Abstract
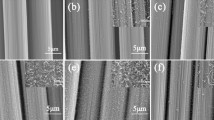
Oxidization treatment has been successfully applied on carbon nanotubes grown carbon fiber (CNTs-CF) to improve the surface activity and the interfacial property of CNTs-CF/epoxy resin (CNTs-CF/EP) composite. The surface element, morphology, and mechanical property of CNTs-CF have been systematically studied by X-ray photoelectron spectrum (XPS), scanning electron microscope (SEM), and single fiber tensile strength tester, respectively. The results indicate that the oxygen content on the CNTs-CF surface has been markedly increased from 2.5% to 19.4% after oxidization treatment, while the tensile strength shows no significant decrease. The CNTs layer on the surface protected the carbon fiber from corrosive oxidization agent, at the cost of collapsing and falling off of itself. Contact angle measurement and shear strength test have been introduced to investigate the interfacial property of CNTs-CF/EP composite. The result shows that the contact angle of resin to fiber has been reduced from ~39° to ~35° after oxidization, while the interfacial shear strength (IFSS) and interlaminar shear strength (ILSS) has been improved by 14.32% and 12.4% compared with untreated CNTs-CF/EP, respectively. A model is proposed to explain the wave-shaped fracture surface phenomenon of the composite. This work could reveal a novel approach to further improve the surface property of carbon fiber after growing carbon nanotubes.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets generated and studied during the current work are available form the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Peter, M.: Carbon Fibers and Their Composite. CRC Press, Boca Raton (2005)
Das, T.K., Ghosh, P., Das, N.C.: Preparation, development, outcomes, and application versatility of carbon fiber-based polymer composites: a review. Adv. Compos. Hybrid. Mater. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42114-018-0072-z
Zheng, H., Zhang, W., Li, B., Zhu, J., Wang, C., Song, G., Ma, L.: Recent advances of interphases in carbon fiber-reinforced polymer composites: A review. Compos. B. Eng. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2022.109639
Alshammari, B.A., Alsuhybani, M.S., Almushaikeh, A.M., Alotaibi, B.M., Alenad, A.M., Alqahtani, N.B., Alharbi, A.G.: Comprehensive review of the properties and modifications of carbon fiber-reinforced thermoplastic composites. Polymers. 13(15), 2474 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13152474
Liu, J., Chen, X., Liang, D., Xie, Q.: Development of pitch-based carbon fibers: a review. Energy. Sources. A. Recovery. Util. Environ. Eff. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1080/15567036.2020.1806952
Xu, B., Wang, X., Lu, Y.: Surface modification of polyacrylonitrile-based carbon fiber and its interaction with imide. Appl. Surf. Sci. 253(5), 2695–2701 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2006.05.044
Yuan, J.M., Fan, Z.F., Yang, Q.C., Li, W., Wu, Z.J.: Surface modification of carbon fibers by microwave etching for epoxy resin composite. Compos. Sci. Technol. 164, 222–228 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compscitech.2018.05.043
Fu, J., Zhang, M., Jin, L., et al.: Enhancing interfacial properties of carbon fibers reinforced epoxy composites via Layer-by-Layer self assembly GO/SiO2 multilayers films on carbon fibers surface. Appl. Surf. Sci. 470, 543–554 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.11.168
He, M., Xu, P., Zhang, Y., Liu, K., Yang, X.: Phthalocyanine nanowires@ GO/carbon fiber composites with enhanced interfacial properties and electromagnetic interference shielding performance. Chem. Eng. J. 388, 124255 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.124255
Zheng, L., Wang, Y., Qin, J., Wang, X., Lu, R., Qu, C., Wang, C.: Scalable manufacturing of carbon nanotubes on continuous carbon fibers surface from chemical vapor deposition. Vacuum. 152, 84–90 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vacuum.2018.03.011
Yao, Z., Wang, C., Qin, J., Su, S., Wang, Y., Wang, Q., Wei, H.: Interfacial improvement of carbon fiber/epoxy composites using one-step method for grafting carbon nanotubes on the fibers at ultra-low temperatures. Carbon. 164, 133–142 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2020.03.060
