Abstract
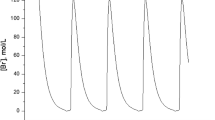
This paper addresses the existence of Hopf bifurcations in a directed acyclic network of neurons, each of them being modeled by a Hindmarsh–Rose (HR) neuronal model. The bifurcation parameter is the small parameter corresponding to the ratio of time scales between the fast and the slow dynamics. We first prove that, under certain hypotheses, the single uncoupled neuron can undergo a Hopf bifurcation. Hopf bifurcation occurrences in a directed acyclic network of HR neurons are then discussed. Numerical simulations are carried out to observe these bifurcations and to illustrate the theoretical results.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arena P, Fortuna L, Frasca M, La Rosa M (2006) Locally active hindmarsh–rose neurons. Chaos Solitons Fractals 27(2):405–412
Buzzi C, Llibre J, Medrado J (2016) Hopf and zero-hopf bifurcations in the hindmarsh–rose system. Nonlinear Dyn 83(3):1549–1556
Corson N, Aziz-Alaoui M (2009) Asymptotic dynamics of hindmarsh–rose neuronal system. Dyn Contin Discrete Impuls Syst Ser B Appl Algorithms 16:535–549
Crofts JJ, Higham DJ (2011) Googling the brain: discovering hierarchical and asymmetric network structures, with applications in neuroscience. Internet Math 7(4):233–254
de Lange E (2006) Neuron models of the generic bifurcation type: network analysis. Thesis, EPFL
González-Miranda J (2007) Complex bifurcation structures in the hindmarsh–rose neuron model. Int J Bifurcat Chaos 17(09):3071–3083
Haken H (2008) Brain dynamics. An introduction to models and simulations. Springer, Berlin
Harary F (2004) Graph theory. 1994. Addison-Wesley, Boston
Hassard B, Wan Y (1978) Bifurcation formulae derived from center manifold theory. J Math Anal Appl 63(1):297–312
Hassard BD, Kazarinoff ND, Wan YH (1981) Theory and applications of Hopf bifurcation, volume 41 of London mathematical society lecture note series. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Hindmarsh J, Rose R (1982) A model of the nerve impulse using two first-order differential equations. Nature 296(5853):162–164
Hindmarsh J, Rose R (1984) A model of neuronal bursting using three coupled first order differential equations. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 221(1222):87–102
Hodgkin AL, Huxley AF (1952) A quantitative description of membrane current and its application to conduction and excitation in nerve. J Physiol 117(4):500–544
Innocenti G, Morelli A, Genesio R, Torcini A (2007) Dynamical phases of the hindmarsh–rose neuronal model: studies of the transition from bursting to spiking chaos. Chaos Interdiscip J Nonlinear Sci 17(4):043,128
Izhikevich EM (2004) Which model to use for cortical spiking neurons? IEEE Trans Neural Netw 15(5):1063–1070
Izhikevich EM (2007) Dynamical systems in neuroscience. MIT press, Cambridge
Li-Xia D, Qi-Shao L (2005) Codimension-two bifurcation analysis in hindmarsh–rose model with two parameters. Chin Phys Lett 22(6):1325
Lü J, Zhou T, Chen G, Zhang S (2002) Local bifurcations of the chen system. Int J Bifurc Chaos 12(10):2257–2270
MacKay R, Sepulchre JA (1995) Multistability in networks of weakly coupled bistable units. Phys D Nonlinear Phenom 82(3):243–254
Meyer CD (2000) Matrix analysis and applied linear algebra. Siam
Storace M, Linaro D, de Lange E (2008) The hindmarsh–rose neuron model: bifurcation analysis and piecewise-linear approximations. Chaos Interdiscip J Nonlinear Sci 18(3):033,128
Wang H, Wang Q, Lu Q, Zheng Y (2013) Equilibrium analysis and phase synchronization of two coupled hr neurons with gap junction. Cognit Neurodyn 7(2):121–131
Zhou X, Wu Y, Li Y, Wei Z (2008) Hopf bifurcation analysis of the liu system. Chaos Solitons Fractals 36(5):1385–1391
Acknowledgments
The project is co-financed by the European Union with the European regional development fund (ERDF).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Corson, N., Lanza, V. & Verdière, N. Hopf Bifurcations in Directed Acyclic Networks of Linearly Coupled Hindmarsh–Rose Systems. Acta Biotheor 64, 375–402 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10441-016-9288-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10441-016-9288-x