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 44(1), 183–198 (2006)
Li, R., Gao, Y., Li, J., Chen, Z.: Discontinuous finite volume element method for a coupled non-stationary Stokes-Darcy problem. J. Sci. Comput. 74(2), 693–727 (2018)
Wang, G., He, Y., Li, R.: Discontinuous finite volume methods for the stationary Stokes-Darcy problem. Int. J. Numer. Meth. Eng. 107(5), 395–418 (2016)
Yin, Z., Jiang, Z., Xu, Q.: A discontinuous finite volume method for the Darcy-Stokes equations. J. Appl. Math. 2012(3), 401–430 (2012)
Chen, S.: A discontinuous finite volume method for a coupled fracture model. Comput. Math. Appl. 78(10), 3429–3449 (2019)
Zhang, T., Tang, L.: A discontinuous finite volume element method based on bilinear trial functions. Int. J. Comp. Meth-Sing. 14(03), 1750025 (2017)
Kumar, S., Ruiz-Baier, R., Sandilya, R.: Discontinuous finite volume element methods for the optimal control of Brinkman equations. Springer, Cham, pp. 307–315 (2017)
Chou, S., Ye, X.: Unified analysis of finite volume methods for second order elliptic problems. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 45, 1639–1653 (2007)
Diegel, A.E., Wang, C., Wang, X., Wise, S.M.: Convergence analysis and error estimates for a second order accurate finite element method for the Cahn-Hilliard-Navier-Stokes system. Numer. Math. 137, 495–534 (2017)
Feng, X., Tang, T., Yang, J.: Stabilized Crank-Nicolson/Adams-Bashforth schemes for phase field models. E. Asian. J. Appl. Math. 3(1), 59–80 (2013)
Yan, Y., Chen, W., Wang, C., Wise, S.M.: A second-order energy stable BDF numerical scheme for the Cahn-Hilliard equation. Commun. Comput. Phys. 23(2), (2018)
Cheng, K., Feng, W., Wang, C., Wise, S.M.: An energy stable fourth order finite difference scheme for the Cahn-Hilliard equation. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 362(2), 574–595 (2019)
Chen, W., Wang, X., Yan, Y., Zhang, Z.: A second order BDF numerical scheme with variable steps for the Cahn-Hilliard equation. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 57(1), 495–525 (2019)
Guo, J., Wang, C., Wise, S.M., Yue, X.: An \(h^2\) convergence of a second-order convex-splitting, finite difference scheme for the three-dimensional Cahn-Hilliard equation. Commun. Math. Sci. 14(2), 489–515 (2016)
Cheng, K., Wang, C., Wise, S.M., Yue, X.: A second-order, weakly energy-stable pseudo-spectral scheme for the Cahn-Hilliard equation and its solution by the homogeneous linear iteration method. J. Sci. Comput. 39(3), 1083–1114 (2016)
Diegel, A.E., Wang, C., Wise, S.M.: Stability and convergence of a second-order mixed finite element method for the Cahn-Hilliard equation. IMA. J. Numer. Anal. 36(4), 1867–1897 (2016)
Guo, J., Wang, C., Wise, S.M., Yue. X.: An improved error analysis for a second-order numerical scheme for the Cahn-Hilliard equation. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 388, 113300 (2021)
Cheng, K., Wang, C., Null, S., Wu, Y.: A third order accurate in time, BDF-type energy stable scheme for the Cahn-Hilliard equation. Numer. Math-Theory. Me. 15(2), 279–303 (2022)
Yang, X.: Linear, first and second-order, unconditionally energy stable numerical schemes for the phase field model of homopolymer blends. J. Comput. Phys. 327, 294–316 (2016)
Shen, J., Xu, J., Yang, J.: The scalar auxiliary variable SAV approach for gradient flows. J. Comput. Phys. 353, 407–416 (2018)
Shen, J., Xu, J., Yang, J.: Discontinuous finite volume element method for a coupled Navier-Stokes-Cahn-Hilliard phase field model. Adv. Comput. Math. 46(2), 1–35 (2020)
Akrivis, G., Li, Y., Li, D.: Energy-decaying extrapolated RK-SAV methods for the Allen-Cahn and Cahn-Hilliard equations. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 41, A3703–A3727 (2019)
Gao, M., Wang, X.: A gradient stable scheme for a phase field model for the moving contact line problem. J. Comput. Phys. 231(4), 1372–1386 (2012)
Chen, L.: iFEM: an innovative finite element methods package in MATLAB. University of Maryland, Preprint (2008)
Yang, X.: A novel fully decoupled scheme with second-order time accuracy and unconditional energy stability for the Navier-Stokes equations coupled with mass-conserved Allen-Cahn phase-field model of two-phase incompressible flow. Int. J. Numer. Meth. Eng. 122(5), 1283–1306 (2021)
Zhang, F., Xu, Y., Chen, F., Guo, H.: Interior penalty discontinuous Galerkin based isogeometric analysis for Allen-Cahn equations on surfaces. Commun. Comput. Phys. 18(05), 1380–1416 (2015)
Funding
Jian Li is financially supported in part by NSF of China (No. 11771259)Shaanxi Provincial Joint Laboratory of Artificial Intelligence (No. 2022JC-SYS-05), Innovative team project of Shaanxi Provincial Department of Education (No. 21JP013) and Shaanxi Province Natural Science basic research program key project (No. 2023-JC-ZD-02). Rui Li is financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 11901372), the Young Talent fund of University Association for Science and Technology in Shaanxi (No. 20200504), the Fundamental Research Fund for the Central Universities of China (No. GK202103004), and Sinopec Key Laboratory of Geophysics.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests. We confirm that the manuscript is original, has been submitted solely to this journal and is not published, in press, or submitted elsewhere.
Additional information
Communicated by: Long Chen
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, J., Zeng, J. & Li, R. An adaptive discontinuous finite volume element method for the Allen-Cahn equation. Adv Comput Math 49, 55 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10444-023-10031-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10444-023-10031-5