Zhao, F., Huang, Y., Liu, L., Bai, Y., Xu, L.: Formation of a carbon fiber/polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane/carbon nanotube hybrid reinforcement and its effect on the interfacial properties of carbon fiber/epoxy composites. Carbon. 49(8), 2624–2632 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2011.02.026
Giebel, E., Herrmann, T., Simon, F., Fery, A., Buchmeiser, M.R.: Surface Modification of Carbon Fibers by Free Radical Graft-Polymerization of 2-Hydroxyethyl Methacrylate for High Mechanical Strength Fiber-Matrix Composites. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 302(12), 1700210 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1002/mame.201700210
Stojcevski, F., Hilditch, T.B., Gengenbach, T.R., Henderson, L.C.: Effect of carbon fiber oxidization parameters and sizing deposition levels on the fiber-matrix interfacial shear strength. Compos. A. Appl. Sci. Manuf. 114, 212–224 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesa.2018.08.022
Li, J., Sun, F.F.: The effect of nitric acid oxidization treatment on the interface of carbon fiber-reinforced thermoplastic polystyrene composite. Polym. Plast. Technol. Eng. 48(7), 711–715 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1080/03602550902824580
Wen, Z., Xu, C., Qian, X., Zhang, Y., Wang, X., Song, S., Zhang, C.: A two-step carbon fiber surface treatment and its effect on the interfacial properties of CF/EP composites: The electrochemical oxidation followed by grafting of silane coupling agent. Appl. Surf. Sci. 486, 546–554 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.04.248
Terrones, M.: Carbon nanotubes: synthesis and properties, electronic devices and other emerging applications. Int. Mater. Rev. 49(6), 325–377 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1179/174328004X5655
Brown, N.M., You, H.X.: A scanning tunnelling microscopy study of PAN-based carbon fibre in air. Surf. Sci. 237(1–3), 273–279 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1016/0039-6028(90)90539-K
Kara, M., Ak, S., Uyaner, M., Gunoz, A., Kepir, Y.: The effect of hydrothermal aging on the low-velocity impact behavior of multi-walled carbon nanotubes reinforced carbon fiber/epoxy composite pipes. Appl. Compos. Mater. 28(5), 1567–1587 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10443-021-09923-w
Çetin, M.E.: Investigation of carbon nanotube reinforcement to polyurethane adhesive for improving impact performance of carbon fiber composite sandwich panels. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 112, 103002 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijadhadh.2021.103002
Çetin, M.E.: The effect of carbon nanotubes modified polyurethane adhesive on the impact behavior of sandwich structures. Polym. Compos. 42(9), 4353–4365 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1002/pc.26153
Baker, R.T.K., Harris, P.S., Thomas, R.B., Waite, R.J.: Formation of filamentous carbon from iron, cobalt and chromium catalyzed decomposition of acetylene. J. Catal. 30, 86–95 (1973). https://doi.org/10.1016/0021-9517(73)90055-9
Makris, T.D., Giorgi, R., Lisi, N., Pilloni, L., Salernitano, E., De Riccardis, M.F., Carbone, D.: Carbon nanotube growth on PAN-and pitch-based carbon fibres by HFCVD. Fuller. Nanotub. Carbon. Nanostruct. 13(S1), 383–392 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1081/FST-200039380
Wang, W., Xia, Y., Zeng, L., Liang, J., Lei, D., Chen, S., Zhao, H.F.: Synthesis and characterization of carbon nanotubes on carbon microfibers by floating catalysts method. Appl. Surf. Sci. 253, 6807–6810 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2007.01.129
De Greef, N., Zhang, L., Magrez, A., Forró, L., Locquet, J.P., Verpoest, I., Seo, J.W.: Direct growth of carbon nanotubes on carbon fibers: Effect of the CVD parameters on the degradation of mechanical properties of carbon fibers. Diam. Relat. Mater. 51, 39–48 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diamond.2014.11.002
Kumar, M., Ando, Y.: Chemical vapor deposition of carbon nanotubes: a review on growth mechanism and mass production. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 10(6), 3739–3758 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1166/jnn.2010.2939
Pozegic, T.R., Hamerton, I., Anguita, J.V., Tang, W., Ballocchi, P., Jenkins, P., Silva, S.R.P.: Low temperature growth of carbon nanotubes on carbon fibre to create a highly networked fuzzy fibre reinforced composite with superior electrical conductivity. Carbon 74, 319–328 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2014.03.038
Zhu, S., Su, C.H., Lehoczky, S.L., Muntele, I., Ila, D.: Carbon nanotube growth on carbon fibers. Diam. Relat. Mater. 12(10–11), 1825–1828 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0925-9635(03)00205-X
Fan, W., Wang, Y., Wang, C., Chen, J., Wang, Q., Yuan, Y., Niu, F.: High efficient preparation of carbon nanotube-grafted carbon fibers with the improved tensile strength. Appl. Surf. Sci. 364, 539–551 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2015.12.189
Qin, J., Wang, C., Lu, R., Su, S., Yao, Z., Zheng, L., Wei, H.: Uniform growth of carbon nanotubes on carbon fiber cloth after surface oxidation treatment to enhance interfacial strength of composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 195, 108198 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compscitech.2020.108198
Qin, J., Wang, C., Wang, Y., Su, S., Yao, Z., Ma, Z., Wei, H.: Preparation carbon nanotube-decorated carbon fibers under low pressure for epoxy-based unidirectional hierarchical composites with enhanced interlaminar shear strength. Polym. Test. 93, 106892 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymertesting.2020.106892
Khan, S., Bedi, H.S., Agnihotri, P.K.: Augmenting mode-II fracture toughness of carbon fiber/epoxy composites through carbon nanotube grafting. Eng. Fract. Mech. 204, 211–220 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfracmech.2018.10.014
Yao, Z., Wang, C., Lu, R., Su, S., Qin, J., Wang, Y., Wang, Q.: Fracture investigation of functionalized carbon nanotubes-grown carbon fiber fabrics/epoxy composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 195, 108161 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compscitech.2020.108161
Qin, J., Wang, C., Yao, Z., Ma, Z., Gao, Q., Wang, Y., Wei, H.: Growing carbon nanotubes on continuous carbon fibers to produce composites with improved interfacial properties: A step towards commercial production and application. Compos. Sci. Technol. 211, 108870 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compscitech.2021.108870
Wang, X., Qian, X., Zhang, Y., Wang, X., Song, S., Zhang, C.: Surface oxidation of PAN-based ultrahigh modulus carbon fibers (UHMCFs) and its effect on the properties of UHMCF/EP composites. Carbon. Lett. 31(3), 449–461 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42823-020-00173-7
Lu, W.B., Wang, C.G., Yuan, H., Hu, X.Y.: Liquid-phase oxidation modification of carbon fiber surface. Adv. Mater. Res. 430, 2008–2012 (2012). https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.430-432.2008
Gulyás, J., Földes, E., Lázár, A., Pukánszky, B.: Electrochemical oxidation of carbon fibres: surface chemistry and adhesion. Compos. A. Appl. Sci. Manuf. 32(3–4), 353–360 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1359-835X(00)00123-8
Bauer, M., Beratz, S., Ruhland, K., Horn, S., Moosburger-Will, J.: Anodic oxidation of carbon fibers in alkaline and acidic electrolyte: Quantification of surface functional groups by gas-phase derivatization. Appl. Surf. Sci. 506, 144947 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.144947
Sun, Y., Lu, Y., Yang, C.: Stripping mechanism of PAN-based carbon fiber during anodic oxidation in NaOH electrolyte. Appl. Surf. Sci. 486, 128–136 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.05.018
Xing, Y., Deng, S., Feng, S., Wang, Q., Hou, Y.: Selective oxidation of carbon to enhance both tensile strength and interfacial adhesion of carbon fiber. J. Adhes. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1080/00218464.2018.1528152
Li, W., Li, R., Li, C., Zhang, L.: Surface characterization and electrical property of carbon fibers modified by air oxidation. Surf. Interface. Anal. 47(3), 325–330 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1002/sia.5711
Wang, M.W.: Alignment and Surface Modification of Multiwall Carbon Nanotubes Polymeric Composites. Adv. Mater. Res. 881, 872–881 (2014). https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.881-883.872
Wang, S.: Optimum degree of functionalization for carbon nanotubes. Curr. Appl. Phys. 9(5), 1146–1150 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cap.2009.01.004
Meena, S., Choudhary, S.: Effects of functionalization of carbon nanotubes on its spin transport properties. Mater. Chem. Phys. 217, 175–181 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2018.06.077
Valipour, P., Ghasemi, S.E., Khosravani, M.R., Ganji, D.D.: Theoretical analysis on nonlinear vibration of fluid flow in single-walled carbon nanotube. J. Theor. Appl. Phys. 10(3), 211–218 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40094-016-0217-9
Bai, Y., Wu, F., Lin, D., Xing, B.: Aqueous stabilization of carbon nanotubes: effects of surface oxidization and solution chemistry. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 21(6), 4358–4365 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-013-2304-7
Siva, R., Valarmathi, T.N., Palanikumar, K., Samrot, A.V.: Study on a Novel natural cellulosic fiber from Kigelia africana fruit: Characterization and analysis. Carbohyd. Polym. 244, 116494 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.116494
Selvan, M.T.G.A., Binoj, J.S., Moses, J.T.E.J., Sai, N.P., Siengchin, S., Sanjay, M.R., Liu, Y.: Extraction and characterization of natural cellulosic fiber from fragrant screw pine prop roots as potential reinforcement for polymer composites. Polym. Compos. 43(1), 320–329 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1002/pc.26376
Liu, J., Bai, Y., Tian, Y., Huang, X., Wang, C., Liang, J.: Effect of the process of electrochemical modification on the surface structure and properties of PAN-based carbon fibers. Acta. Mater. Compos. Sin. 29(2), 16–25 (2012). https://doi.org/10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.2012.02.008
Fairley, N., Fernandez, V., Richard-Plouet, M.J., et al.: Systematic and collaborative approach to problem solving using X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. Appl. Surf. Sci. Adv. 5, 100112 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsadv.2021.100112
Hinterreiter, A.P., Duchoslav, J., Kehrer, M., Truglas, T., Lumetzberger, A., Unterweger, C., Stifter, D.: Determination of the surface chemistry of ozone-treated carbon fibers by highly consistent evaluation of X-ray photoelectron spectra. Carbon 146, 97–105 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2019.01.081
Kettle, A.P., Beck, A.J., O’toole, L., Jones, F.R., Short, R.D.: Plasma polymerisation for molecular engineering of carbon-fibre surfaces for optimised composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 57(8), 1023–1032 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0266-3538(96)00162-5
Xu, X., Huang, S., Hu, Y., Lu, J., Yang, Z.: Continuous synthesis of carbon nanotubes using a metal-free catalyst by CVD. Mater. Chem. Phys. 133(1), 95–102 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2011.12.059
Kim, K.J., Yu, W.R., Youk, J.H., Lee, J.: Degradation and healing mechanisms of carbon fibers during the catalytic growth of carbon nanotubes on their surfaces. ACS. Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 4(4), 2250–2258 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1021/am3002499
Naito, K., Yang, J.M., Inoue, Y., Fukuda, H.: The effect of surface modification with carbon nanotubes upon the tensile strength and Weibull modulus of carbon fibers. J. Mater. Sci. 47(23), 8044–8051 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-012-6694-6
Bamane, S.S., Gaikwad, P.S., Radue, M.S., Gowtham, S., Odegard, G.M.: Wetting Simulations of High-Performance Polymer Resins on Carbon Surfaces as a Function of Temperature Using Molecular Dynamics. Polymers 13(13), 2162 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13132162
Lee, J., Kessler, S.S., Wardle, B.L.: Void-Free Layered Polymeric Architectures via Capillary-Action of Nanoporous Films. Adv. Mater. Interfaces. 7(4), 1901427 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1002/admi.201901427
Funding
This paper has no known competing financial interest or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the reported work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, C., Chen, G., Wang, Q. et al. Improving Surface Property of Carbon Nanotube Grown Carbon Fiber by Oxidization Post-treatment. Appl Compos Mater 29, 1695–1713 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10443-022-10032-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10443-022-10032-5